Up to DwarfMiddlewareTutorial, forward to DwarfMiddlewareTutorialLesson3, back to DwarfMiddlewareTutorialLesson1
What will happen to these services once they are started?
 Exercise 2.2 Run the
Exercise 2.2 Run the  Exercise 2.3 Take a look at what the service manager is doing when it appears to be doing nothing. Set the environment variable
Exercise 2.3 Take a look at what the service manager is doing when it appears to be doing nothing. Set the environment variable
Up to DwarfMiddlewareTutorial, forward to DwarfMiddlewareTutorialLesson3, back to DwarfMiddlewareTutorialLesson1 -- AsaMacWilliams - 17 Jul 2003
Lesson 2: Set up two communicating services
In this lesson, you will set up two simple services that communicate via CORBA method calls.Start the service manager
Open two terminals in thebin directory of your installation.
In one terminal, start the service manager with run-servicemgr. In a second, start DIVE as in Lesson 1, and select "update continously".
Build and install the time client and server
Make sure you have all the installed components of Lesson 1. In addition, you will now build a simple time-of-day service and a client for it. Runmake all in (top build directory)/src/tutorials/middleware/lesson2. If no errors occur, run make install. This will install the following four files in your install directory:
-
bin/TimeService- the executable for the time service -
bin/TimeClient- the executable for the time client -
share/TimeService.xml- the service description of the time service -
share/TimeClient.xml- the service description of the time client.
13:28:15.642 32495 2 servicemgr.cpp 171 ServiceManager_i 33/ 1 services: newServiceDescription(TimeService) 13:28:15.658 32495 2 servicemgr.cpp 171 ServiceManager_i 34/ 1 services: newServiceDescription(TimeClient)
Needs and abilities in XML
Let us take a look at the XML service descriptions, side by side:| TimeService | TimeClient |
|---|---|
<service name="TimeService">
<ability name="giveTime" type="TimeOfDay">
<connector protocol="ObjrefExporter"/>
</ability>
</service>
|
<service name="TimeClient">
<need name="time" type="TimeOfDay">
<connector protocol="ObjrefImporter"/>
</need>
</service>
|
- The
TimeServicehas an ability of typeTimeOfDay, and theTimeClienthas a need of the same type. Thus, the need and ability match each other. - The
TimeService'sability has anObjrefExporterconnector, and theTimeClient'sNeed has anObjrefImporterconnector. Since these connectors match as well, the two services can actually communicate with one another. - Thus, once both services are started, the service manager will export an object reference from the
TimeServiceand import it to theTimeClient. - What happens with the object reference after that is up to the services.
Start and register a service
Open two new terminals in thebin directory of your installation.
In the third terminal, start the time service with TimeService. You will see:
atbruegge11:~/test/bin$ ./TimeService 13:31:54.559 825 10 TimeService.cpp 079 : Initializing CORBA 13:31:54.563 825 10 corbainit.cpp 063 : ORB_init successful done 13:31:54.580 825 10 corbainit.cpp 069 : RootPOA successful resolved and narrowed 13:31:54.581 825 10 corbainit.cpp 073 : POA manager activated 13:31:54.582 825 10 corbainit.cpp 079 : command line resolution done 13:31:54.583 825 10 corbainit.cpp 082 : ServiceManagerHostString created 13:31:54.587 825 10 corbainit.cpp 095 : service manager resolved and narrowed 13:31:54.588 825 10 TimeService.cpp 082 : Creating Service 13:31:54.589 825 10 TimeService.cpp 044 TimeService_impl : constructor 13:31:54.590 825 10 TimeService.cpp 085 : registering Service 13:31:54.605 832 10 TimeService.cpp 050 TimeService_impl : getStatus 13:31:54.612 825 1 TimeService.cpp 088 : Starting Time Service, exit with Control-C 13:31:57.635 832 10 TimeService.cpp 050 TimeService_impl : getStatus 13:32:00.665 832 10 TimeService.cpp 050 TimeService_impl : getStatus 13:32:03.700 832 10 TimeService.cpp 050 TimeService_impl : getStatusAt the same time, in the service manager's terminal, you will see:
13:31:54.592 831 2 servicemgr.cpp 141 ServiceManager_i 35/ 1 services: registerService(TimeService)What is going on? Upon startup, the
TimeService contacts the service manager on the local host and registers itself. The service manager then associates this running instance of the TimeService with a service description generated from the TimeService.xml file. It periodically calls getStatus on the service to make sure the service is still alive.
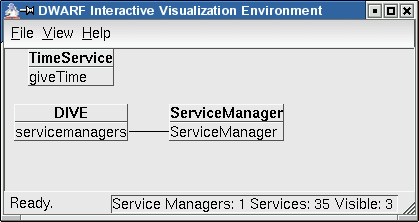
In DIVE, you will see a lonely TimeService:

Start another service
In the fourth terminal, runTimeClient. You will see:
atbruegge11:~/test/bin$ ./TimeClient 13:33:28.926 835 10 TimeClient.cpp 104 : Initializing CORBA 13:33:28.931 835 10 corbainit.cpp 063 : ORB_init successful done 13:33:28.937 835 10 corbainit.cpp 069 : RootPOA successful resolved and narrowed 13:33:28.938 835 10 corbainit.cpp 073 : POA manager activated 13:33:28.939 835 10 corbainit.cpp 079 : command line resolution done 13:33:28.940 835 10 corbainit.cpp 082 : ServiceManagerHostString created 13:33:28.949 835 10 corbainit.cpp 095 : service manager resolved and narrowed 13:33:28.949 835 10 TimeClient.cpp 107 : Creating Service 13:33:28.951 835 10 TimeClient.cpp 049 TimeClient_impl : constructor 13:33:28.952 835 10 TimeClient.cpp 110 : registering Service 13:33:28.973 835 1 TimeClient.cpp 113 : Starting Time Client, exit with Control-C 13:33:28.984 835 10 TimeClient.cpp 083 TimeClient_impl : no time service found yet 13:33:28.986 842 10 TimeClient.cpp 061 TimeClient_impl : getStatus 13:33:29.047 842 10 TimeClient.cpp 069 TimeClient_impl : importObjref 13:33:31.066 842 10 TimeClient.cpp 061 TimeClient_impl : getStatus current time is: 13:33:31 13:33:34.095 842 10 TimeClient.cpp 061 TimeClient_impl : getStatus current time is: 13:33:35 13:33:37.125 842 10 TimeClient.cpp 061 TimeClient_impl : getStatus current time is: 13:33:38In the service manager terminal, you will see:
13:33:28.954 841 2 servicemgr.cpp 141 ServiceManager_i 35/ 2 services: registerService(TimeClient)Finally, in the
TimeService terminal, you will see:
13:33:31.996 845 10 TimeService.cpp 060 TimeService_impl : getDayTime 13:33:33.075 832 10 TimeService.cpp 050 TimeService_impl : getStatus 13:33:35.005 845 10 TimeService.cpp 060 TimeService_impl : getDayTime 13:33:36.105 832 10 TimeService.cpp 050 TimeService_impl : getStatus 13:33:38.015 845 10 TimeService.cpp 060 TimeService_impl : getDayTimeWhat is going on? The
TimeClient registers itself with the service manager, as the TimeServer has already done. After a fer seconds, the service manager creates a connection between the two services and calls importObjref on the TimeClient, giving it a reference to the TimeService. The TimeClient then periodically calls getDayTime on the TimeService and prints the current time of day it has retrieved.
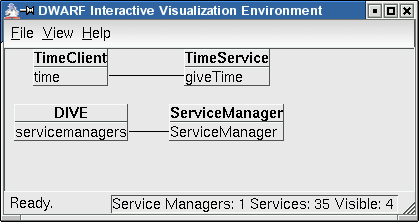
In DIVE, you will see the TimeClient connected to the TimeService:

Stop and restart the services
Press Control-C in theTimeClient terminal. The program will terminate. In the service manager terminal, you will see:
14:06:52.751 2693 2 activeservicedesc.cp 782 ActiveServiceDescription_i TimeClient,Started: lost connection to service 14:06:52.785 2693 2 servicemgr.cpp 266 ServiceManager_i 35/ 3 services: deletedServiceDescription(TimeClient) 14:06:57.726 32495 2 servicemgr.cpp 171 ServiceManager_i 34/ 3 services: newServiceDescription(TimeClient)The service manager detects that the
getStatus method call has failed, since the TimeClient has terminated, and deletes the service's description. It then re-reads the service description from the XML file.
If you start and stop the TimeClient repeatedly, it will reconnect to the TimeService.
Hunt some bugs
Now, with aTimeClient running, stop the TimeService. Now, the TimeClient will crash the next time it tries to call getDayTime, reporting:
14:17:59.234 3271 10 TimeClient.cpp 117 : Caught CORBA::Exception.The service manager will report that it has lost the connection to both services. In the course of starting and stopping services, you may be able to produce an error message in the service manager:
********************************************** * Detected run-time error in thread 1338 * 14:17:59.739 1338 0 servicemgr.cpp 373 ServiceManager_i 34/ 2 services: invalid service name 14:17:59.737 1338 10 servicemgr.cpp 368 ServiceManager_i 34/ 2 services: safeGetServiceDescription(TimeClient) 14:17:59.737 1338 10 servicemgr.cpp 210 ServiceManager_i 34/ 2 services: getServiceDescription(TimeClient) **********************************************This comes from DIVE, which is trying to retrieve information about the
TimeClient service just after the service has died, but before TimeClient.xml has been parsed again. In the DIVE terminal, you will see an error message as well:
14:17:59.742 3287 8 dwarfsystemmodel.cpp 160 : Exception when updating service TimeClient@atbruegge11Exercise 2.1 Wildly start and stop services, and try to get the service manager to crash. Then report how you did it.
 Exercise 2.2 Run the
Exercise 2.2 Run the TimeService and write a script that periodically starts and stops the TimeClient. Run top in another terminal, sort the processes by memory use (press 'M'), and watch to see if the memory use of DIVE and the service manager increases. If so, you have found a memory hole. Feel free to fix it.  Exercise 2.3 Take a look at what the service manager is doing when it appears to be doing nothing. Set the environment variable
Exercise 2.3 Take a look at what the service manager is doing when it appears to be doing nothing. Set the environment variable DWARF_DEBUGLEVEL to a higher value than the default of 2 for the service manager, e.g. run:
atbruegge11:~/test/bin$ DWARF_DEBUGLEVEL=5 ./run-servicemgr
Look at the source
Open the three relevant source files and browse through them:-
src/tutorials/middleware/lesson2/TimeService.cpp -
src/tutorials/middleware/lesson2/TimeClient.cpp -
src/idl/DWARF/Tutorial.idl
interface Clock {
TimeOfDay getDayTime();
};
interface TimeService : Service, Clock {
};
The interface TimeService is assembled from two parts. It inherits from the Service interface which is mandatory for
every DWARF service and from the Clock interface which provides the application logic. This structure demonstrates the separation
of internal (DWARF) logic and application logic.
The resulting aggregation interface is implemented by the TimeService_impl class of the TimeService. To do this, the TimeService has only to implement the method getStatus() from Service interface and the method getDayTime() from the Clock interface:
class TimeService_impl :
public POA_DWARF::TimeService,
public Debuggable
{
public:
TimeService_impl();
virtual ~TimeService_impl();
//Service interface
char* getStatus();
// Clock interface
DWARF::TimeOfDay getDayTime();
};
Because we have chosen communication via object references,
we need not to implement any further methods for communication.
The TimeClient that should act a client to our TimeService also has to be a DWARF service, i.e. it has also to implement getStatus(). Beside this, it does not need to implement additional application logic methods. But because of the communication style, it has to implement importObjref(Object objref) inherited from SvcProtObjrefImporter, and maintain a variable to store the CORBA object reference to the TimeService:
class TimeClient_impl :
public POA_DWARF::Service_ObjrefImporter,
public Debuggable
{
DWARF::Clock_var myTimeService;
public:
TimeClient_impl();
virtual ~TimeClient_impl();
//Service interface
char* getStatus();
//SvcProtObjrefImporter interface
void importObjref(CORBA::Object * objref);
//the work
void run();
};
Exercise 2.4 Add better error handling to the TimeClient, so that it will simply ignore a failed getDayTime call.
Exercise 2.5 Trace the definition of the interface Service_ObjrefImporter back through Service.idl.
Exercise 2.6 These aggregation interfaces are clumsy. Try to implement the TimeService_impl class using multiple inheritance, such as thus:
class TimeService_impl : public POA_DWARF::Service, //invalid multiple inheritance in CORBA! public POA_DWARF::Clock, //invalid multiple inheritance in CORBA! public DebuggableEven if you fix the compiler error (hint: try a cast to
POA_DWARF::Service*), you will get a run-time error later on. Why?
Up to DwarfMiddlewareTutorial, forward to DwarfMiddlewareTutorialLesson3, back to DwarfMiddlewareTutorialLesson1 -- AsaMacWilliams - 17 Jul 2003
