Digital Tomosynthesis in X-Ray Phase Contrast Imaging
Digitale Tomosynthese in der Röntgenphasenkontrastbildgebung
Tomosynthèse numérique pour l’imagerie à contraste de phase par rayons X
Student Research Project Details
| Student: | Lorenz König |
| Supervisor: | Prof. Nassir Navab |
| Advisors: | Alberto Bravin, Paola Coan, Tobias Lasser |
| Facilities: | ESRF, Grenoble; CAMP, TUM, München |
| Project finished: | 2009 |
| In phase constrast imaging, interference of partially coherent waves is exploited to produce images of weak gradients of the refractive index. Conventional radiography is insensitive to these weak variations, therefore being an inapt tool for the examination of soft tissues. Phase contrast imaging, on the other hand, promises superior results in, for instance, mammography and cartilage imaging. | Die Phasenkontrastbildgebung macht sich die Interferenz teilweise kohärenter Wellen zunutze, um schwache Gradienten der Brechzahl kontrastreich abzubilden. Herkömmliche Röntgenbildgebungsverfahren sind diesen gegenüber unempfindlich, was sie ungeeignet zur Untersuchung von Weichgewebe macht. Die Phasenkontrastbildgebung verspricht hier Fortschritte, etwa in der Mammographie und Knorpelbildgebung. | Dans le cadre de l’imagerie à contraste de phase on profite de l’interférence des ondes cohérentes afin de reproduire des faibles gradients de l’indice de réfraction auxquelles la radiographie traditionnelle est insensible. Cette dernière ansi étant inapte à l’imagerie des tissus mous, l’imagerie à contraste de phase promet d’améliorer les resultats, par exemple, de la mammographie et de l’imagerie des cartilages. |
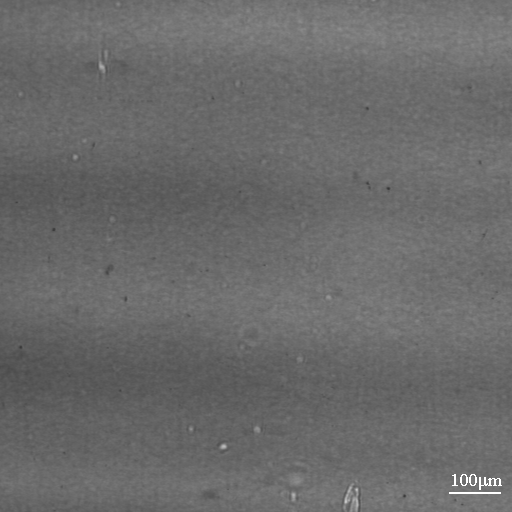
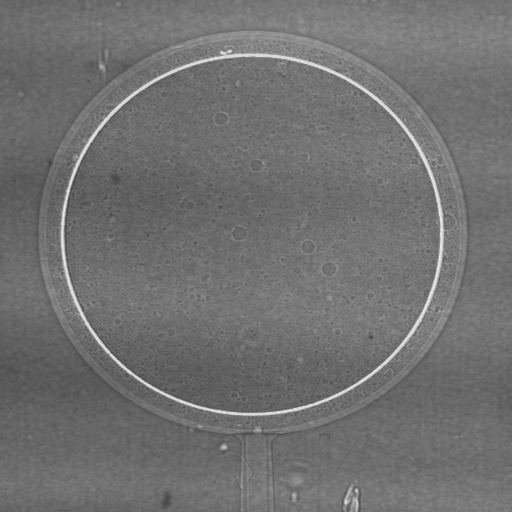
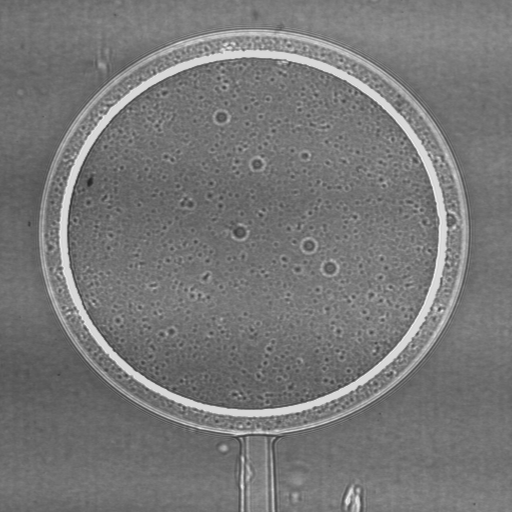
Fig. 1: An example of phase contrast: Radiograph of a double-layered plastic hollow ball using monochromatic x-rays and three different object-detector distances: left 0,003 m, middle 0,19 m, right 0,83 m. Due to the small distance, the left radiograph does not show any significant interference effects, therefore in terms of contrast corresponding to a conventional radiograph. (from [1])
Abb. 1: Beispiel für Phasenkontrast: Radiographie einer doppelwandigen Kunststoffhohlkugel mit monochromatischem Röntgenlicht bei drei verschiendenen Gegenstand-Detektor-Abständen; links 0,003 m, Mitte 0,19 m, rechts 0,83 m. Bei der linken Aufnahme treten aufgrund des kleinen Abstandes zum Detektor keine nennenswerten Interferenzeffekte auf, das Ergebnis entspricht daher einer konventionellen Röntgenaufnahme. (nach [1])
Fig. 1 : Exemple sur le contraste de phase: Radiographie d’une sphère à deux couches plastifiées; rayons X monochromatiques; trois distances objet–detecteur: à gauche 0,003 m, au milieu 0,19 m, à droite 0,83 m. À cause de la petite distance l’image à gauche ne présente que des effets d’interférence insignificants, ansi le resultat correspond à une radiographie traditionelle. (d’après [1])
|
Tomosynthesis is a three-dimensional imaging technique allowing for the reconstruction of volume images from |
Die Tomosynthese ist ein Bildgebungsverfahren zur Rekonstruktion von Volumenbildern aus |
La tomosynthèse est une technique d’imagerie tridimensionnelle permettant de reconstruire des volumes à partir des ensembles de projections incomplets. Cela la rend apte au traitement des cas d’une géometrie d’acquisition restreinte et/ou d’un faible nombre de projections. |
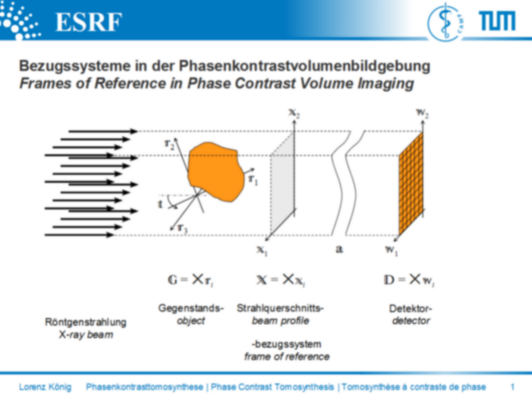
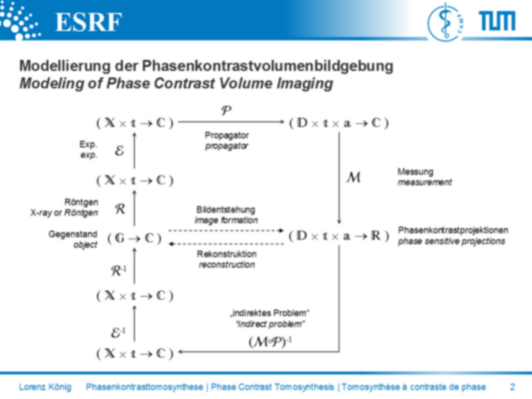
Fig. 2: Frames of reference in phase contrast volume imaging
Abb. 2: Bezugssysteme in der Phasenkontrastvolumenbildgebung
Fig. 2 : Systèmes des coordonnées en imagerie de volumes à contraste de phase
References |
Literatur |
Références |
| Students.ProjectForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Digital Tomosynthesis in Phase Contrast X-Ray Imaging |
| Abstract: | |
| Student: | Lorenz König |
| Director: | Nassir Navab |
| Supervisor: | Tobias Lasser, Alberto Bravin, Paola Coan |
| Type: | Diploma Thesis |
| Area: | Medical Imaging |
| Status: | finished |
| Start: | |
| Finish: | |
| Thesis (optional): | |