Evaluation of Advanced real-time Visualization Techniques for Medical Augmented Reality
Student: Matthias Wieczorek
Advisor: Prof. Nassir Navab
Supervision by: Oliver Kutter
Table of Contents
Abstract
In recent years GPUs have evolved from fixed pipeline to fully programmable highly parallel architectures. These advances have led to equal improvements in the field of real-time medical image visualization. Combined with modern video see-through head-mounted displays this offers great opportunities for real-time, high-quality augmented reality visualization of medical data in interventional or surgical settings. Especially in minimally-invasive procedures, detailed, task-specific, visualization aids the physician in understanding the patient-specific anatomy and supports the navigation of medical instruments to the region of interest, in absence of a direct line of sight onto the operating situs.A possible medical AR configuration is to overlay real video camera images of e.g. a torso with a virtual image generated from 3D patient data. Recent approaches have dealt with the integration of hardware accelerated volume rendering into such an environment.
This work investigates the integration of advanced rendering techniques, such as virtual mirror and focus and context rendering for an improved visual perception of the augmented reality scene. Furthermore, real-time occlusion handling of real and virtual objects has been added. The techniques have been efficiently implemented in GPU programs and allow real-time visualization on computationally demanding stereo video see through AR systems.
Further Description
This thesis presents means to improve medical, in-situ AR visualization by enhanced embedding of tracked medical instruments into the scene. A major focus was to enable correct occlusion handling of instruments and virtual objects in the scene. This improves the visual feedback of the positioning and orientation of the instrument for the physician using the system. Additionally, the virtual mirror and multi-planar reformation were integrated and enriched with focus and context rendering.The realized system is able to augment real images with volume rendering, rendering of medical instruments, virtual mirror and focus and context embedded multi-planar reformations. By taking advantage of modern GPUs this can be achieved in real-time even for a computationally demanding stereo camera configuration.
Additionally, these developed techniques were used to setup a realistic drilling experiment for shoulder surgery. During the evaluation of the results of this experiments, the advantages of the developed techniques and the benefits of VM-based visualization techniques were shown.
Download
Images
- Instrument:
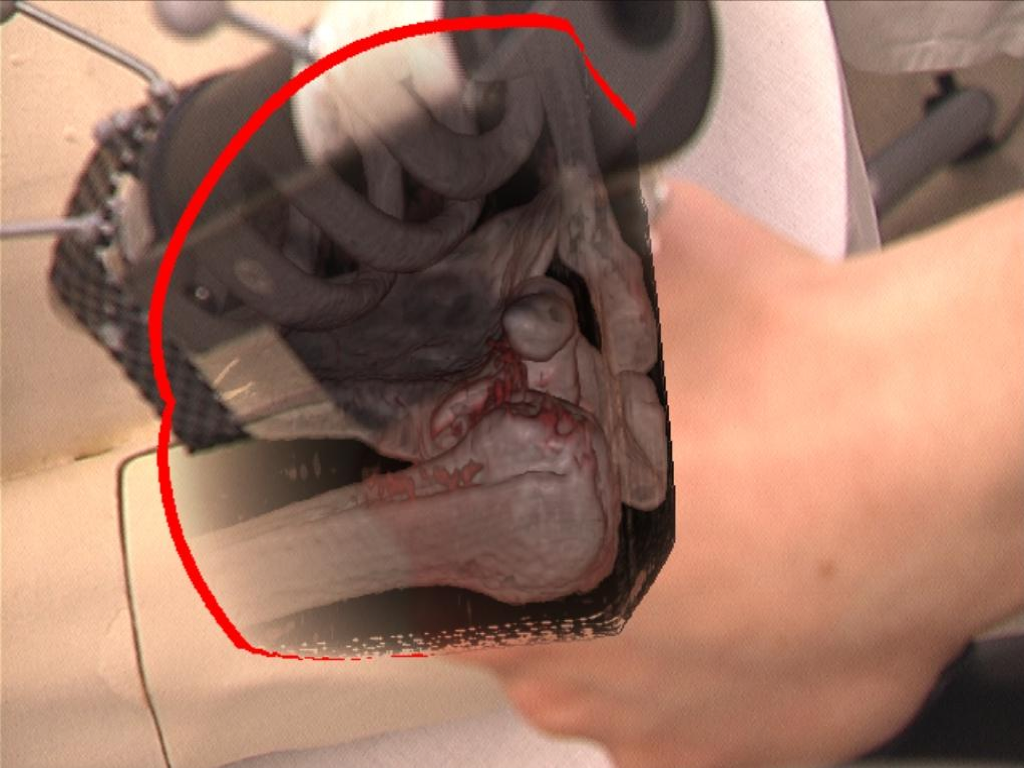
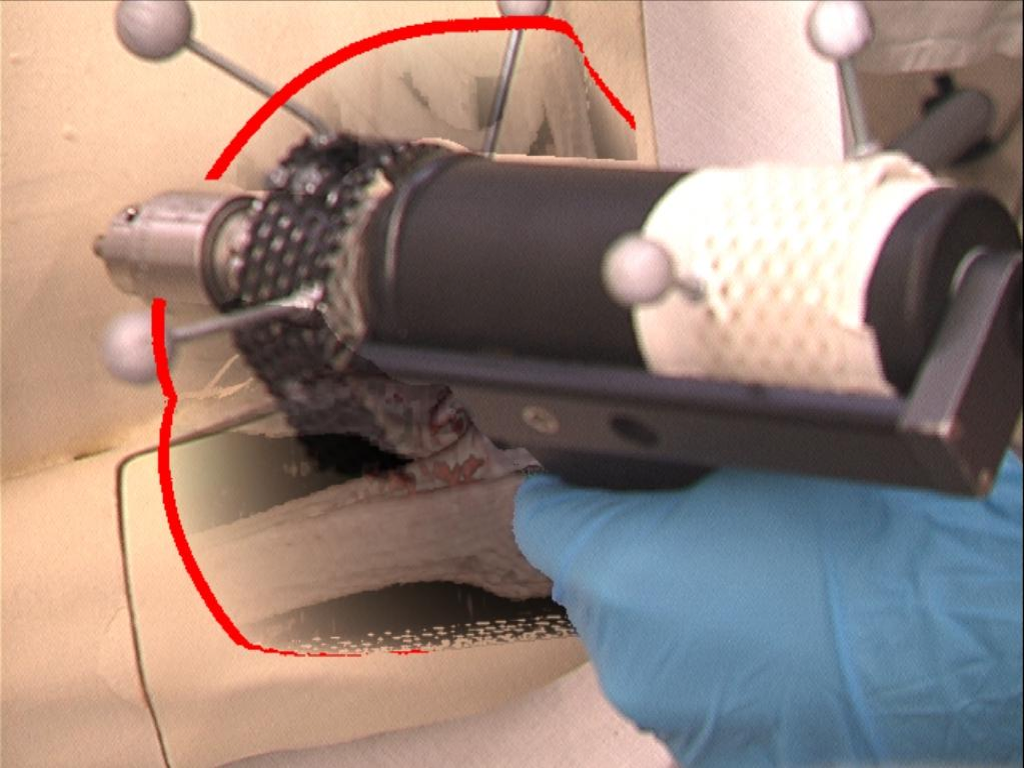
No occlusion handling (left) and instrument and glove occlusion handling (right)
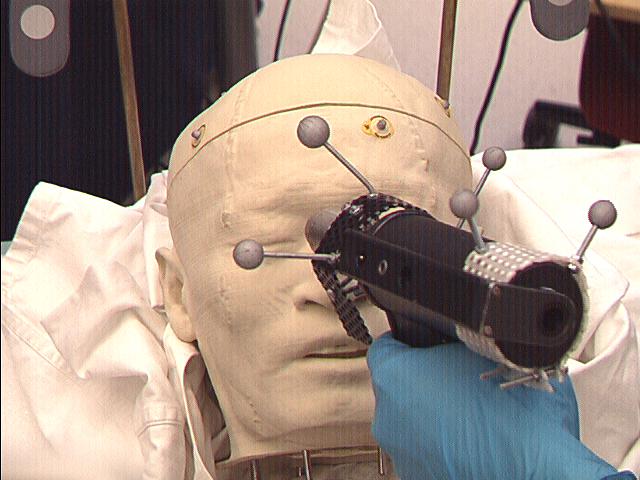
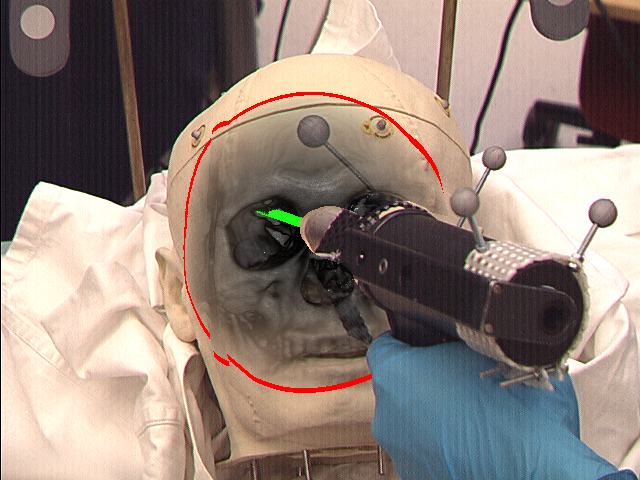
Video image (left) and augmented scene with volume rendering and instrument (right)
- Virtual Mirror:

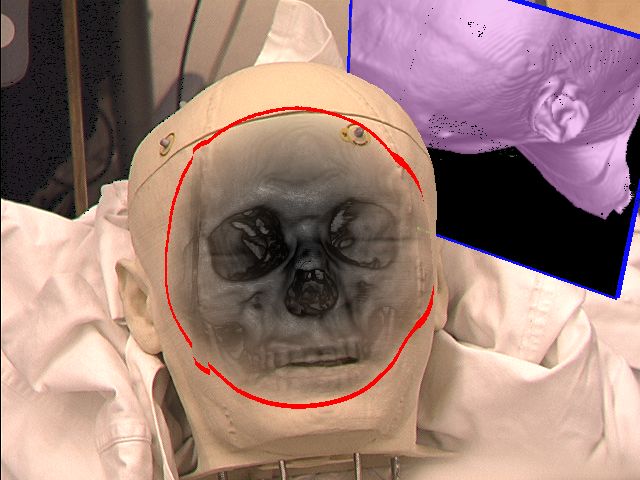
Mirror texture (left) and augmented scene with mirror (right)
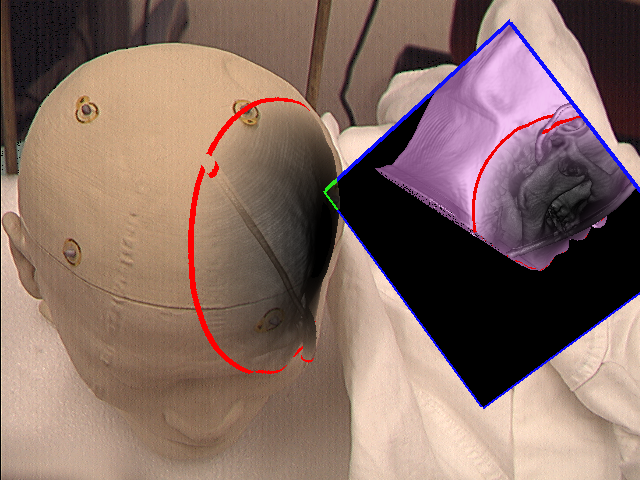
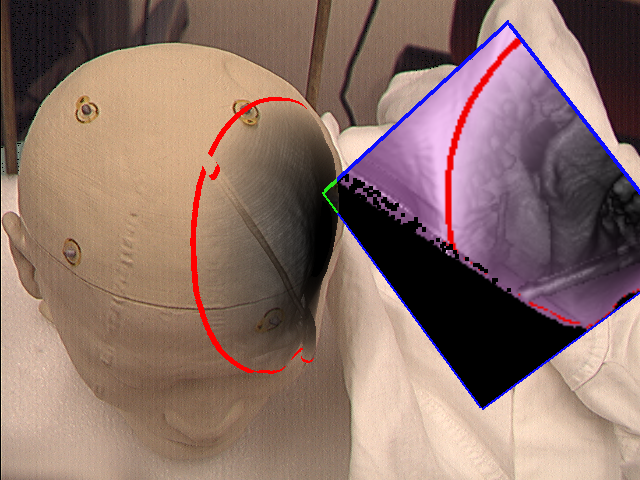
Mirror without (left) and with zoom (right)
- Multi-planar reformation:
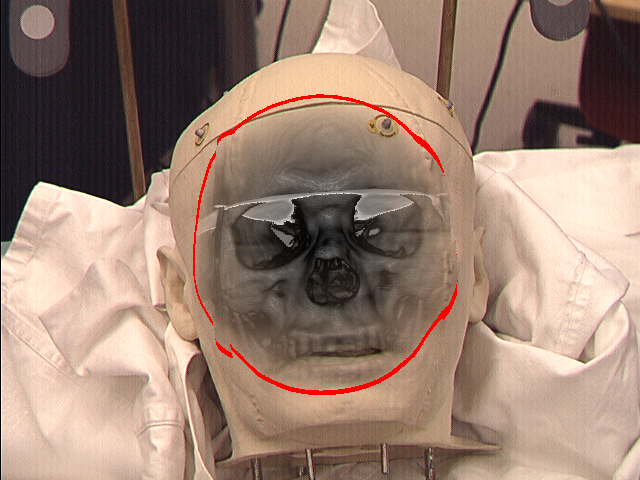
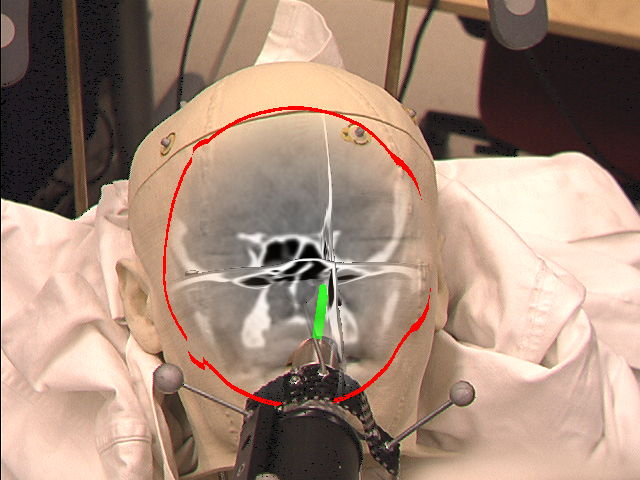
MPR and volume rendering (left) and instrument aligned MPR (right)
| ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Evaluation of Advanced real-time Visualization Techniques for Medical Augmented Reality |
| Abstract: | In recent years GPUs have evolved from fixed pipeline to fully programmable highly parallel architectures. These advances have led to equal improvements in the field of real-time medical image visualization. Combined with modern video see-through head-mounted displays this offers great opportunities for real-time, high-quality augmented reality visualization of medical data in interventional or surgical settings. Especially in minimally-invasive procedures, detailed, task-specific, visualization aids the physician in understanding the patient-specific anatomy and supports the navigation of medical instruments to the region of interest, in absence of a direct line of sight onto the operating situs. A possible medical AR configuration is to overlay real video camera images of e.g. a torso with a virtual image generated from 3D patient data. Recent approaches have dealt with the integration of hardware accelerated volume rendering into such an environment. This work investigates the integration of advanced rendering techniques, such as virtual mirror and focus and context rendering for an improved visual perception of the augmented reality scene. Furthermore, real-time occlusion handling of real and virtual objects has been added. The techniques have been efficiently implemented in GPU programs and allow real-time visualization on computationally demanding stereo video see through AR systems. |
| Student: | Matthias Wieczorek |
| Director: | Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Oliver Kutter |
| Type: | Bachelor Thesis |
| Area: | Registration / Visualization, Medical Imaging, Computer-Aided Surgery, Medical Augmented Reality |
| Status: | finished |
| Start: | 2009/01/15 |
| Finish: | 2009/06/15 |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | |