Master thesis or Master IDP:
Count rate saturation effects in handheld gamma detectors: Evaluation and influence on 3D intra-operative imaging
|
Master thesis by: (open) Advisors: Nassir Navab Supervision by: Philipp Matthies |
|
|
PDF of the thesis call
Topic
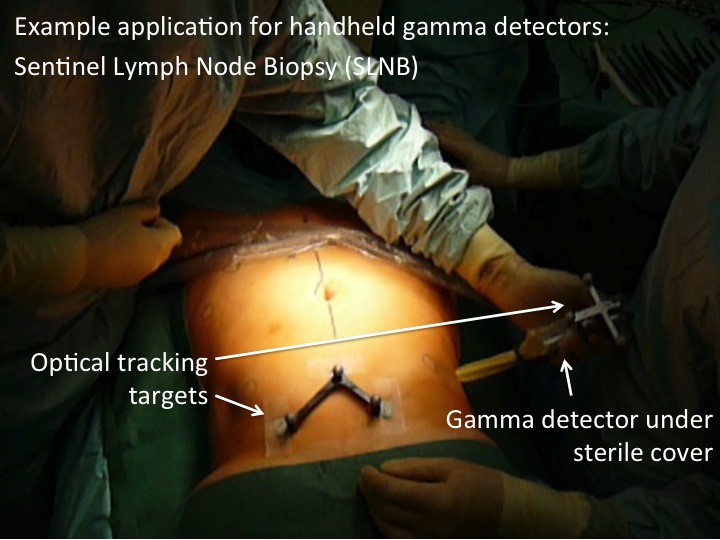
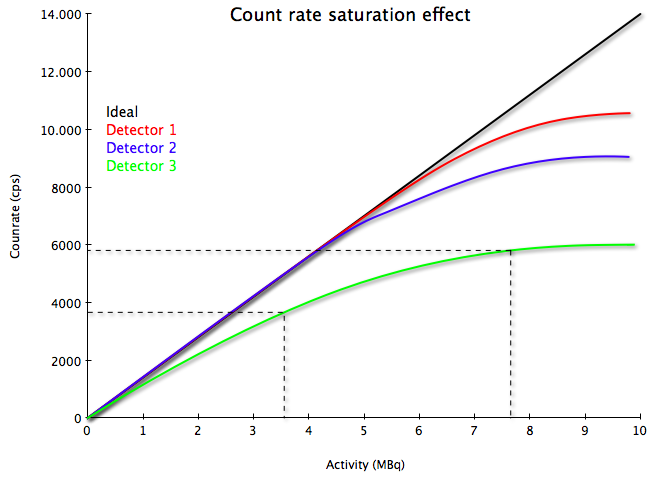
Gamma detectors are widely used in nuclear medicine, especially for localization of malign structures (e.g. cancer) that are not palpable or not visible using other imaging modalities such as ultrasound or computed tomography. In radio-guided surgery, hand-held gamma detectors are used to guide the surgeon to structures marked by radiotracers such as tumors and metastatic lymph nodes. Combining such detectors with optical tracking systems enables 3D imaging inside the operating room to improve guidance and to verify that all potentially malign structures have been removed during surgery. However, image quality is degraded by several factors, one of which is the count rate saturation in such detectors. Count rate saturation can have different origins, e.g. dead time in the detection material (scintillation crystal or semiconductor) or pulse pile-up. The purpose of this project is to study this behavior with different detectors and come up with a model to adjust for it in order to improve image quality.The student working on this project will have the possibility of working in a clinical environment with patient contact as well as gaining experience in project management with an industrial partner.
Requirements
The student should be interested in the topic of medical imaging and novel nuclear medicine applications. He or she should be open to work with the detector hardware communication. Basic Matlab and C++ knowledge is required. Knowledge about signal processing is advantageous.Supervision / Contact
This project is proposed by Prof. Nassir Navab (I16, Department of Informatics, TUM). Supervision will be provided by Philipp Matthies and Dr. Thomas Wendler. Working environment will be provided at IFL, Klinikum rechts der Isar, TUM, and SurgicEye GmbH, München.| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Count rate saturation effects in handheld gamma detectors: Evaluation and influence on 3D intra-operative imaging |
| Abstract: | Gamma detectors are widely used in nuclear medicine, especially for localization of malign structures (e.g. cancer) that are not palpable or not visible using other imaging modalities such as ultrasound or computed tomography. In radio-guided surgery, hand-held gamma detectors are used to guide the surgeon to structures marked by radiotracers such as tumors and metastatic lymph nodes. Combining such detectors with optical tracking systems enables 3D imaging inside the operating room to improve guidance and to verify that all potentially malign structures have been removed during surgery. However, image quality is degraded by several factors, one of which is the count rate saturation in such detectors. Count rate saturation can have different origins, e.g. dead time in the detection material (scintillation crystal or semiconductor) or pulse pile-up. The purpose of this project is to study this behavior with different detectors and come up with a model to adjust for it in order to improve image quality. The student working on this project will have the possibility of working in a clinical environment with patient contact as well as gaining experience in project management with an industrial partner. |
| Student: | |
| Director: | Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Philipp Matthies |
| Type: | DA/MA/BA |
| Area: | |
| Status: | open |
| Start: | 2012/10/01 |
| Finish: | |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | /twiki/pub/Students/MaCoRaSat/CountRateSaturation_Graph_Sample.png |