Bachelor/Master Thesis: Machine Learning for Automatic Tissue Characterization in Intra-Vascular Optical Coherence Tomography Images
Description
|
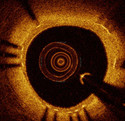
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) uses light rather than ultrasound to record high-resolution images that permits a precise assessment of biological tissue. Used intra-vascular, OCT is increasingly used for assessing safety and efficacy of intra-coronary devices, such as drug-eluting stents and bioabsorbable stents. Obtained images provide insights regarding stent malposition, overlap, and neointimal thickening, among others. Recent OCT histopathology correlation studies have shown that OCT can be used to identify plaque composition, and hence it is possible to distinguish “normal” from “abnormal” neointimal tissue based on its visual appearance. The aim of this project is to develop machine learning algorithms for automatic analysis of tissue in intra-vascular OCT.
|
Expected results
During this project, machine learning algorithms should be developed that learn a model for specific tissue types based on information extracted from annotated intra-vascular OCT images (learning phase).
After constructing the model, it should be applied to images without annotations and automatically classify pixels in the image belonging to one of the tissues available in the learning phase.
Performance of the algorithm should be judged by quantitative evaluation metrics (accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, etc.).
Requirements
- Interest in interdisciplinary research field
- Very good programming skills in C++ and/or Python
- Basic knowledge of machine learning principles and image processing
Contact
This project is supervised by
Sebastian Pölsterl in collaboration with physicians at Deutsches Herzzentrum in Munich.
Literature
- Malle et al. (2013). Tissue characterization after drug-eluting stent implantation using optical coherence tomography. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 33(6), 1376–83. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301227
- Ughi et al. (2014). Automatic characterization of neointimal tissue by intravascular optical coherence tomography. Journal of biomedical optics, 19(2), 21104. doi:10.1117/1.JBO.19.2.021104

