Tracking in Interactive Spaces
Diplomarbeit / Master's thesis
Location: Universitat Pompeu Fabra in Barcelona, Spain
Background about the group
The laboratory for
Synthetic Perceptive, Emotive and Cognitive Systems – SPECS - uses synthetic methods to study and construct the neuronal, psychological and behavioural principles underlying perception, emotion and cognition. The synthetic approach of SPECS combines real-world systems, such as robots, virtual reality systems and interactive installations with anatomically, physiologically and behaviorally constrained computational models. It is in this constructive approach that we retain a system’s view on mind, brain and behaviour. Moreover, this approach directly gives rise to novel brain based artefacts and these synthetic perceptive, emotive and cognitive systems in turn can provide novel technologies for real-world problems including the enhancement of the quality of life.
Description of the topic
Before the group moved from Zurich to Barcelona, they had created the interactive space
Ada for the Swiss Expo.02. Ada consisted of 180m2 space equiped with projection screens, illuminated pressure-sensitive floor tiles, moving spot lights and various sensors, such as cameras and microphones. The system was controlled by a large-scale neuronal network and has attracted more than 550.000 visitors.


In the scope of the
PRESENCCIA project, an improved version of this space, the "eXperience Induction Machine" (XIM) is to be built, with better sensors and improved algorithms for sensing and control. One of the goals is to enable visitors the interaction with avatars of remotely present people projected onto the screens and with purely synthetic characters in a large distributed mixed-reality environment.
In order to react to visitors, XIM needs to be aware of their exact position and needs to be able to track them unambiguously over longer periods of time. This will be done by combining information from cameras, microphones and the pressure-sensitive floor.
The topic of the thesis will be in the areas of sensor/image data processing and/or sensor fusion and can be tailored to the interests of the student. The thesis is to be carried out in a highly interdisciplinary team of psychologists and computer scientists at
Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) in Barcelona in tight cooperation with a supervisor in Munich.
Abstract
The task of people tracking in the interactive space XIM is solved by
using Particle Filters, one type of Bayesian estimation, for estimating
humans' states within the environment. The Particle Filter uses a four
dimensional motion model to predict the human behavior. An innovative
approach to evaluate images from a ceiling mounted infrared camera is
applied to calculate the probabilities for each of the Particle Filters'
hypotheses about the human's states. Additional a simple concept to
detect newly arriving visitors and leaving visitors is introduced to
enable the system to work complete automatically without manual
interaction using the pressure sensitive floor.
Human Representation
Ellipses and ellipsoids are choosen as the 2- and 3-dimensional representation of the human shape as they are:
- one geometric shape,
- easy to describe,
- match the human contour very well and
- ellipses can be generated by the projection of ellipsoids on the image plane.
Comparsion of ellipse and human shape under projection by a top view camera:

Particle Filters
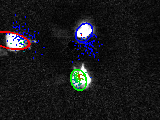
Particle Filtes are used to represent the belief about a human's position on a 2-dimensional plane. Each particle represents one hypothesis about the position and a change is done by applying a motion model that represents human behaviour.
- Illustration of particle filters representing human positions. The colors of the dots mark the weight of the particle:
Important Literature in Bayesian Estimation, especially Particle Filters
[1] Thomas Bayes. Essay Toward Solving a Problem in the Doctrine of Chances. Philosphical Transactions of the Royal Society, 53:370–418, 1763.
[2] A. Doucet, N. de Freitas, and N. Gordon. Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Practice. Springer-Verlag, 2001.
[3] D. Fox, J. Hightower, L. Liao, D. Schulz, and G. Borriello. Bayesian Filtering for Location Estimation. Pervasive Computing, IEEE, 2, Issue 3:24 – 33, 2003.
[4] N.J. Gordon, D.J. Salmond, and A.F.M. Smith. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation. Radar and Signal Processing, IEE Proceedings F, 140(2):107–113, 1993.
[5] T. Osawa, X. Wu, K. Wakabayashi, and T. Yasuno. Human Tracking by Particle Filtering Using Full 3D Model of Both Target and Environment. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06)-Volume 02, 2:25–28, 2006.
Final Thesis
Multi-Modal Sensor Fusion for People Tracking in Interactive Spaces:
Master Thesis - Technische Universitaet Muenchen (
bib)
