Master Thesis: Human Shape Adaptation with Skeletons and Pressure Measurement
Student: -Advisor: Prof. Dr. Nassir Navab
Supervised by: Chun-Hao Paul Huang, Dr. Stefanie Demirci, Dr. Diana Mateus
Overview
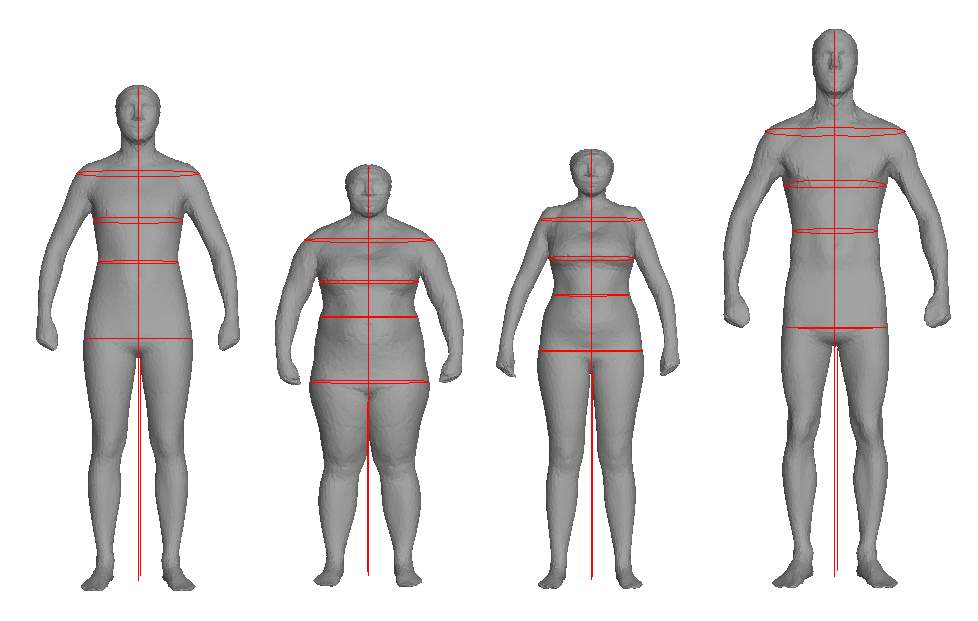
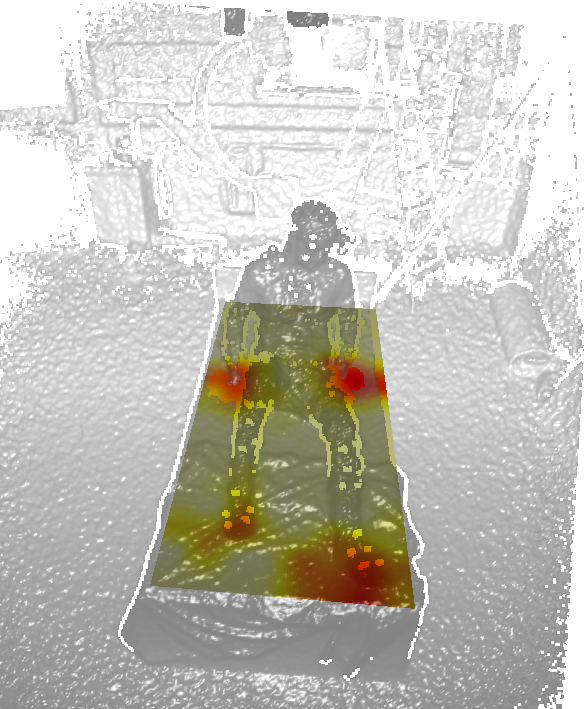
| Human shape recovery can in general be categorized in two classes: top-down vs. bottom-up. The former estimates poses by deforming a pre-defined 3D humanoid template non-rigidly frame by frame and avoids unreasonable poses by enforcing constraints on surface deformations. The latter starts with the detected 2D body parts or skeletons, then back-projects the points into 3D space either via depth data or triangulating multiple views. While the top-down scenario has been widely covered and applied in multiple view studios, e.g., Kinovis, the bottom-up approach is less studied and discussed. In this project, we aim at advancing the bottom-up approach. Specifically, one first recovers rough 3D skeletal poses with state-of-the-art bottom-up approach as initialization, and deform pre-defined human surfaces to fit to those poses. The generic human surface has to be adapted according to the size/scale of the skeleton, so as to yield correct anthropometric measurements (height, length of arms and circumference of waists, etc), as depeicted in the left figure. Skeleton-based animation such as linear-blend skinning, dual-quaternion-blend skinning is also worthwhile a look. Furthermore, besides relying on skeletal poses, we would also like to investigate the possibility of adjusting/refining human shapes according to the pressure measurements, as shown in the right figure. |
|
|
Requirements
- The student should have experience in C++ and/or Matlab.
- Knowledge in optimization and mesh processing is also helpful.
Literature & Resource
MPI Perceiving Systems:- SCAPE: Anguelov, D., Srinivasan, P., Koller, D., Thrun, S., Rodgers, J., & Davis, J., SCAPE: shape completion and animation of people. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2005 (Vol. 24, No. 3, pp. 408-416).
- MoSh?: Loper, M., Mahmood, N., & Black, M. J., MoSh?: Motion and shape capture from sparse markers. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 33(6), 220. 2014.
- SMPL: Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G., & Black, M. J., SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2015, 34(6), 248.
- Dyna: Pons-Moll, G., Romero, J., Mahmood, N., & Black, M. J., Dyna: A model of dynamic human shape in motion. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2015, 34(4), 120.
- Rupprecht, C., Pauly, O., Theobalt, C., & Ilic, S., 3d semantic parameterization for human shape modeling: Application to 3d animation. In 3DV 2013.
- Kavan, L., Collins, S., ˇįra, J., & O'Sullivan, C., Geometric skinning with approximate dual quaternion blending. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2008, 27(4), 105.
- Ye, M., & Yang, R., Real-time simultaneous pose and shape estimation for articulated objects using a single depth camera. In CVPR 2014 (pp. 2345-2352).
Contact
- Send your CV and transcripts to Chun-Hao Paul Huang, or drop by room 03.13.042.
| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Human Shape Adaptation with with skeletons and pressure measurement |
| Abstract: | |
| Student: | |
| Director: | Prof. Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Chun-Hao Paul Huang, Dr. Stefanie Demirci, Dr. Diana Mateus |
| Type: | DA/MA/BA |
| Area: | |
| Status: | open |
| Start: | |
| Finish: | |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | |