Automatic Robotic Ultrasound Scan--Stage II
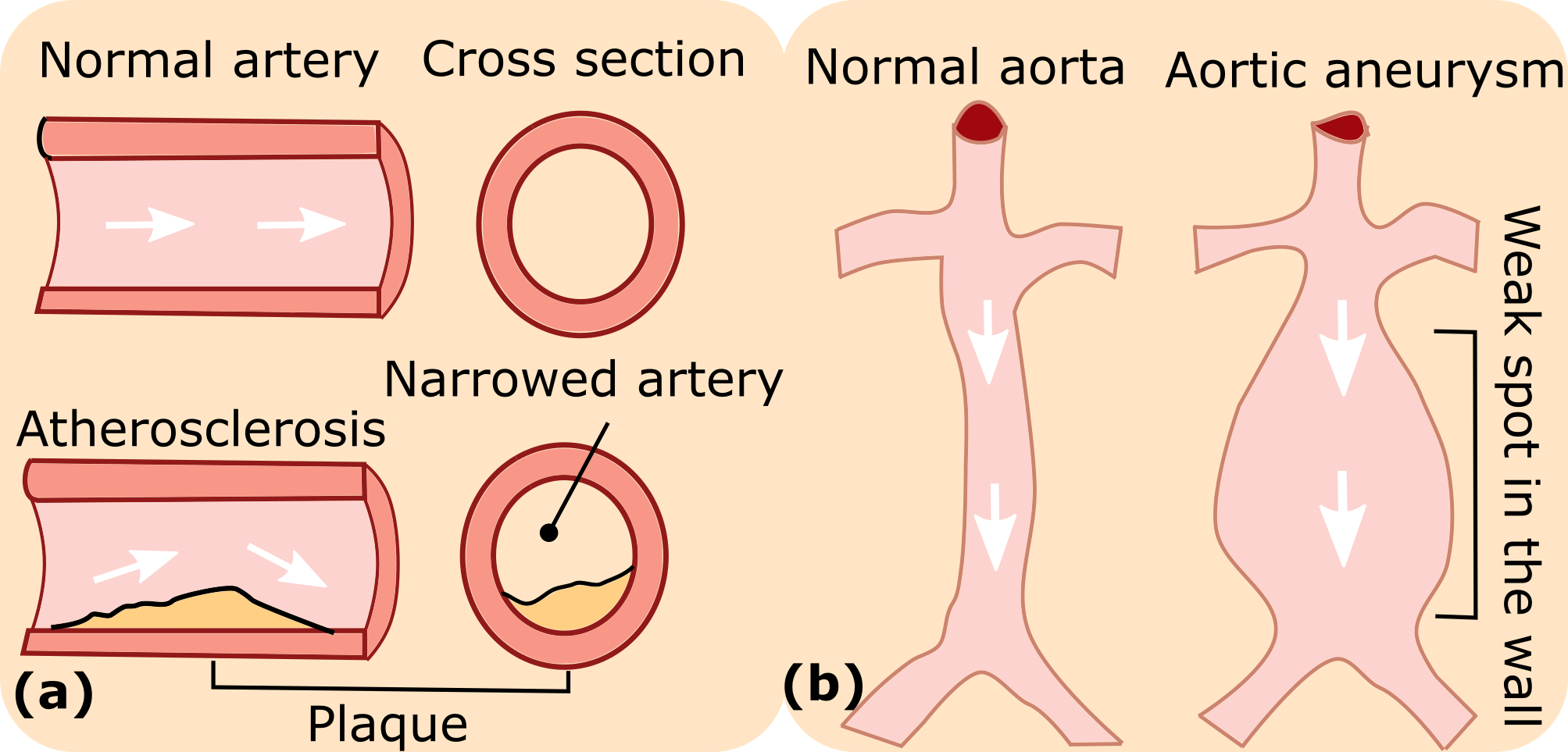
We are looking for motivated students to work on the research topic in the field of medical robotics. In this project, we aim to develop a robotic ultrasound system to automatically complete the ultrasound scan task and even give basic diagnosis results. Some sub-projects listed as follows: 1) Automatic Robotic Ultrasound Screening of Tubular Structures; 2) Vision-Based 3D Ultrasound Imaging for Long Blood Vessel.1) Automatic Robotic Ultrasound Screening of Tubular Structures Ultrasound (US) imaging is widely employed for diagnosis and staging of peripheral vascular diseases (PVD), mainly due to its high availability and the fact it does not emit radiation. However, high inter-operator variability and a lack of repeatability of US image acquisition hinder the implementation of extensive screening programs. To address this challenge, the robot is employed to facilitate obtaining accurate and repeatable US scans [1]. Benefited from the compliant controller, the contact force between the probe and scanned tissue can be accurately maintained during the scan. To better visualize the target blood vessel, the probe orientation aligned in normal to the scanned blood vessel itself. Thus, the US acquisition (force, orientation and contact point) [2] have been accurately represented. This is an extended work of [3]. The goal of the thesis is to develop an intelligent robotic ultrasound system using shared control and MPC to quickly and accurately tuning the US probe pose (position and orientation) for repeatable and accurate US images using only the real-time US imaging feedback.
