Implementation and Evaluation of Motion-Based Input for a Volleyball Game
Thesis by: Johannes SchmidtAdvisor: Gudrun Klinker
Supervision by: Andreas Dippon
Due date: 2012/12/15
Abstract
An existing volleyball game which is optimized for Xbox 360 controller input serves as basis for testing different motion-based input schemes. A Microsoft Kinect sensor recog- nizes the players in front of the screen. By moving your body and waving your hands you can control the player. The various input schemes will be tested and evaluated by different user groups. In the end you will know if motion-based input can be added to an existing game while preserving or even increasing the fun factor.Overview
The Bachelor thesis covers implementation and evaluation. During two iterations an implementation part is always followed by an evaluation.1. Iteration
- Implementation: Several controlling schemes like leaning left/right and moving hands are realized.
- Evaluation: User tests for qualitative feedback. By interviewing the testers you find out which controlling schemes are working properly.
2. Iteration
- Implementation: Improve system based on the feedback of the first iteration.
- Evaluation: User tests for quantitative feedback (Questionnaires)to compare the two best controlling schemes.
Implementation and comparison of controlling schemes
Controlling schemes
Several different controlling schemes have been implemented and combined: Running left and right, leaning, moving hips, jumping and moving hands. Furthermore a gesture recognizer is able to recognize the following volleyball-like gestures: Setting, smashing, digging and blocking. After the first iteration people tested the game and preferred two controlling schemes:- Direct Control: The user moves left and right and uses one hand to control the ingame player's hand.
- Volleyball Gestures: The user moves back and forth (imagining the volleyball net in front of him) and performs volleyball-like gestures which the ingame player replicates.
Results
The conclusion based on the user acceptance test of the second iteration:- Direct Control: Is more accurate but your arm gets exhausted.
- Volleyball Gestures: Feels more like volleyball but often you trigger unintended gestures.
Pictures
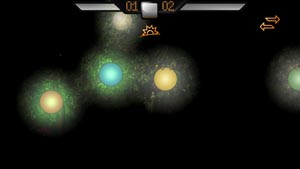
- Screenshots of the original game which show different levels and powerups:


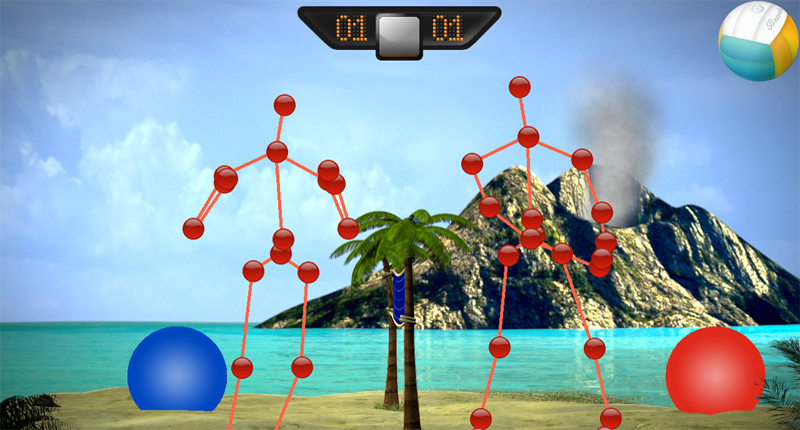
- A settings overlay allows adjusting Kinect settings ingame. The skeletons which are managed by the Kinect framework can also be displayed (for debugging reasons).

