Diploma thesis
|
Thesis by:
Advisor: Nassir Navab
Supervision by: Tassilo Klein, Ahmad Ahmadi
Due date: open
Abstract
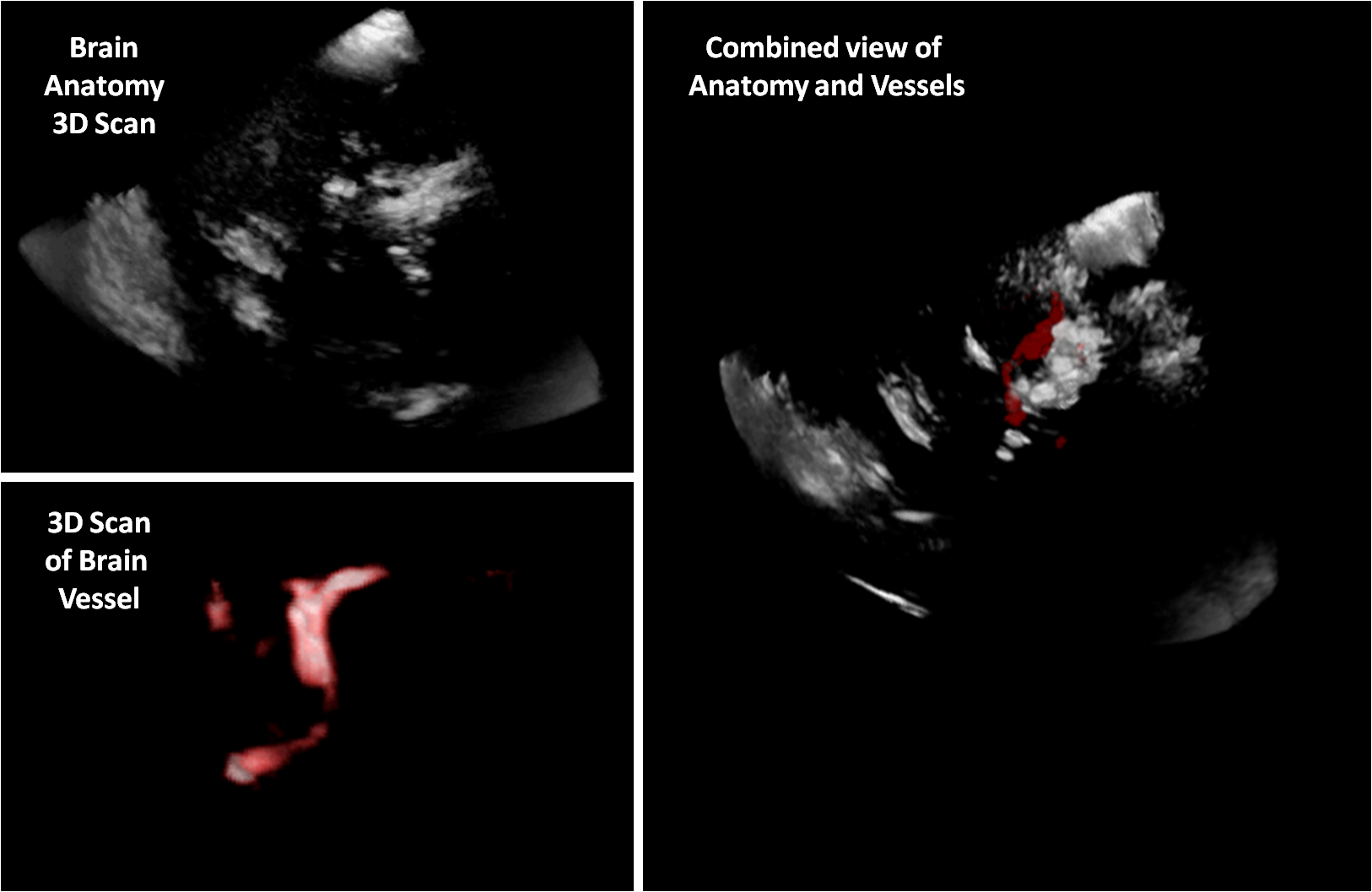
Ultrasound navigation is a desirable technique for guided neurosurgery. Blood vessels are among the most important anatomic structures which the surgeon needs for orientation. In 3D Freehand Ultrasound, we are (already) able to make 3D scans by sweeping an optically tracked ultrasound probe and combining many 2D slices with their respective pose into a 3D volume. In order to correctly visualize blood vessels, we would like to investigate improved reconstruction (or compounding) of blood vessels which are visualized with Doppler ultrasound. The improved images can be greatly useful for the surgeon to see anatomy correctly and have improved spatial context himself in a 3D ultrasound scan.Objectives and Methods
- We currently think of three basic approaches:
- Approach 1 (Fewest prior knowldege): There are two basic assumptions about vessels: they are not self-contained, but always connected, unless they capillarize and vanish in the tissue; thus, they can either continue, branch, or vanish. This knowledge can be incorporated into the reconstruction algorithm.
- Approach 2 (Medium prior knowledge): A vascular atlas can be incorporated in order to guide the 3D Freehand reconstruction of vessels (see also Approach 3).
- Approach 3 (Most prior knowledge): MRA (MRI Angiography) or CTA (CT angiography) can be used as a guide for 3D reconstruction of vessels. We would suggest to start with this approach.
- An extensive literature study should help in the beginning to identify already existing approaches.
- Developing a suitable method for 3D Freehand Doppler Angiography and integrating it into our existing software framework at CAMP.
Expected Results:
- Ideally, the reconstruction of vessels with the new method creates sharper and geometrically improved vessel structures.
Literature
- PhD Thesis Hastenteufel, Neue Methoden des 3D Ultraschalls zur Geschwindigkeitsrekonstruktion und intraoperativen Navigation, 2005
- O. Rygh, T. Nagelhus Hernes, F. Lindseth, T. Selbekk, T. Brostrup Müller, G. Unsgaard, Intraoperative navigated 3-dimensional ultrasound angiography in tumor surgery, Surgical Neurology, Volume 66, Issue 6, Pages 581-592
| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | 3D Freehand Ultrasound Compounding for Ultrasound Doppler Angiography |
| Abstract: | Ultrasound navigation is a desirable technique for guided neurosurgery. Blood vessels are among the most important anatomic structures which the surgeon needs for orientation. In 3D Freehand Ultrasound, we are (already) able to make 3D scans by sweeping an optically tracked ultrasound probe and combining many 2D slices with their respective pose into a 3D volume. In order to correctly visualize blood vessels, we would like to investigate improved reconstruction (or compounding) of blood vessels which are visualized with Doppler ultrasound. The improved images can be greatly useful for the surgeon to see anatomy correctly and have improved spatial context himself in a 3D ultrasound scan. |
| Student: | |
| Director: | Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Tassilo Klein, Ahmad Ahmadi |
| Type: | DA/MA/BA |
| Area: | Registration / Visualization, Medical Imaging |
| Status: | finished |
| Start: | |
| Finish: | |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | |