Dr. Oliver Schoppe
Image-Based Biomedical Modeling Group (Prof. Dr. Bjoern Menze)I finished my PhD in 2020 and I am not with the chair anymore

Office
Center for Translational Cancer Research (TranslaTUM)
Klinikum rechts der Isar, Trogerstr 1, 81675 Munich
My TUM email address is not active anymore. In case of questions, please contact my colleagues at the chair or reach out to me via LinkedIn
Research Focus
My research interest is motivated by the tremendous potential impact of making Deep Learning-based computer vision applicable in everyday settings in clinical and pre-clinical research. This entails developing deep convolutional networks for detection, localization, and segmentation tasks in medical images of various modalities. Ensuring applicability in everyday settings typically requires elaborate strategies to deal with limited availability of annotated data, for instance making use of Transfer Learning or Data Augmentation.
I cooperate with Ali Ertürk's Lab at the Helmholtz Center Munich where I am leading the Artificial Intelligence Group. This work comprises research questions like automatic image segmentation and classification problems for general 3D anatomy, but also specific questions in the fields of stroke, dementia, and cancer.
Center for Translational Cancer Research (TranslaTUM)
Klinikum rechts der Isar, Trogerstr 1, 81675 Munich
My TUM email address is not active anymore. In case of questions, please contact my colleagues at the chair or reach out to me via LinkedIn
Research Focus
My research interest is motivated by the tremendous potential impact of making Deep Learning-based computer vision applicable in everyday settings in clinical and pre-clinical research. This entails developing deep convolutional networks for detection, localization, and segmentation tasks in medical images of various modalities. Ensuring applicability in everyday settings typically requires elaborate strategies to deal with limited availability of annotated data, for instance making use of Transfer Learning or Data Augmentation.
I cooperate with Ali Ertürk's Lab at the Helmholtz Center Munich where I am leading the Artificial Intelligence Group. This work comprises research questions like automatic image segmentation and classification problems for general 3D anatomy, but also specific questions in the fields of stroke, dementia, and cancer.
DeepMACT - Deep learning based Metastasis Analysis in Cleared Tissue
The DeepMACT pipeline is an end-to-end procedure that enables highly automated detection and characterization of tumor micro-metastasis in large volumetric scans of whole cleared mice. This pipeline comprises two core technologies: DISCO tissue clearing and deep learning. For details, please refer to web resources and the article published in Cell (2019) Press coverage
Press coverage
- TV interview on DeepMACT by N-TV (German)
- TUM press statement (German)
- Helmholtz-Zentrum press statement (English)
- Frankfurter Rundschau (German)
- Wissenschaftsjahr 2019 (German)
- 20 Minutos (Spanish)
- QQ News(Chinese)
- Hürriyet (Turkish)
- Scienza e Tecnica (Italian)
AIMOS - AI-based Mouse Organ Segmentation
The AIMOS pipeline is an end-to-end procedure that enables fully automated segmentation of major organs (brain, lungs, heart, liver, kidneys, spleen, bladder, stomach, intestine) and the skeleton in large volumetric scans of whole mice. This method is independent of the imaging modality (we implemented it for light-sheet microscopy, native micro-CT, and contrast-enhanced micro-CT). In addition to the 3D segmentations for each organ, AIMOS can also provide a heatmap highlighting ambiguous image regions, allowing to localize and quantify inherent uncertainty. Besides the code and the pre-trained models, we also provide manually labeled datasets. For details, please refer to web resources and the article published in Nature Communications (2020) Press coverage
Press coverage
- TUM press statement (German)
- Healthcare in Europe (German)
- Science Daily (English)
- Big Data Insider (German)
- Innovation Origins (English)
- Lab Roots (English)
- Interview with KI Note (German)
Projects for students
We expect all students to have:
- Prior theoretical knowledge on deep learning
- Some practical experience with deep learning (PyTorch or TensorFlow)
- Good Python coding skills
- Ideally experience in computer vision / medical image analysis
Deep learning-based tumor detection in 3D scans

Deep transfer learning for 3D brain vessel segmentation

Deep learning-based tracing of single neurons and neural pathways
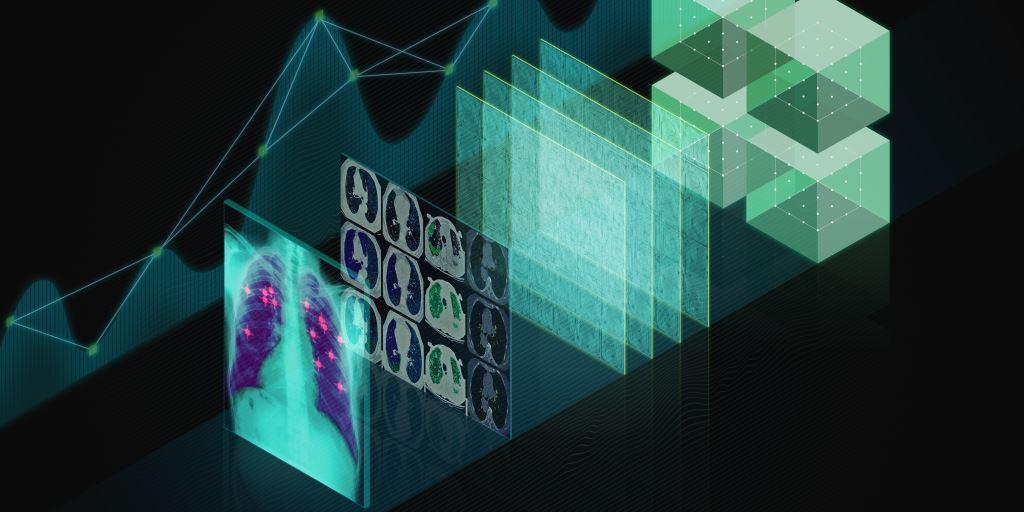
Distributed deep learning for large-scale medical image analysis
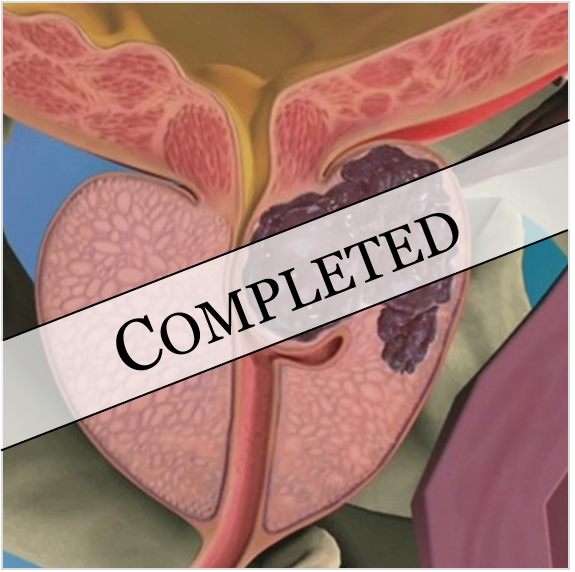
Deep learning-based 3D segmentation of prostate lesions
Analysis of CT scans from automotive OEM with deep learning

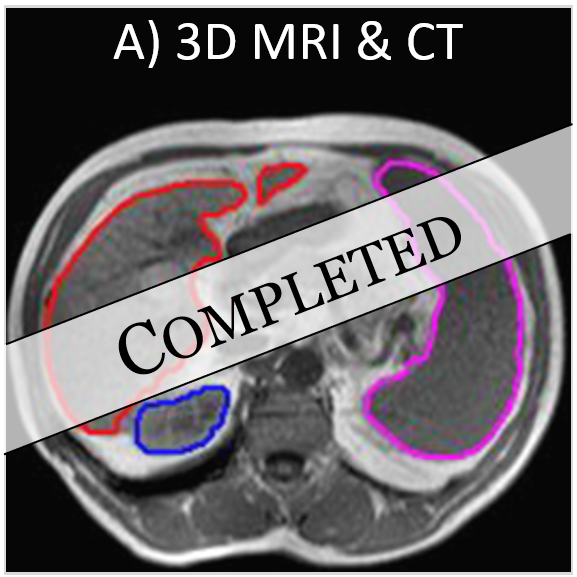
Deep learning-based multi-organ segmentation for MRI & CT
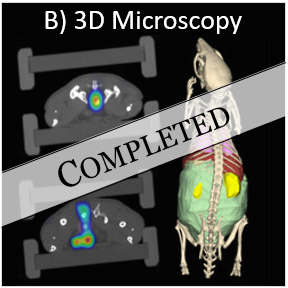
Deep learning-based multi-organ segmentation for 3D microscopy
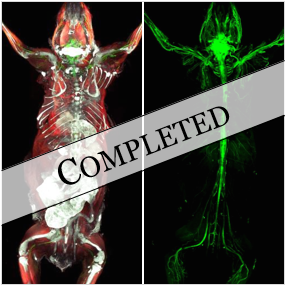
Deep learning for multi-channel microscopy
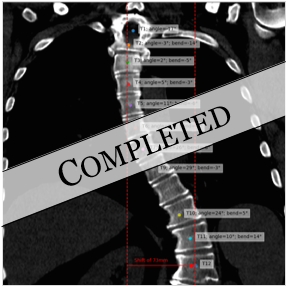
Clinical application of deep learning for spine analysis
Machine learning analysis of sensor data for autonomous driving

NLP approaches to radiology report analysis
Background
- 2018 - 2020: Ph.D. candidate at IBBM group (TU Munich) with Prof. Dr. Bjoern Menze and AI Group Leader at Helmholtz Center Munich
- since 2015: Consultant with McKinsey & Co., Inc.
- 2015: M.Sc. in Electrical Engineering and Information Technology from TU Munich
- 2014-15: Research stays at Oxford University (neuroscience, artificial neural networks)
- 2013: B.Sc. in Electrical Engineering and Information Technology from TU Munich
- 2011-12: Visiting student at Harvard University & MIT (neuroscience, business, law)
Publications
- O Schoppe, C Pan, J Coronel, H Mai, Z Rong, M Todorov, A Müskes, F Navarro, H Li, A Ertürk & B Menze. Deep learning-enabled multi-organ segmentation in whole-body mouse scans. Nature Communications 2020
- A Qasim*, I Ezhov*, S Shit, O Schoppe, J Paetzold, A Sekuboyina, F Kofler, J Lipkova, H Li, B Menze. Red-GAN: Attacking class imbalance via conditioned generation. Yet another medical imaging perspective. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research 2020
- M Kimm, M Shevtsov, C Werner, W Sievert, Z Wu, O Schoppe, B Menze, E Rummeny, R Proksa, O Bystrova, M Martynova, G Multhoff, S Stangl. Gold Nanoparticle Mediated Multi-Modal CT Imaging of 3 Hsp70 Membrane Positive Tumors. Cancers
- S Zhao, M Todorov, R Cai, R al-Maskari, H Steinke, E Kemter, H Mai, Z Rong, M Warmer, K Stanic, O Schoppe, J Paetzold, B Gesierich, M Wong, T Huber, M Duering, O Bruns, B Menze, J Lipfert, V Puelles, E Wolf, I Bechmann, A Ertürk. Cellular and Molecular Probing of Intact Human Organs. Cell 2020
- M Todorov*, J Paetzold*, O Schoppe, G Tetteh, V Efremov, K Voelgyi, M Duering, M Dichgans, M Piraud, B Menze, A Ertürk. Machine learning analysis of whole mouse brain vasculature. Nature Methods 2020 (free bioRxiv preprint (old version))
- C Pan*, O Schoppe*, A Parra-Damas*, R Cai, M Todorov, G Gondi, B v. Neubeck, N Böğürcü-Seidel, S Seidel, K Sleiman, C Veltkamp, B Förstera, H Mai, Z Rong, O Trompak, A Ghasemigharagoz, M Reimer, A Cuesta, J Coronel, I Jeremias, D Saur, A Acker-Palmer, T Acker, B Garvalov, B Menze, R Zeidler, A Ertürk. Deep learning reveals cancer metastasis and therapeutic antibody targeting in entire body. Cell 2019 (free bioRxiv preprint (old version))
- J Paetzold*, O Schoppe*, R Al-Maskari, G Tetteh, V Efremov, M Todorov, R Cai, H Mai, Z Rong, A Ertürk, B Menze. Transfer learning from synthetic data reduces need for labels to segment brain vasculature and neural pathways in 3D. MIDL 2019 (London)
- O Schoppe, NS Harper, BDB Willmore, AJ King, JWH Schnupp. Measuring the performance of neural models. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience 2016
- BDB Willmore*, O Schoppe*, AJ King, JWH Schnupp, NS Harper. Incorporating midbrain adaptation to mean sound level improves models of auditory cortical processing. Journal of Neuroscience 2016
- NS Harper*, O Schoppe*, BDB Willmore, Z Cui, JWH Schnupp, AJ King. Network receptive field modeling reveals extensive integration and multi-feature selectivity in auditory cortical neurons. PLoS Computational Biology 2016
- M Rudnicki, O Schoppe, M Isik, F Völk, W Hemmert. Modeling auditory coding: from sound to spikes. Cell and Tissue Research 2015
- Q Wan, O Schoppe*, S Gunasekaran, D Holland, E Roche, H-C Hur, C Walsh. Multifunctional Laparoscopic Trocar With Built-in Fascial Closure and Stabilization. Journal of Medical Devices 2013
Google Scholar profile
Code
- Matlab code for performance measures of computational neural models
- DeepMACT: Protocol and Python/PyTorch code for 3D tumor metastasis detection
- AIMOS: Labeled datasets and Python/PyTorch code for 3D organ segmentation