Evaluation of Software Defined Radio for Parasitic Tracking
Thesis by: Reissner UlrichAdvisor: Manuel Huber
Director: Gudrun Klinker
Due date: 26.09.2007
Abstract
This Sep focus on meassuring IEEE 802.11(Wireless Lan) signal strength with the Universal Software Radio Peripheral(USRP) and GNU-Radio.The 802.11 signal is converted from analog to digital with the USRP, an later demodulated with GNU-Radio. This demodulated signal is used to extract the needed data, like signal strength, type and MAC-Address.
On the other side, data received with an Intel Corporation PRO/Wireless 3945ABG controler integrated into a Laptop, is used for comparsion.
At the end, a visualisation of both signals is done with MagicMap.
Parasitic Tracking
- tracking infrastructure is not everywhere
- use all posibilities for tracking
- standard situation:
- extra hardware
- fixed application programming interface
- in our case:
- use only one hardware for all kind of tracking
- use detail information to get better results
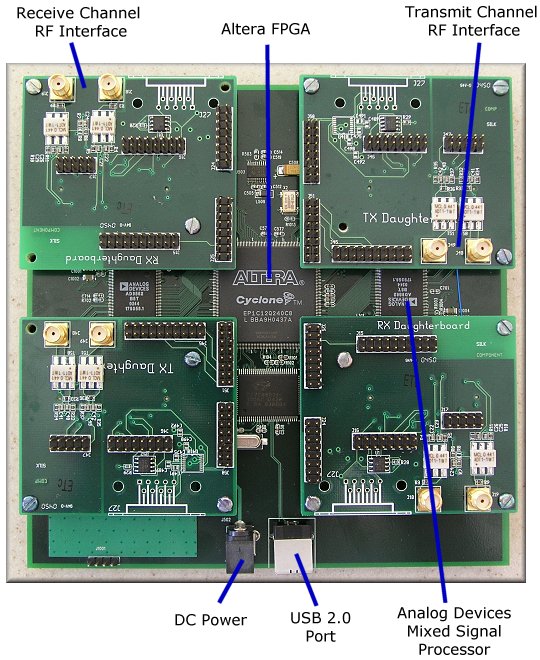
Hardware - Universal Software Radio Peripheral(USRP)
- Altera FPGA
- USB 2.0
- up to 4 daughterboars with range form 1MHz to 3GHz
Software - GNU-Radio
- software defined radio
- turns radio hardware problems into software problems
Signal Measurement
- IEEE 802.11
- Receive Signal Strength Indicator(RSSI) specified as optinal
- value between 0 and RSSI_MAX
- RSSI_MAX diffrent for each vendor
- USRP
- calculated over a definable number of bits received
- RSSI_MAX can be self defined
Evaluation
- Comparsion USRP - INTEL 3945ABG
- empty room, only tables and chairs
- 4 access points with fixed positions
- 7 independent measurements, each 300 s long
- USRP
- 62699 values
- standard deviation : 4,67
- values per access point per second : 7,46
- INTEL
- 9905 values
- standard deviation : 4,11
- values per access point per second : 1,18
- Advantages of USRP and GNU-Radio
- use all packets, not only beacons
- focus only on needed channels
- calculate the RSSI over the complete frame
- higher packet rate
- combination with rfid, dect, bluetooth
- Disadvanteges of USRP and GNU-Radio
- need of extra hardware
- more expensive than off the shelf hardware
- lower range
- higher power usage
- high cpu workload
- a bit higher standard deviation
- only works with 1 Mbit/s at the moment
Further Work
- implement channel hopping for USRP
- improve RSSI calculation
- use new gnuradio version
- implement new functions
- use new USRP version, to work with more than 1Mbit/s
- expand for dect, rfid, bluetooth tracking
- implement positioning algorithm
- implement api for Ubitrack
| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Evaluation of Software Defined Radio for Parasitic Tracking |
| Abstract: | This Sep focus on meassuring IEEE 802.11(Wireless Lan) signal strength with the Universal Software Radio Peripheral(USRP) and GNU-Radio. The 802.11 signal is converted from analog to digital with the USRP, an later demodulated with GNU-Radio. This demodulated signal is used to extract the needed data, like signal strength, type and MAC-Address. On the other side, data received with an Intel Corporation PRO/Wireless 3945ABG controler integrated into a Laptop, is used for comparsion. At the end, a visualisation of both signals is done with MagicMap. |
| Student: | Reissner Ulrich |
| Director: | Gudrun Klinker |
| Supervisor: | Manuel Huber |
| Type: | SEP |
| Area: | Industrial Augmented Reality |
| Status: | finished |
| Start: | 2006/11/01 |
| Finish: | 2007/09/31 |