|
|
In medical collaboration with:
Dr. Holger Poppert, Dr. Lorena Esposito, Prof. Dr. Eckstein (Klinikum rechts der Isar)
Scientific Director: Prof. Dr. Nassir Navab
Contact Person(s): Olivier Pauly
|
Keywords: Segmentation, Machine Learning for Medical Applications,
IFL
Abstract
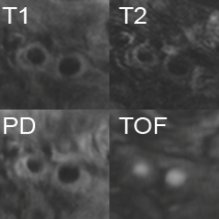
Stroke is the third leading cause of death in Germany. It is a neurology injury, whereby the oxygen supply to parts of the brain gets cut off. About 80% of these strokes are due to ischemia, i.e. an occlusion of a blood vessel leading to an interrupted blood flow. Stenosis inside the carotid artery imaged using four different MR weightings Special setting in this project is the arteria carotis. Plaque is most likely to develop at the branching of the arteria carotis communis into the arteria carotis interna (leading to the brain) and the arteria carotis externa. This can lead to an abnormal narrowing, called a stenosis. According to the American Heart Association these plaques can be divided into different types, based on their consistency and structure. Until now the decision about a surgery was only based on the degree of the stenosis and not on the type of plaque causing it. This is a faulty approach since there is a plaque type (Type IV) which constitutes a relevant clinical danger, although it does not necessary come along with a stenosis. Unlike most other image modalities MR images do not only give information about the degree of the stenosis, but also about the consistency of the plaque. Using different weighted MR images it is possible to correctly classify plaque into the types defined by the AHA. The main goal of this project is to create a classification tool based on T1, T2, Proton Density and 'Time of flight' weighted images. To achieve this goal the arteria carotis and the plaque have to be segmented from the images. Furthermore various features of the plaque have to be extracted in order to get information needed for the classification.
Pictures
|
|
Figure 1: MR T1, T2, PD and TOF images of the Carotid artery
|
|
|
|
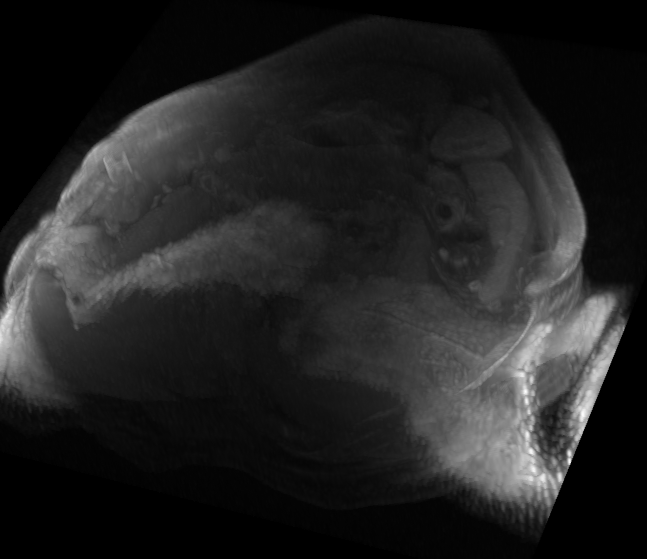
Figure 2: MR T1 3D volume of the Carotid artery
|
|
|
|
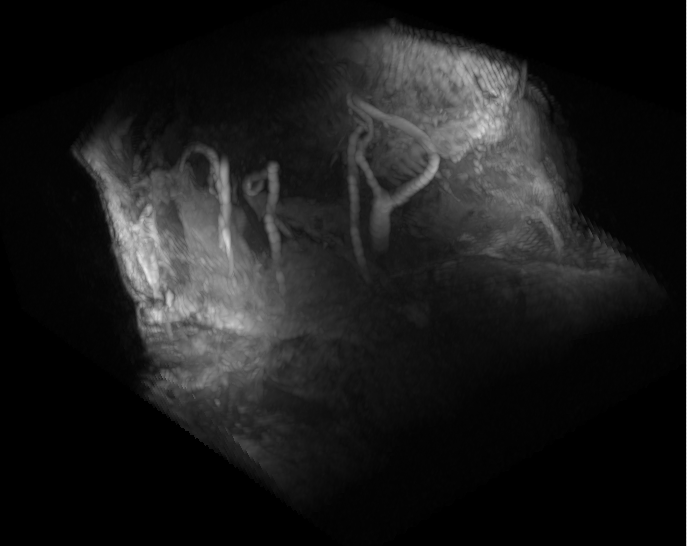
Figure 3: MR T1 3D volume of the Carotid artery
|
|
|
|
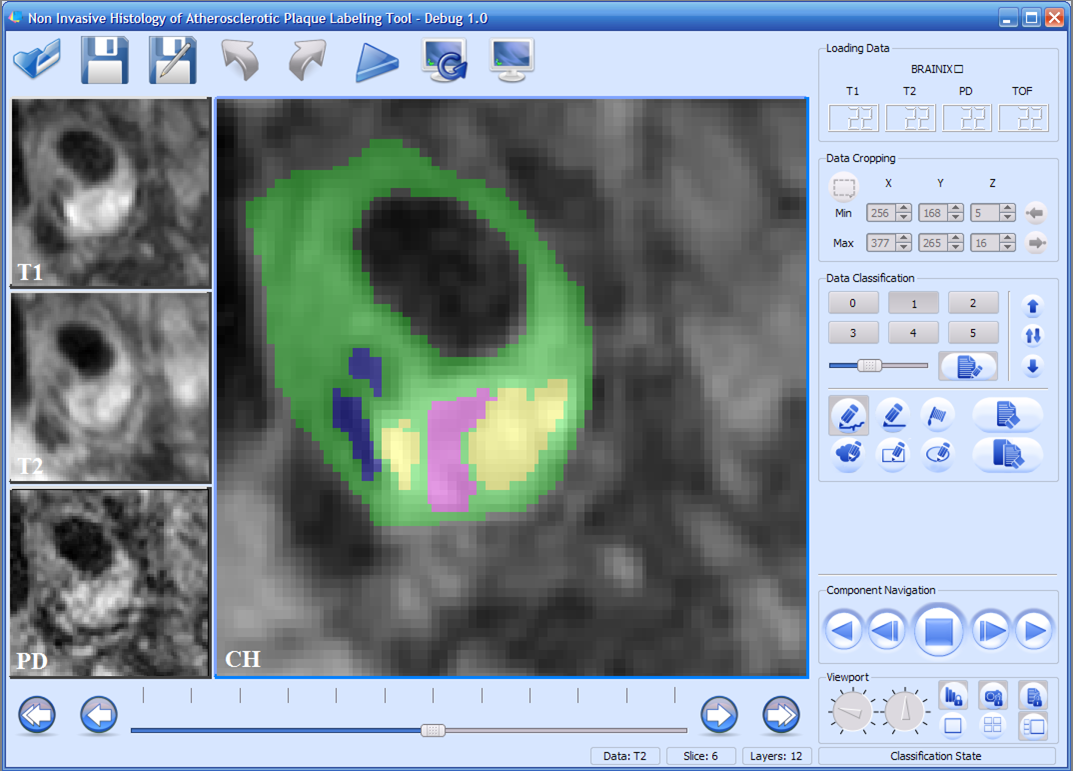
Figure 4: NIHAP Tool Version 1.0
|
|
Team
Contact Person(s)
Working Group
Alumni
Location
 Visit our lab at Garching.
Visit our lab at Garching.
 Visit our lab at Klinikum rechts der Isar.
internal project page
Visit our lab at Klinikum rechts der Isar.
internal project page
Please contact
Olivier Pauly for available student projects within this research project.