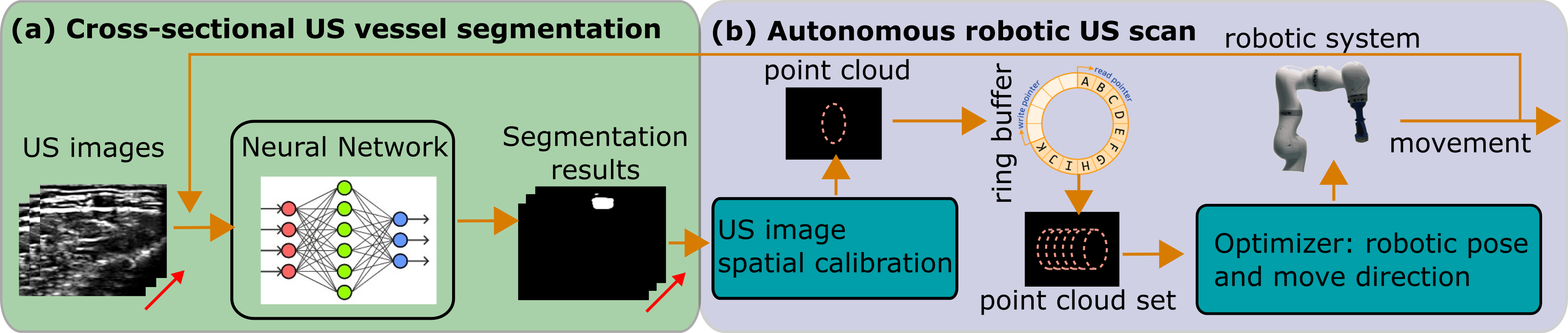
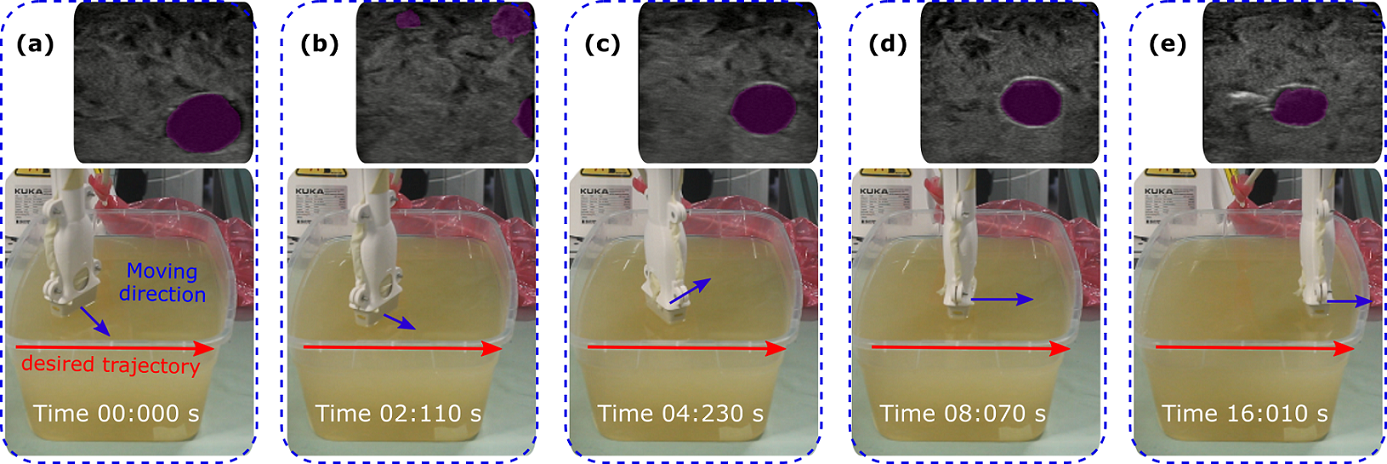
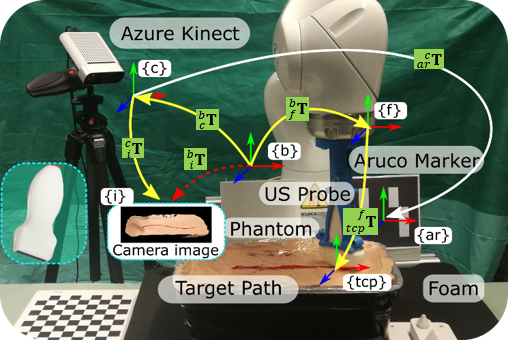
2) Vision-Based 3D Ultrasound Imaging for Long Blood Vessel Ultrasound (US) imaging is widely used for real-time diagnosis of internal tissue and organs. It provides the B-scan with low cost and no radiation in real-time. Traditional 2D US scan dynamically displays 2D images of the region of interest. However, the lack of 3D anatomy information makes the diagnosis results heavily depend on the doctors’ experience and very hard to repeatedly place the probe in the same position, even for experienced operators. Thus, the robot is employed to facilitate obtaining accurate and repeatable US scans [1]. Benefited from the compliant controller, the contact force between the probe and scanned tissue can be accurately maintained during the scan. However, due to the limitation of robotic workspace, current robotic US systems are not able to complete a full US sweep for visualizing whole limb artery. To address this challenge, a RGBD image of limb is registered to a generic MRI or CT volume to extract the trajectory of the target blood vessel [4]. Then the object movement is monitored by the depth camera and further computes the transformation between the pre- and post-movement object surface. Then the sweep is able to be resumed from break point. The goal of the thesis is to realize accurately robotic-assisted 3D US imaging for large-scale scans (e.g. whole leg or arm).
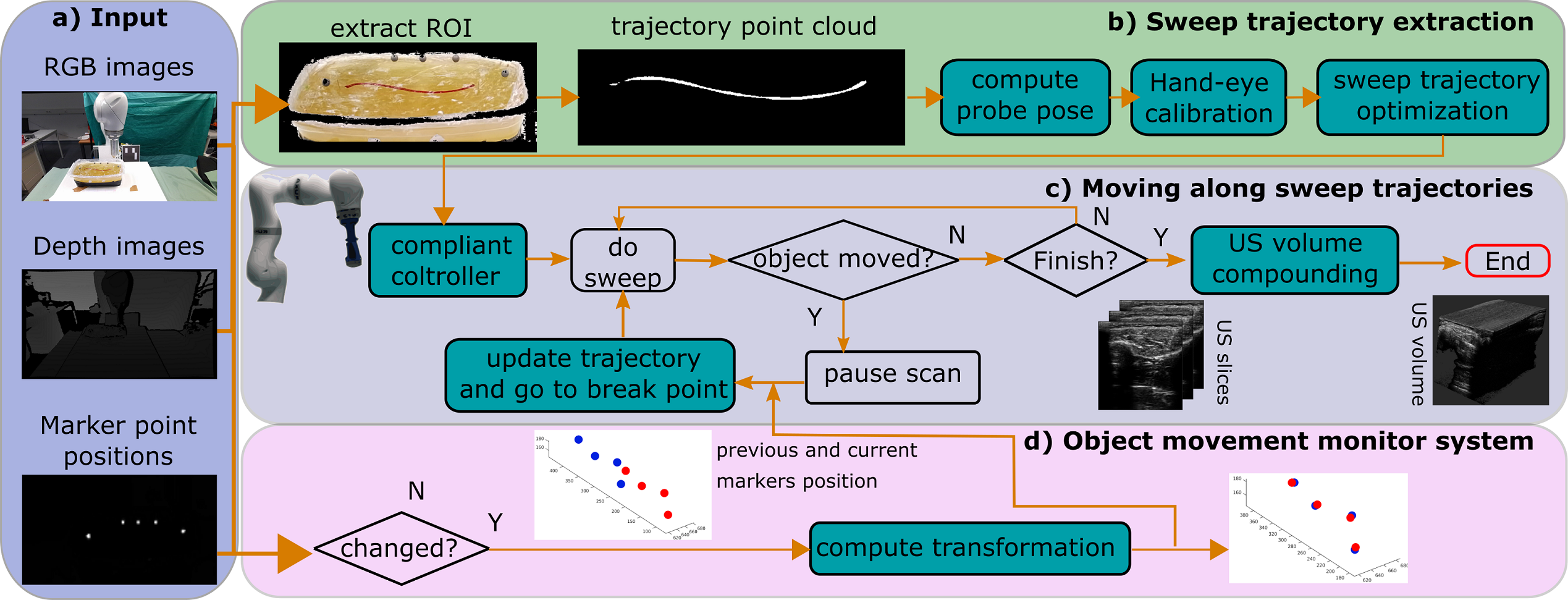
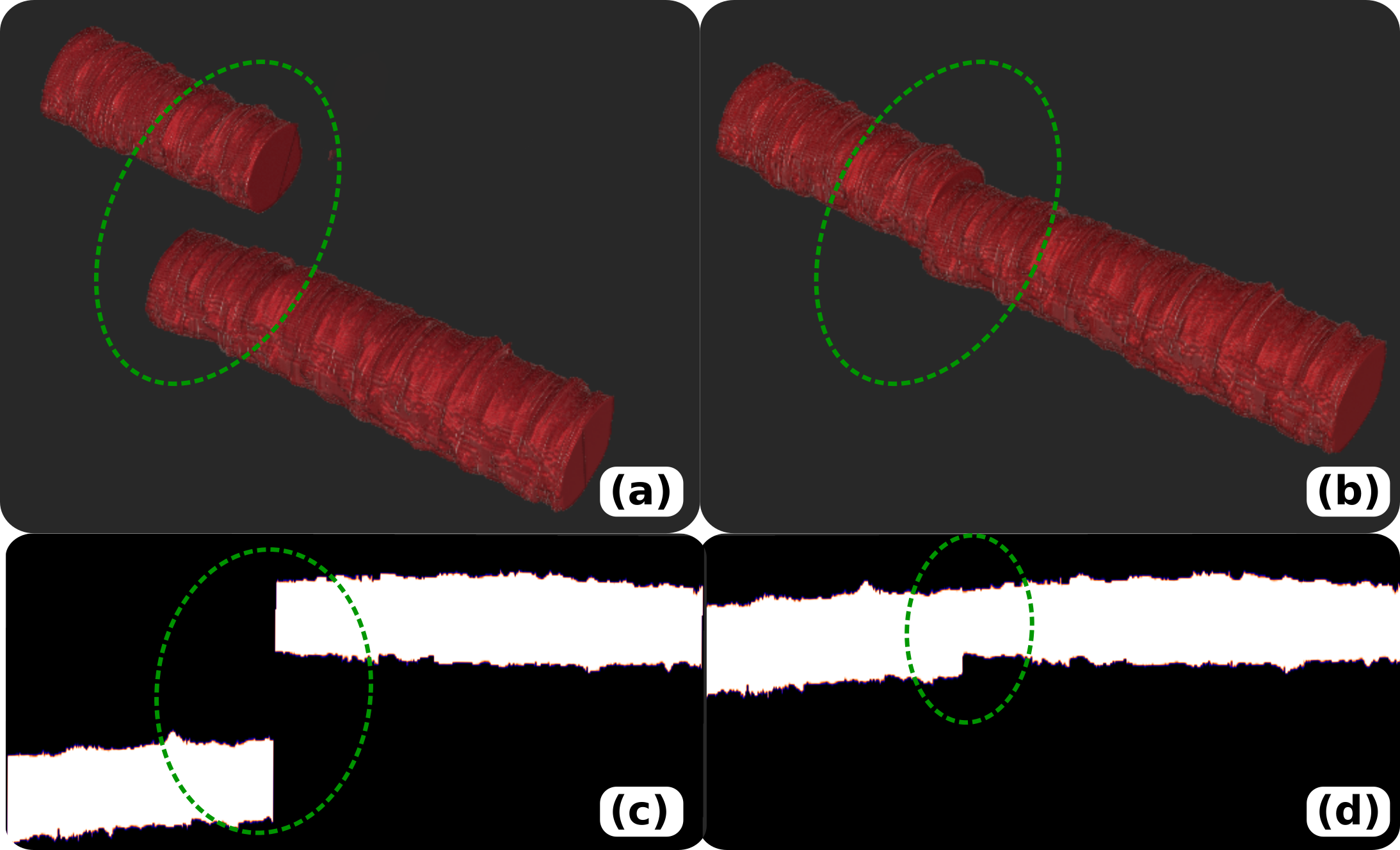
Skills and Qualifications: The candidate should have a good motivation to work on challenging and new ideas. Good skill in C++ and python. Familiar with ROS and basic imaging processing methods. Familiar with robotic control concept. REFERENCE
- [1] Jiang et al. Automatic Normal Positioning of Robotic Ultrasound Probe based only on Confidence Map Optimization and Force Measurement. RAL (presented in ICRA2020)
- [2] Jiang et al. " Autonomous Robotic Screening of Tubular Structures based only on Real-Time Ultrasound Imaging Feedback " arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.00099 (2020).
- [3] Gilbertson et al. "Force and position control system for freehand ultrasound." IEEE Transactions on Robotics 31.4 (2015): 835-849.
- [4] Langsch et al. “Robotic Ultrasound for Catheter Navigation in Endovascular Procedures” IROS2019.
- [5] Jiang et al. “Motion-Aware Robotic 3D Ultrasound” ICRA2021.
| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Automatic Robotic Ultrasound Scan--Stage II |
| Abstract: | |
| Student: | |
| Director: | Prof. Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Zhongliang Jiang; Dr. Mingchuan Zhou |
| Type: | Master Thesis |
| Area: | Machine Learning, Medical Imaging, Computer-Aided Surgery |
| Status: | open |
| Start: | |
| Finish: | |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | |