Fluid Simulation - Realistic simulation of cement flow
Thesis by: tbaAdvisor: Prof. Dr. Nassir Navab
Supervision by: Patrick Wucherer, Philipp Stefan
Overview
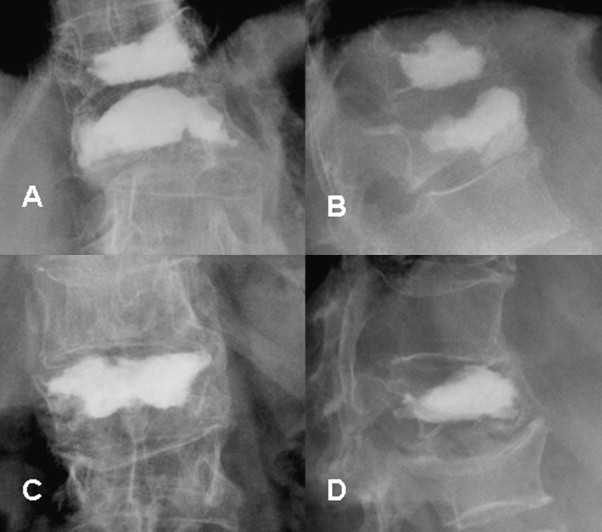 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0720048X10000276
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0720048X10000276
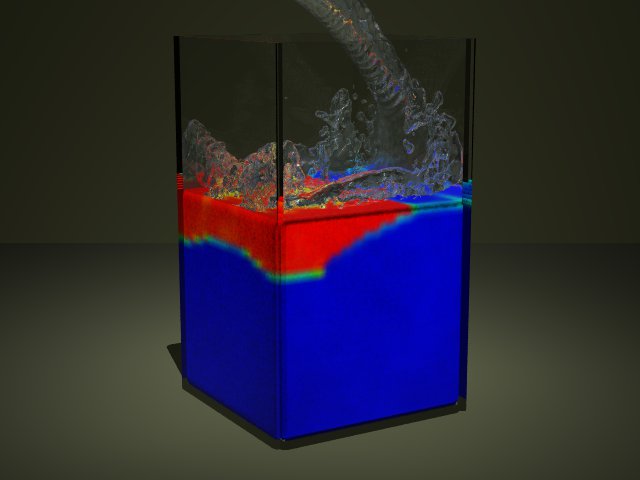 [Lenaerts2008]
[Lenaerts2008]
Topic
The objective of this research work is the formulation of a computational model for realistic real-time simulation of the brittle, porous material of the bone and the interaction of bone cement and instruments with it. This is achieved using a GPU-accelerated mesh-free SPH approach based on the CT imaging data.Contribution
The research goal contributes to the complete simulation of a minimally invasive surgery (MIS) called “kyphoplasty”. The procedure is conducted on patients with fractured vertebrae in order to set the spine into an upright position and stabilize the vertebrae. First a cavity with a balloon catheter in the vertebra is created. Afterwards the cavity is filled up with cement [Hillmeier2003].What do we offer
- Experience different fields of research in computer science: Visualization, Software Engineering, Real-time Simulation, GPU Programming
- Your thesis and degree. (and also submission to prestigious conferences/journals depending on student performance)
- We offer an intensive supervision, but initiative is very welcome. Working environment will be provided at the NARVIS lab.
Requirements
- Interest in fluid mechanics
- Knowledge of a programming environment (for example Matlab or Python or C++) is required
- Not mandatory: Arduino programming experience
Literature
- A Particle-Based Model for Prediction of Cement Diffusion during Osteoporotic Hip Augmentation Surgery: Theory and Validation, Proceedings ASME International Mechanical Engineering Conference Exposition, Nov, Basafa, E. and Otake, Y. and Kutzer, M. D. and Armiger, R. S. and Armand, M., 2010, pp. 12–18
- Z. Lian, C. Chui, und S. Teoh, „A biomechanical model for real-time simulation of PMMA injection with haptics“, Computers in Biology and Medicine, Feb. 2008.
- C.-K. Chui, J. S. K. Ong, Z.-Y. Lian, Z. Wang, J. Teo, J. Zhang, C.-H. Yan, S.-H. Ong, S.-C. Wang, H.-K. Wong, C.-L. Teo, und S.-H. Teoh, „Haptics in computer-mediated simulation: Training in vertebroplasty surgery“, Simulation & Gaming, Bd. 37, Nr. 4, S. 438–451, Dez. 2006.
- A. Hérault, G. Bilotta, A. Vicari, E. Rustico, and C. D. Negro, “Numerical simulation of lava flow using a GPU SPH model”, Ann. Geophys., vol. 54, no. 5, Dec. 2011. „Computer simulation of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement flow“, ANZIAM, Nr. J.47, S. C404–C418, 2006.
- [Lenaerts2008] T. Lenaerts, B. Adams, und P. Dutré, „Porous flow in particle-based fluid simulations“, in ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 papers on - SIGGRAPH ’08, Los Angeles, California, 2008, S. 1.
- [Hillmeier2003] J. Hillmeier, P. Meeder, G. Nöldge, und C. Kasperk, „Minimal invasive Reposition und innere Stabilisierung osteoporotischer Wirbelkörperfrakturen (Ballonikyphoplastie)“, Operative Orthopädie und Traumatologie, Bd. 15, Nr. 4, S. 343–362, 2003.
Contact
| ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Fluid Simulation - Realistic simulation of cement flow |
| Abstract: | The objective of this research work is the formulation of a computational model for realistic real-time simulation of the brittle, porous material of the bone and the interaction of bone cement and instruments with it. This is achieved using a GPU-accelerated mesh-free SPH approach based on the CT imaging data. The research goal contributes to the complete simulation of a minimally invasive surgery (MIS) called “kyphoplasty”. The procedure is conducted on patients with fractured vertebrae in order to set the spine into an upright position and stabilize the vertebrae. First a cavity with a balloon catheter in the vertebra is created. Afterwards the cavity is filled up with cement. |
| Student: | |
| Director: | Prof. Dr. Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Patrick Wucherer, Philipp Stefan |
| Type: | DA/MA/BA |
| Area: | Registration / Visualization, Medical Augmented Reality |
| Status: | draft |
| Start: | |
| Finish: | |
| Thesis (optional): | |
| Picture: | |