|
Research Interests
- Surgical Workflow Analysis
- Activity Analysis
- Medical Image Registration
- Computer Vision
- Machine Learning
(Past) Research Projects
Surgical Workflow Analysis in Laparoscopy for Monitoring and DocumentationSurgical workflow recovery is a crucial step towards the development of intelligent support systems in surgical environments. The objective of the project is to create a system which is able to recognize automatically the current steps of a surgical laparoscopic procedure using a set of signals recorded from the OR. The project adresses several issues such as the simultaneous recordings of various signals within the OR, the design of methods and algorithms for processing and interpreting the information, and finally the development of a convenient user interface to display context sensitive information inside the OR. The current clinical focus is on laparoscopic cholecystectomies but the concepts developed in the project also apply to laparoscopic surgeries of other kinds. |
Analysis and Modeling of Actions for Advanced Medical Training SystemsProviding feedback to trainees is one of the most important issues to support learning. This project researches how to give quantitative and visual feedback on the performance of a student when training on simulators or phantoms. Statistical analysis and probabilistic models are used to compare the performance of students and experts. Augmented Reality and video is used to give visual feedback like a synchronized replay of the student’s and the expert’s performance. |
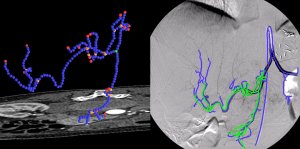
Registration of Angiographic ImagesAngiographic images visualize vascular structure in different modalities like X-Ray, CT, or MR data sets. In many medical applications, a registration and proper visualization of the data sets, especially the vasculature is useful for a better navigation. The focus of this project lies on 2D/3D registration of angiographic data where intensity-based, feature-based, and hybrid approaches are evaluated, the latter two of them requiring an accurate 2D and 3D segmentation of the data. The main clinical partner is the radiology department of the Universitätsklinikum Großhadern (Ludwig-Maximilian Universität München) , industrial partner is Siemens Medical Solutions, Forchheim. |
Non Invasive Histology of Atherosclerotic PlaqueStroke is the third leading cause of death in Germany. It is a neurology injury, whereby the oxygen supply to parts of the brain gets cut off. About 80% of these strokes are due to ischemia, i.e. an occlusion of a blood vessel leading to an interrupted blood flow. Stenosis inside the carotid artery imaged using four different MR weightings Special setting in this project is the arteria carotis. Plaque is most likely to develop at the branching of the arteria carotis communis into the arteria carotis interna (leading to the brain) and the arteria carotis externa. This can lead to an abnormal narrowing, called a stenosis. According to the American Heart Association these plaques can be divided into different types, based on their consistency and structure. Until now the decision about a surgery was only based on the degree of the stenosis and not on the type of plaque causing it. This is a faulty approach since there is a plaque type (Type IV) which constitutes a relevant clinical danger, although it does not necessary come along with a stenosis. Unlike most other image modalities MR images do not only give information about the degree of the stenosis, but also about the consistency of the plaque. Using different weighted MR images it is possible to correctly classify plaque into the types defined by the AHA. The main goal of this project is to create a classification tool based on T1, T2, Proton Density and 'Time of flight' weighted images. To achieve this goal the arteria carotis and the plaque have to be segmented from the images. Furthermore various features of the plaque have to be extracted in order to get information needed for the classification. |
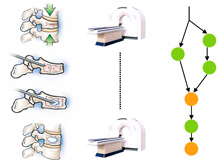
Discovery and Detection of Surgical Activity in Percutaneous VertebroplastiesIn this project, we aim at discovering automatically the workflow of percutaneous vertebroplasty. The medical framework is quite different from a parallel project , where we analyze laparoscopic surgeries. Contrary to cholecystectomies where much information is provided by the surgical tools and by the endoscopic video, in vertebroplasties and kyphoplasties, we believe that the body and hand movement of the surgeon give a key insight into the surgical activity. Surgical movements like hammering of the trocar into the vertebra or the stirring of cement compounds are indicative of the current workflow phase. The objectives of this project are to acquire the workflow related signals using accelerometers, processing the raw signals and detecting recurrent patterns in order to objectively identify the low-level and high-level workflow of the procedure. |
Similarity/Metric/Distance Learning for Medical ApplicationsMany medical applications such as registration or tracking can be seen as the optimization of an objective function which involves a data term or similarity measure. Classical similarity measures rely for instance on image intensities, gradients or intensity statistics. In the case of noise or background clutter which is very frequent in the case of medical imaging, they might lead to registration/tracking errors. In this project, we investigate different approches and applications of learning a similarity measure directly from the data, leading to a more robust data term which is adapted to the image characteristics. |
Workflow Analysis Using 4D Reconstruction DataThis project targets the worklow analysis of an interventional room equipped with 16 cameras fixed on the ceiling. It uses real-time 3D reconstruction data and information from other available sensors to recognize objects, persons and actions. This provides complementary information to specific procedure analysis for the development of intelligent and context-aware support systems in surgical environments. |
Publications
| 2010 | |
| N. Padoy, T. Blum, A. Ahmadi, H. Feußner, M.O. Berger, N. Navab
Statistical Modeling and Recognition of Surgical Workflow Medical Image Analysis (2010), Volume 16, Issue 3, April 2012 (published online December 2010), pp. 632-641. The original publication is available online at www.elsevier.com. (bib) |
|
| 2009 | |
| N. Padoy, D. Mateus, D. Weinland, M.O. Berger, N. Navab
Workflow Monitoring based on 3D Motion Features ICCV Workshop on Video-oriented Object and Event Classification, Kyoto, Japan, September 2009 (IBM Best Paper Award) (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, N. Padoy, H. Poppert, I. Esposito, H-H. Eckstein, N. Navab
Towards Application-specific Multi-modal Similarity Measures: a Regression Approach. MICCAI Workshop on Probabilistic Models in Medical Image Analysis (PMMIA), London, UK, September 2009. (bib) |
|
| A. Ahmadi, N. Padoy, K. Rybachuk, H. Feußner, S.M. Heining, N. Navab
Motif Discovery in OR Sensor Data with Application to Surgical Workflow Analysis and Activity Detection MICCAI Workshop on Modeling and Monitoring of Computer Assisted Interventions (M2CAI), London, UK, September 2009 (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, N. Padoy, H. Poppert, I. Esposito, N. Navab
Wavelet Energy Map: A Robust Support for Multi-modal Registration of Medical Images IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, Florida (USA), June 2009. (bib) |
|
| 2008 | |
| T. Blum, N. Padoy, H. Feußner, N. Navab
Workflow Mining for Visualization and Analysis of Surgeries International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, Volume 3, Number 5, November 2008, pp. 379-386. The original publication is available online at www.springerlink.com. (bib) |
|
| A. Ahmadi, N. Padoy, S.M. Heining, H. Feußner, M. Daumer, N. Navab
Introducing Wearable Accelerometers in the Surgery Room for Activity Detection 7. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft f{\"u}r Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2008) (bib) |
|
| J. Traub, A. Ahmadi, N. Padoy, L. Wang, S.M. Heining, E. Euler, P. Jannin, N. Navab
Workflow Based Assessment of the Camera Augmented Mobile C-arm System International Workshop on Augmented Reality environments for Medical Imaging and Computer-aided Surgery (AMI-ARCS 2008), New York, NY, USA, September 2008 (bib) |
|
| T. Blum, N. Padoy, H. Feußner, N. Navab
Modeling and Online Recognition of Surgical Phases using Hidden Markov Models Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2008), New York, USA, September 2008, pp. 627-635. The original publication is available online at www.springerlink.com. (bib) |
|
| N. Padoy, T. Blum, H. Feußner, M.O. Berger, N. Navab
On-line Recognition of Surgical Activity for Monitoring in the Operating Room Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence (IAAI 2008) held in conjunction with the 23rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Chicago, Illinois, USA, July 2008, pp. 1718-1724 (bib) |
|
| U.F. Klank, N. Padoy, H. Feußner, N. Navab
An Automatic Approach for Feature Generation in Endoscopic Images International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, Volume 3, Number 3-4, Saptember 2008, pp. 331-339 (bib) |
|
| T. Blum, N. Padoy, H. Feußner, N. Navab
Workflow Mining for Visualization and Analysis of Surgeries Proceedings of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (CARS 2008), Barcelona, Spain, June 2008, pp. 134-135 (bib) |
|
| 2007 | |
| N. Padoy, T. Blum, I. Essa, H. Feußner, M.O. Berger, N. Navab
A Boosted Segmentation Method for Surgical Workflow Analysis Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2007), Brisbane, Australia, October 2007, pp. 102-109. The original publication is available online at www.springerlink.com. (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, T. F. Jakobs, N. Padoy, N. Navab
Planning and Intraoperative Visualization of Liver Catheterizations: New CTA Protocol and 2D-3D Registration Method Academic Radiology 14 (11), pp.1324-1339. Special issue of MICCAI 2006 (bib) |
|
| N. Padoy, M. Horn, H. Feußner, M.O. Berger, N. Navab
Recovery of Surgical Workflow: a Model-based Approach Proceedings of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (CARS 2007), 21st International Congress and Exhibition, Berlin, Germany, June 2007 (bib) |
|
| 2006 | |
| J. Cohen, E. Jeannot, N. Padoy, F. Wagner
Messages Scheduling for Parallel Data Redistribution between Clusters IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Volume 17, Number 11, November 2006 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, N. Padoy, T. F. Jakobs, N. Navab
New CTA Protocol and 2D-3D Registration Method for Liver Catheterization Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2006), Copenhagen, Denmark, October 2006 (bib) |
|
| 2005 | |
| M. Groher, T. F. Jakobs, N. Padoy, N. Navab
Towards a Feature-based 2D-3D Registration Method of CTA and 2D Angiograms for Liver Tumor Chemoembolizations 4. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2005), Berlin, Germany, September 2005 (bib) |
|
| 2003 | |
| J. Cohen, E. Jeannot, N. Padoy
Messages Scheduling for Data Redistribution between Clusters Proceedings of Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics, 5th International Conference, PPAM 2003, Czestochowa, Poland, September 2003 (bib) |
|
Supervision
Current:- Discovery and Detection of Surgical Activity in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty by Ahmad Ahmadi (Diploma Thesis 2008/03/31)
- Surgical Workflow Analysis: Representation and Application to Monitoring by Tobias Blum (Diploma Thesis 2007/08/15)
- Automatic Feature Computation for Endoscopic Image Classification by Uli Klank (Diploma Thesis 2007/05/14)
Teaching
- Action Recognition and Analysis: From Signals to Models. Technische Universität München. Hauptseminar (2008SoSe)
- Information Processing in the Operating Room of the Future. Technische Universität München. Hauptseminar (2007WiSe)
- Algorithmics and Programming I. Université Henri-Poincaré, France. 40 hours classes and exercices. 2006-2007
- Algorithmics and Programming II. Université Henri-Poincaré, France. 20 hours exercices. 2006-2007
- Algorithmics and Programming I. Université Henri-Poincaré, France. 60 hours classes, exercices and practicals. 2005-2006
- Algorithmics and Programming II. Université Henri-Poincaré, France. 20 hours practicals. 2005-2006
- Invited classes in lecture Computer Aided Medical Procedures. 2005.
Other
- Talk at Nagoya University, Kensaku Mori's lab, November 2009
- IBM Best paper award at VOEC Workshop - ICCV 2009, for paper 'Workflow Monitoring based on 3D Motion Features'
- Organizer of M2CAI 2009, September 2009, London
- Talk at Université de Rennes, VisAGeS group, Mai 2008
- Co-organizer of joint seminar between research groups of Prof. Guang-Zhong Yang (Imperial College London) and Prof. Nassir Navab (Technische Universität München), April 2008
- Talks at universities Tehran University of Medical Science, University of Tehran and Sharif University of Technology within DAAD German Iranian - Avicenna Roentgen Collaboration, December 2006
Education
- 2003-2005 - Technische Universität München, Munich
- 2001-2003 - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Lyon
- 1999-2001 - Lycee Louis-le-Grand, Paris
Fun Video
CAMP Gladiators, (c) N.Padoy & O.Pauly 2008| UsersForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Prof. |
| Circumference of your head (in cm): | |
| Firstname: | Nicolas |
| Middlename: | |
| Lastname: | Padoy |
| Picture: |  |
| Birthday: | 12/10/1981 |
| Nationality: | France |
| Languages: | |
| Groups: | Surgical Workflow, Computer Vision, Machine Learning for Medical Applications |
| Expertise: | |
| Position: | Scientific Staff |
| Status: | Alumni |
| Emailbefore: | padoy |
| Emailafter: | cs.tum.edu |
| Room: | MI 03.13.056 |
| Telephone: | +49 89 289 17079 |
| Alumniactivity: | Professor at University of Strasbourg, France |
| Defensedate: | 14 April 2010 |
| Thesistitle: | Workflow and Activity Modeling for Monitoring Surgical Procedures |
| Alumnihomepage: | |
| Personalvideo01: | |
| Personalvideotext01: | |
| Personalvideopreview01: | |
| Personalvideo02: | |
| Personalvideotext02: | |
| Personalvideopreview02: | |