Comparison of different volume renderers for 2D/3D registration
2D/3D or volume-to-image registration needs to compare data of different dimensions. By projecting the volume and comparing the resulting 2D image with the real 2D image using some similarity measure the quality of a registration can be evaluated. Then, the viewpoint is slightly changed, another projection is performed, and the two images are compared again, etc. The process stops once the best viewpoint (with highest similarity between projected and 2D image) is found. Different projection techniques can be used for this first step including purely software-based renderers modeling a raycasting through the volume and hardware-accelerated renderers using textures.This SEP compares these different techniques in terms of speed and accuracy. The different renderers can be provided as well as a general framework for 2D/3D registration. The working steps will be
- adjustment of viewpoint for hardware- and software-based renderers
- Implementation of a class structure encapsulating all entities for 2D/3D registration (renderer, image, similarity measure)
- Testing Hardware-based Renderers on different GPUs and the resulting accuracy of the registration
- Comparing Software- and Hardware-based volume rendering for 2D/3D image registration
A general interest in OpenGL would also be a good point to start from.
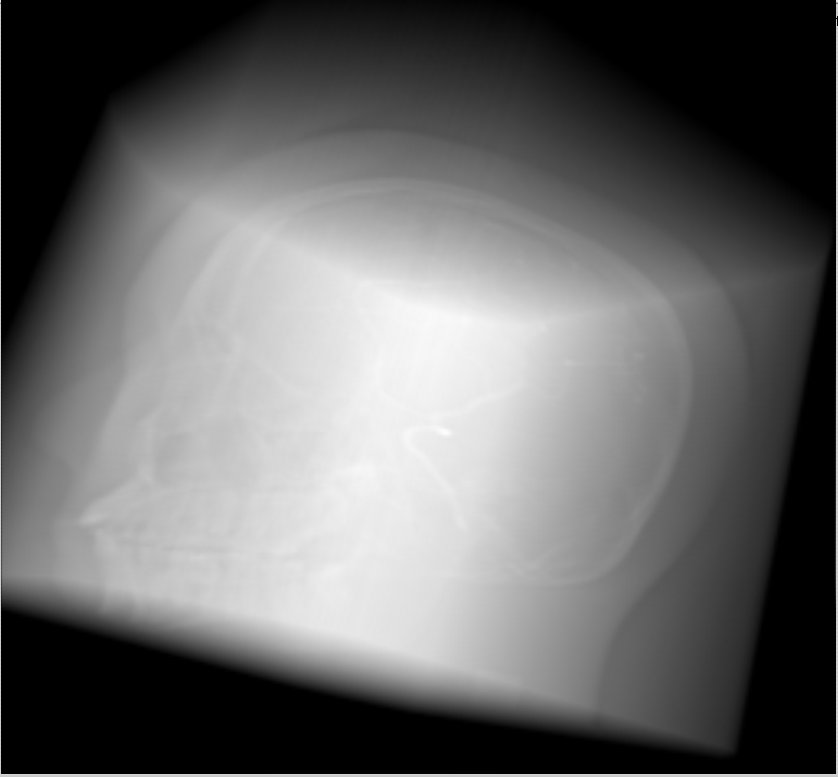
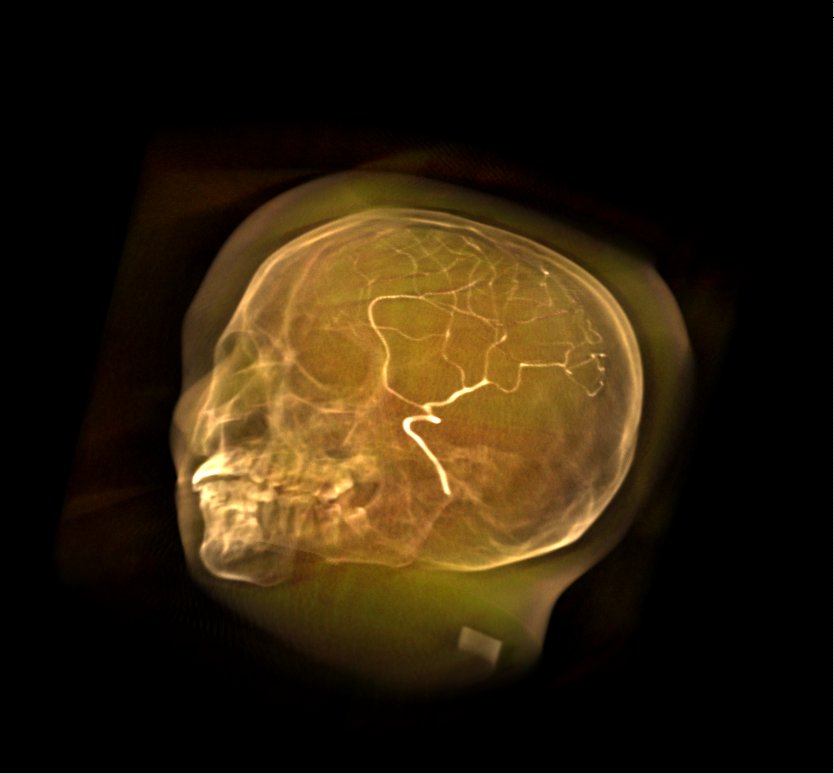
A volume rendered with a software and a hardware-accelerated renderer
| ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Comparison of different volume renderers for 2D/3D registration |
| Abstract: | 2D/3D or volume-to-image registration needs to compare data of different dimensions. By projecting the volume and comparing the resulting 2D image with the real 2D image using some similarity measure the quality of a registration can be evaluated. Then, the viewpoint is slightly changed, another projection is performed, and the two images are compared again, etc. The process stops once the best viewpoint (with highest similarity between projected and 2D image) is found. Different projection techniques can be used for this first step including purely software-based renderers modeling a raycasting through the volume and hardware-accelerated renderers using textures. This SEP compares these different techniques in terms of speed and accuracy |
| Student: | |
| Director: | Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Martin Groher |
| Type: | SEP |
| Area: | |
| Status: | draft |
| Start: | |
| Finish: | |