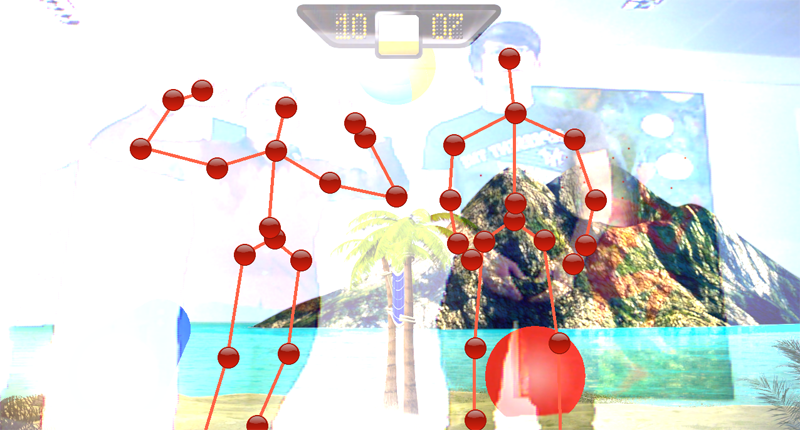
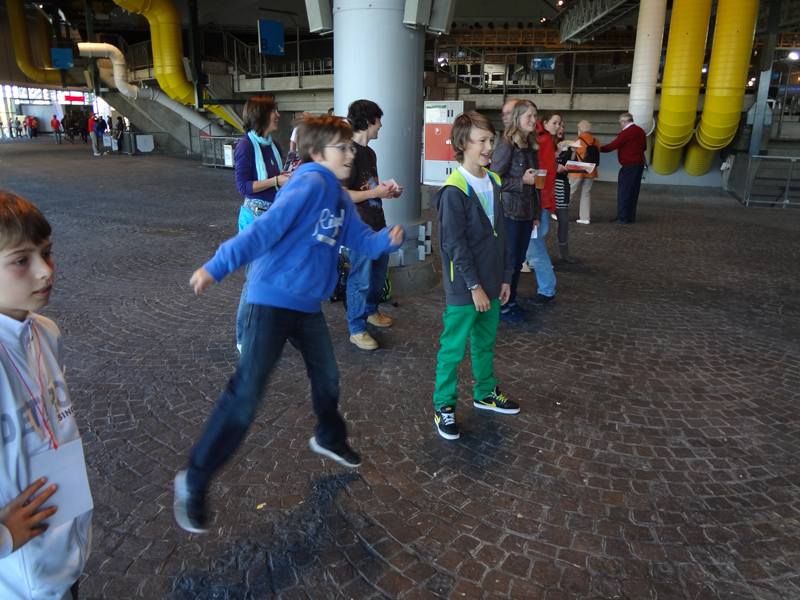
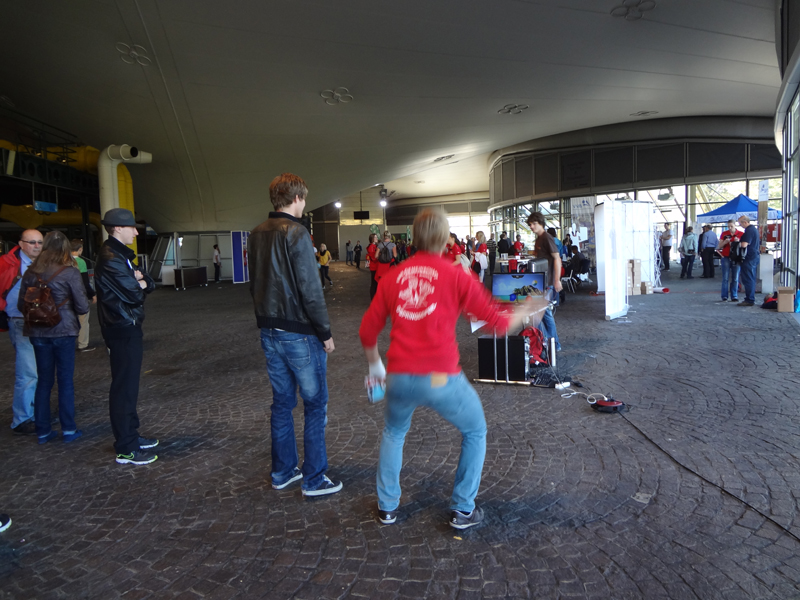
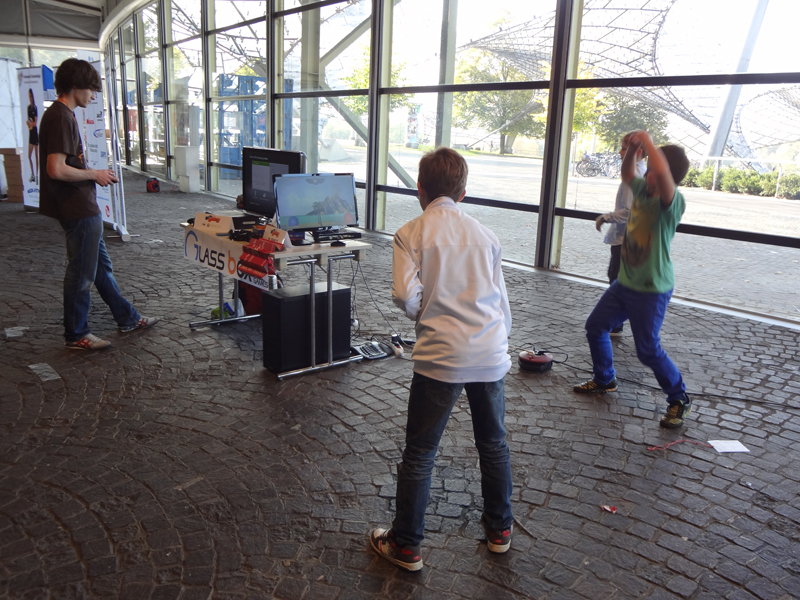
- User acceptance tests which took place at Olympiahalle Munich during a Volleyball event.



Resources
- The exising game: GlassboxGames - Volley
- The Kinect SDK: Kinect SDK 1.5
- Useful Kinect Video Tutorials: Getting started with Kinect development
Literature
- Nielsen, J. (1993). Usability Engineering. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann
- Saffer, D. (2009). Designing Gestural Interfaces. Sebastopol: O'Reilly Media
- Normann, D. (1988). The Design of Everyday Things. New York: Basic Books
| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Implementation and Evaluation of Motion-Based Input for a Volleyball Game |
| Abstract: | |
| Student: | Johannes Schmidt |
| Director: | |
| Supervisor: | Andreas Dippon |
| Type: | Bachelor Thesis |
| Area: | |
| Status: | finished |
| Start: | 2012/08/15 |
| Finish: | 2012/12/15 |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | |