Research in Medical Image Analysis
Table of Content
Contact Person and Group Coordination
|
|
|
|
Maximilian Baust |
Nassir Navab |
|
|
|
Research Projects in Medical Image Analysis
Geodesic pixel neighborhoods for multi-class image segmentationThe problem of multi-class image segmentation is traditionally addressed either with a Conditional Random Field model or by directly classifying each pixel. In this paper we introduce a new classification framework built around the concept of pixel neighborhoods. A standard unary classifier is used to recognize each pixel based on features computed from the image and then a second classifier is trained on the predictions from the first one summarized over the neighborhood of each pixel by a new histogram feature. We define a local and a global pixel neighborhoods which adapt to the image structure by making use of the geodesic distance defined over image intensities. We evaluate our model on three challenging datasets and show that our model is able to capture both local and global context relations. We compare our method to two strongly related, well known methods and show increased performance. |
Estimation of Flow Parameters from X-ray DataThis project focuses on the quantification of blood flow based on 2D and 3D angiographic X-ray image data, which is of particular interest during minimally invasive interventional procedures such as recanalizations of stenotic vessels and embolizations of arteries that feed tumors or vascular malformations in the patient's brain, for example. Our projects cover the evaluation of model-based approaches involving CFD (computational fluid dynamics) simulations as well as methods that aim at estimating the optical flow in the images and deriving quantitative blood flow information from these results. |
Learning and Understanding in 3D Point CloudsPoint offer are a unified representation for 3D data. Whether the sensor is a laser scanner, lidar or a depth camera, the acquired information can be stored in form an unstructured point cloud. This makes such representation ubiquitous. In this project, we aim to adapt state-of-the-art learning algorithms to efficiently handle point cloud data in order to find objects, detect structures, perform segmentation and 3d reconstruction. |
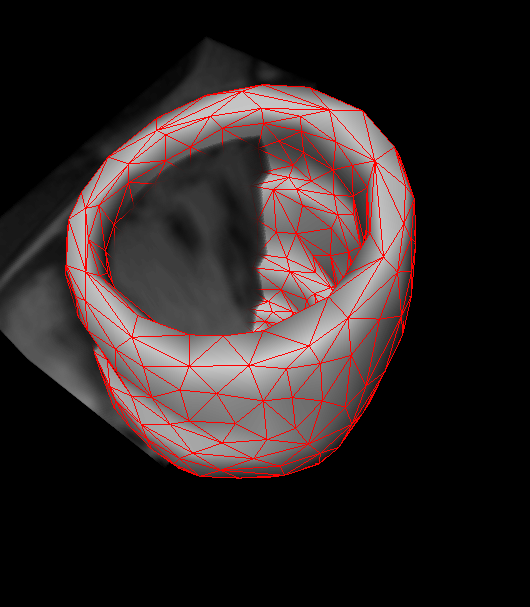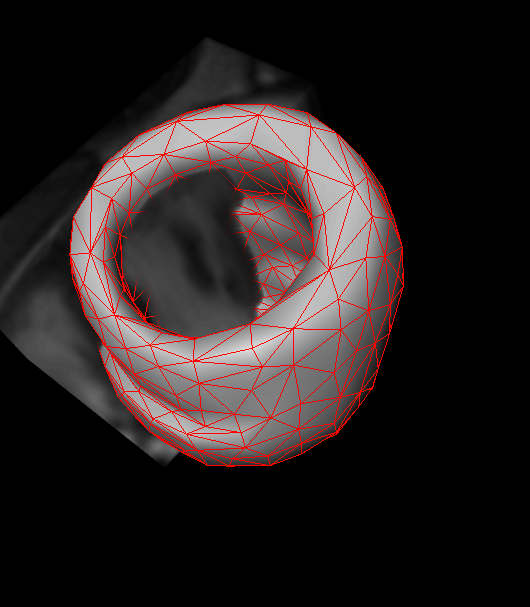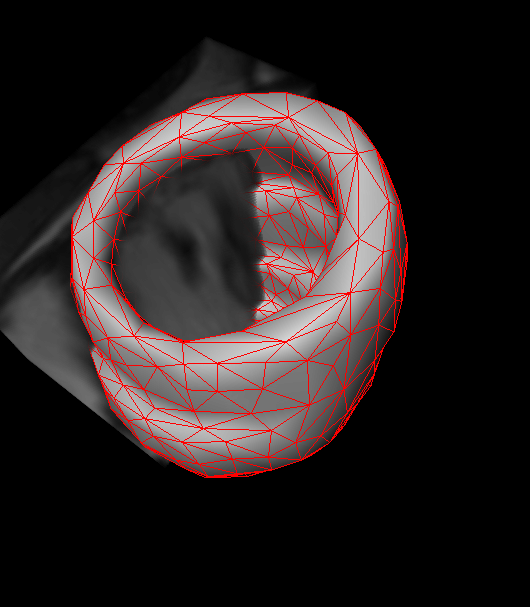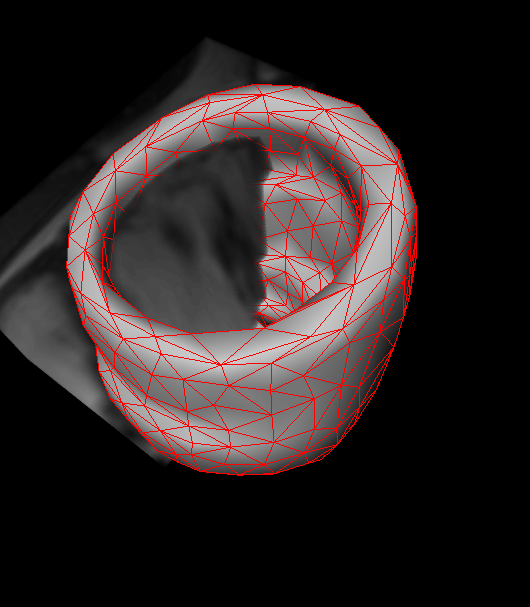
Shape Guided Segmentation of Cardiac BoundariesPrior shape information has been shown to be invaluable for segmenting cardiac boundaries. We develop new methods of exploiting such prior information to guide the segmentation by using techniques of machine learning or formulating the segmentation problem to fit our requirements in segmentation of 4D cardiac data. |
patient-Specific Translational research on Atherosclerosis and Diagnosis (STAnD) |
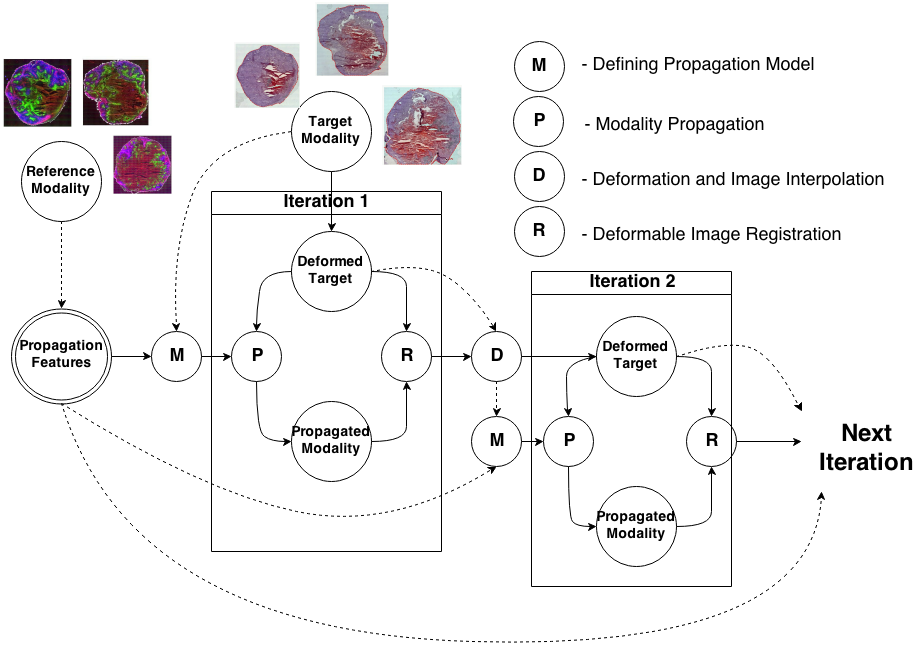
Knowledge Propagation Models for Image RegistrationTo register modalities with complex intensity relationships, we leverage machine learning algorithm to cast it into a mono modal registration problem. This is done by extracting tissue specific features for propagating anatomical/structural knowledge from one modalitiy to an other through an online learnt propagation model. The registration and propagation steps are iteratively performed and refined. For proof-of-concept, we employ it for registering (1) Immunofluorescence to Histology images and (2) Intravascular Ultrasound to Histology Images. |
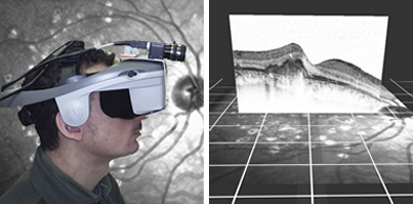
Advanced imaging in Head Mounted Displays (HMD) for Patients with Age-Related Macular DegenerationAge-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the leading causes of low vision worldwide without a medical solution. Nevertheless, enhancement of people's vision by means of mediated reality is conceivable. This project presents a head-mounted magnification system to enhance visual perception acquired with peripheral vision. A hybrid magnification technique is adjusted and implemented on a head-mounted display. Moreover, a system for modeling and correcting distorted vision is proposed. The system obtains a correction model by means of a deformable grid. To evaluate the system, a method for simulating distorted vision is applied. By superimposing the model on OCT macular images, it is suitable to identify macular features, which could help on the development of an automatic correction method. |
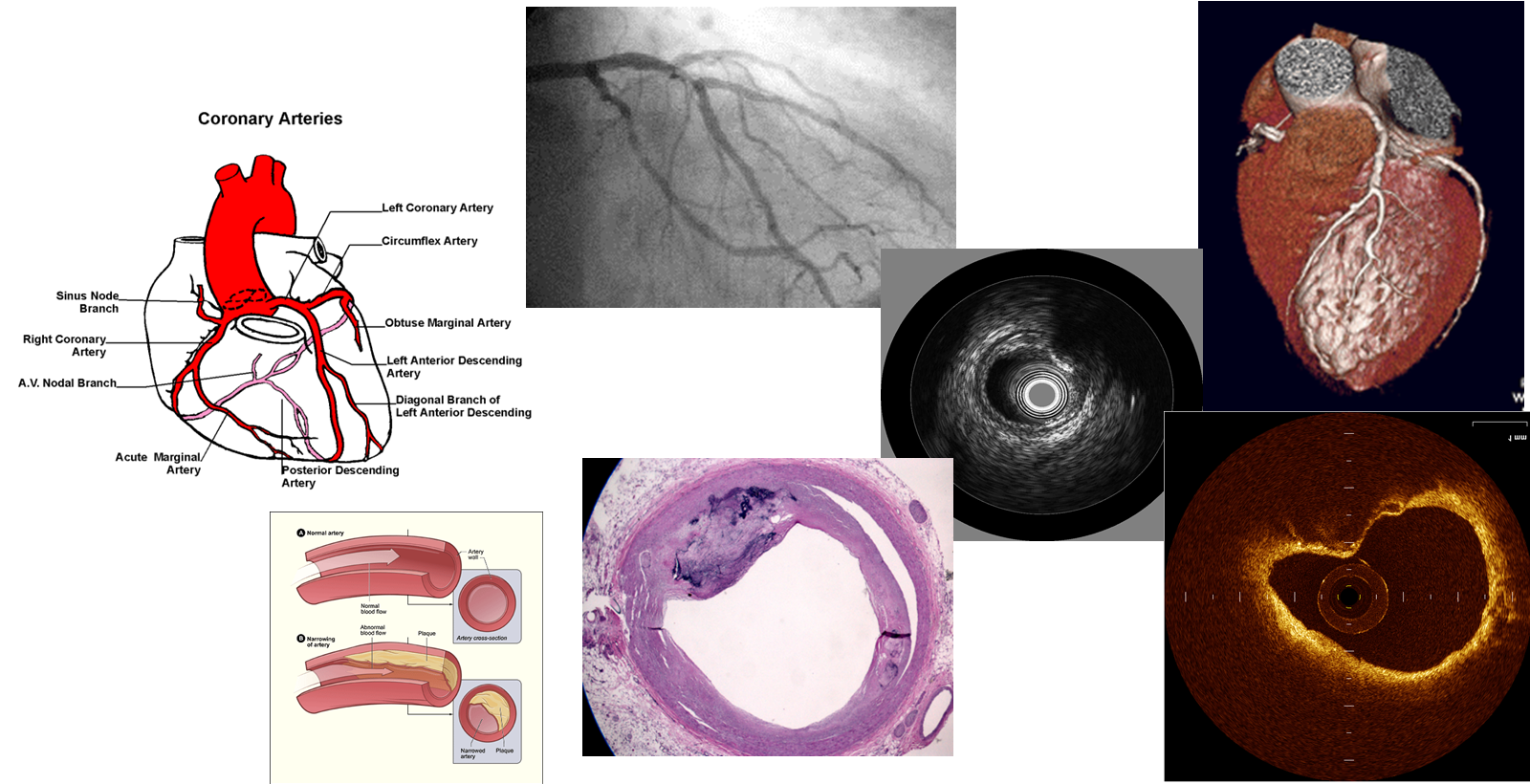
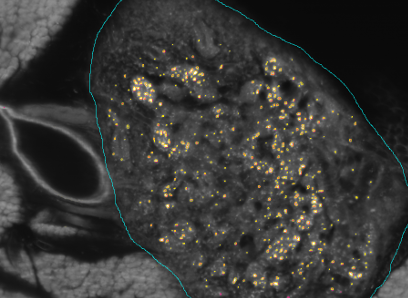
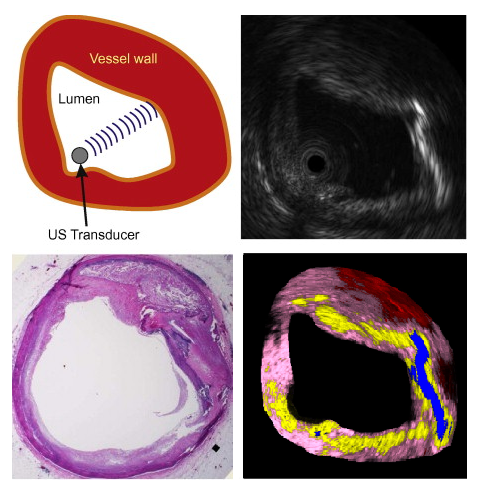
Improvement and Automatic Classification of IVUS-VH (Intravascular Ultrasound – Virtual Histology) ImagesHeart attack and stroke are the major causes of human death and atherosclerotic plaques are the most common effect of cardiovascular disease. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), a diagnostic imaging technique, offers a unique view of the morphology of the arterial plaque and displays the morphological and histological properties of a cross-section of the vessel. Limitations of the grayscale IVUS manual plaque assessment have led to the development of quantitative techniques for analysis of characteristics of plaque components. In vivo plaque characterization with the so called Virtual Histology (VH)-IVUS, which is based on the ultrasound RF signal processing, is widely available for atherosclerosis plaque characterization in IVUS images. However, it suffers from a poor longitudinal resolution due to the ECG-gated acquisition. The focus of this PhD? work is to provide effective methods for image-based vessel plaque characterization via IVUS image analysis to overcome the limitations of current techniques. The proposed algorithms are also applicable to the large amount of the IVUS image sequences obtained from patients in the past, where there is no access to the corresponding radio frequency(RF) data. Since the proposed method is applicable to all IVUS frames of the heart cycle, therefore it outperforms the longitudinal resolution of the so called VH method. |
OCT Tissue ClassificationOptical coherence tomography (OCT), employing light rather than ultrasound, is a high-resolution imaging technology that permits a precise assessment of biological tissue. Used intravascular, OCT is increasingly used for assessing safety and efficacy of intracoronary devices, such as drug-eluting stents and bioabsorbable stents. Obtained images provide insights regarding stent malposition, overlap, and neointimal thickening, among others. Recent OCT histopathology correlation studies have shown that OCT can be used to identify plaque composition, and hence it is possible to distinguish “normal” from “abnormal” neointimal tissue based on its visual appearance. The aim of this project is to develop a novel method for the automatic analysis of tissue in IVOCT. Automatic tissue classification will allow for a quantitative and potentially more time-efficient and objective analysis of IVOCT data. For instance, classifying neointimal tissue as either “mature” or “immature” can be used to assess the disease state of patients; as a potential predictor of late stent-failure events such as stent thrombosis and restenosis. |
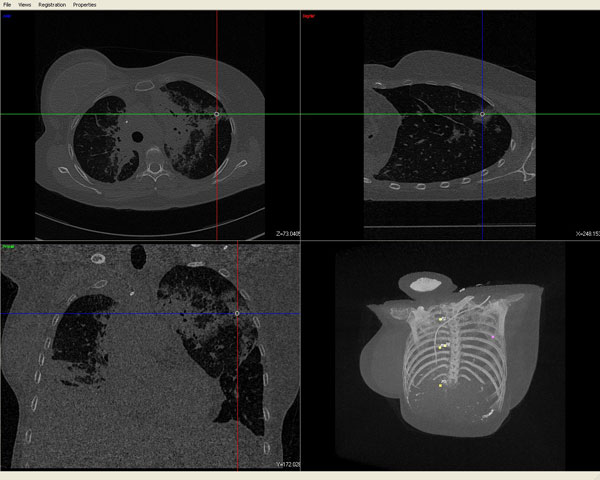
Registration of Angiographic ImagesAngiographic images visualize vascular structure in different modalities like X-Ray, CT, or MR data sets. In many medical applications, a registration and proper visualization of the data sets, especially the vasculature is useful for a better navigation. The focus of this project lies on 2D/3D registration of angiographic data where intensity-based, feature-based, and hybrid approaches are evaluated, the latter two of them requiring an accurate 2D and 3D segmentation of the data. The main clinical partner is the radiology department of the Universitätsklinikum Großhadern (Ludwig-Maximilian Universität München) , industrial partner is Siemens Medical Solutions, Forchheim. |
Prostate Fusion BiopsyTransrectal ultrasound (TRUS) guided biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis. However, it suffers from low sensitivity, leading to an elevated rate of false negative results. On the other hand, the recent advent of PET imaging using a novel dedicated radiotracer, Ga-labelled PSMA (Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen), combined with MR provides improved preinterventional identification of suspicious areas. Thus, MRI/TRUS fusion image-guided biopsy has evolved to be the method of choice to circumvent the limitations of TRUS-only biopsy. We propose a multimodal fusion image-guided biopsy framework that combines PET-MRI images with TRUS. Based on open-source software libraries, it is low cost, simple to use and has minimal overhead in clinical workflow. It is ideal as a research platform for the implementation and rapid bench to bedside translation of new image registration and visualization approaches. |
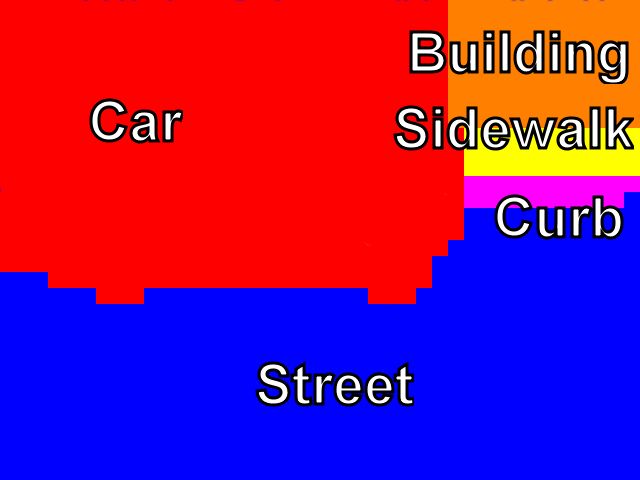
Scene Understanding From a Moving CameraModern vehicles are equipped with multiple cameras which are already used in various practical applications. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) are of particular interest because of the safety and comfort features they offer to the driver. Camera based scene understanding is an important scientific problem that has to be addressed in order to provide the information needed for camera based driver assistance systems. While frontal cameras are widely used, there are applications where cameras observing lateral space can deliver better results. Fish eye cameras mounted in the side mirrors are particularly interesting, because they can observe a big area on the side of the vehicle and can be used for several applications for which the traditional front facing cameras are not suitable.We present a general method for scene understanding using 3D reconstruction of the environment around the vehicle. It is based on pixel-wise image labeling using a conditional random field (CRF). Our method is able to create a simple 3D model of the scene and also to provide semantic labels of the different objects and areas in the image, like for example cars, sidewalks, and buildings. We demonstrate how our method can be used for two applications that are of high importance for various driver assistance systems - car detection and free space estimation. We show that our system is able to perform in real time for speeds of up to 63 km/h. |
Deformable Semantic SLAMIn the scope of this project we are interested in creating a dataset for deformable, semantic SLAM. The goal is to recognize, segment and reconstruct different object categories in real, indoor environments. The focus is live, dynamic objects, such as people and animals. Still, to this date, accurate segmentation in real-time of deformable surfaces is a challenging problem. |
Kooperationsprojekt SFB 824 (3. Förderperiode) & BFSThe SFB824 (Sonderforschungsbereich 824: Central project for histopathology, immunohistochemistry and analytical microscopy) represents an interdisciplinary consortium which aims at the development of novel imaging technologies for the selection and monitoring of cancer therapy as an important support for personalized medicine. Z2, the central unit for comparative morphomolecular pathology and computational validation, provides integration, registration and quantification of data obtained from both macroscopic and (sub-)cellular in-vivo as well as ex-vivo imaging modalities with tissue-based morphomolecular readouts as the basis for the development and establishment of personalized medicine. In order to develop novel imaging technologies, co-annotation and validation of image data acquired by preclinical or diagnostic imaging platforms via tissue based quantitative morphomolecular methods is crucial. Light sheet microscopy will continue to close the gap between 3D data acquired by in-vivo imaging and 2D histological slices especially focusing on tumor vascularization. The Multimodal ImagiNg Data Flow StUdy Lab (MINDFUL) is a central system for data management in preclinical studies developed within SFB824. Continuing the close collaboration of pathology, computer sciences and basic as well as translational researchers from SFB824 will allow the Z2 to develop and subsequently provide a broad variety of registration and analysis tools for joint imaging and tissue based image standardization and quantification.The goal of the BFS Project: ImmunoProfiling using Neuronal Networks (IPN2) is to develop a method based on neuronal networks and recent advances in Deep Learning to allow characterization of a patient's tumor as ″hot″ or ″cold″ tumor depending on the identified ImmunoProfile. Recent research has shown that many tumors are infiltrated by immuno-competent cells, as well as that the amount, type and location of the infiltrated lymph nodes in primary tumors provide valuable prognostic information. In contrast to a ″cold tumor″, a ″hot tumor″ is characterized by an active immune system which the tumor has identified as threat. This identification provides the basis for selecting the therapy best suitable for the individual patient. |
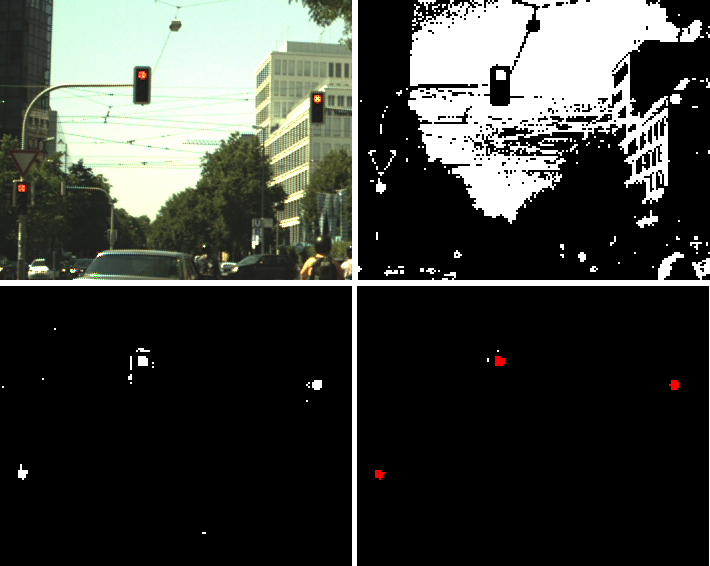
Semantic segmentation based traffic light detection at day and at nightTraffic light detection from a moving vehicle is an important technology both for new safety driver assistance functions as well as for autonomous driving in the city. In this paper we present a machine learning framework for detection of traffic lights that can handle in real-time both day and night situations in a unified manner. A semantic segmentation method is employed to generate traffic light candidates, which are then confirmed and classified by a geometric and color features based classifier. Temporal consistency is enforced by using a tracking by detection method. We evaluate our method on a publicly available dataset recorded at daytime in order to compare to existing methods and we show similar performance. We also present an evaluation on two additional datasets containing more than 50 intersections with multiple traffic lights recorded both at day and during nighttime and we show that our method performs consistently in those situations. |
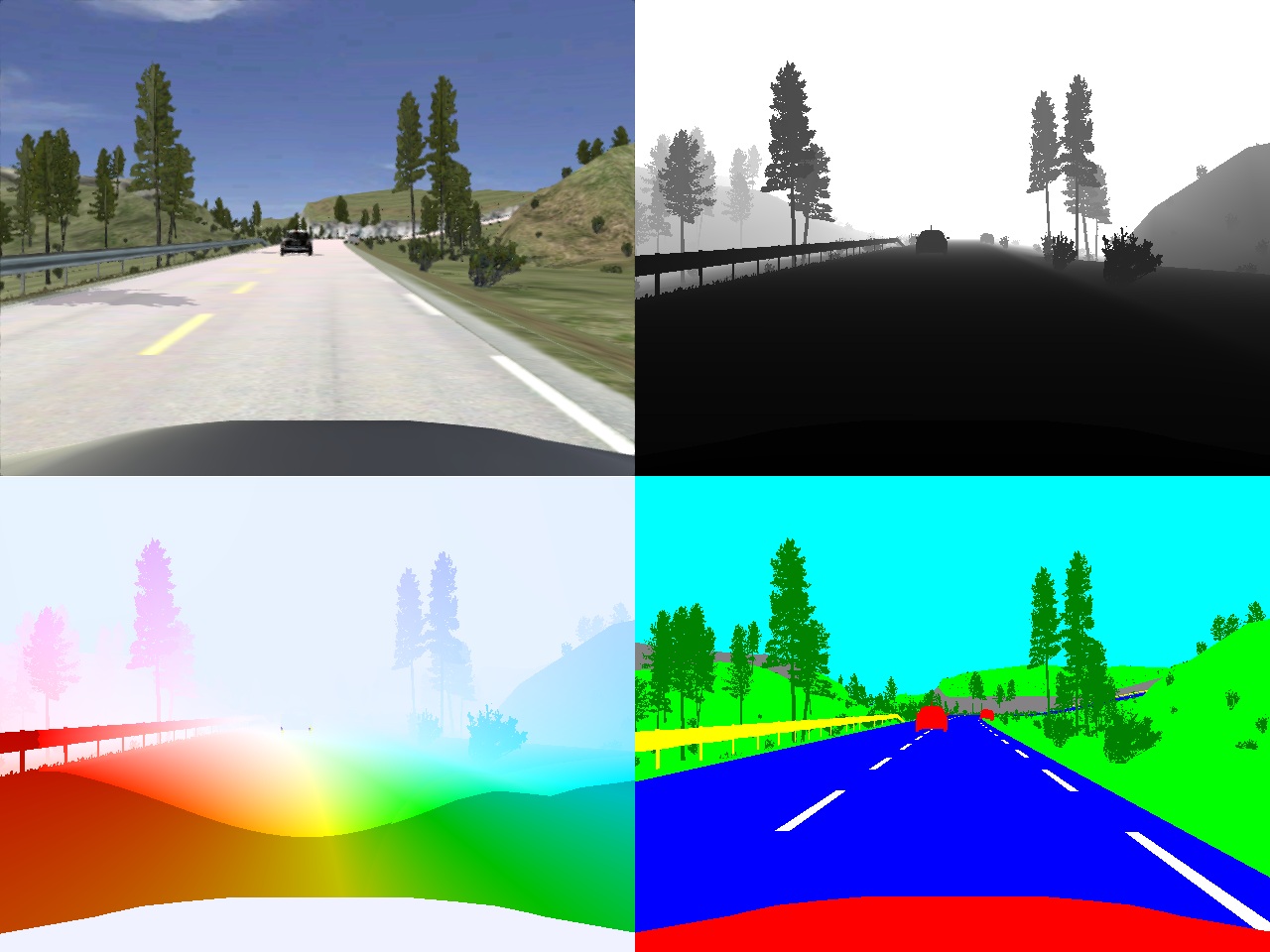
Framework for generation of synthetic ground truth data for driver assistance applicationsHigh precision ground truth data is a very important factor for the development and evaluation of computer vision algorithms and especially for advanced driver assistance systems. Unfortunately, some types of data, like accurate optical flow and depth as well as pixel-wise semantic annotations are very difficult to obtain.In order to address this problem, in this paper we present a new framework for the generation of high quality synthetic camera images, depth and optical flow maps and pixel-wise semantic annotations. The framework is based on a realistic driving simulator called VDrift [1], which allows us to create traffic scenarios very similar to those in real life. We show how we can use the proposed framework to generate an extensive dataset for the task of multi-class image segmentation. We use the dataset to train a pairwise CRF model and to analyze the effects of using various combinations of features in different image modalities. |
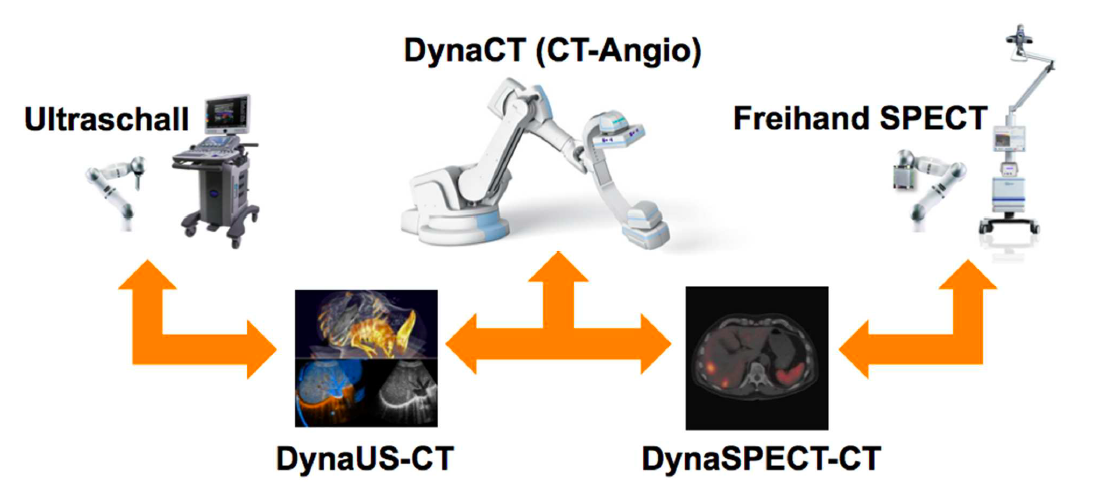
Advanced Robotics for Multi-Modal Interventional Imaging (RoBildOR)This project aims at developing advanced methods for robotic image acquisitions, enabling more flexible, patient- and process-specific functional and anatomical imaging with the operating theater. Using robotic manipulations, co-registered and dynamic imaging can be provided to the surgeon, allowing for optimal implementation of preoperative planning. In particular, this projects is the first one developing concepts for intraoperative SPECT-CT, and introduces intraoperative robotic Ultrasound imaging based on CT trajectory planning, enabling registration with angiographic data. With distinguished partners from Bavarian industry, this project has a fundamental contribution in developing safe, reliable, flexible, and multi-modal imaging technologies for the operating room of the future. |
Reconstruction and Registration of Histology and Phase Contrast Images for Clinical Validation of Imaging ModalitiesBefore its introduction into the hospital, a new imaging modality has to be validated. In other words, appearing structures need to be correlated to the imaged tissues. Such a cross validation is only meaningful when performed against the gold standard which is histology. Currently, cross validation is performed by qualitative comparison of 3D datasets to 2D histology slices. Since the acquisition of a consistent 3D histology volume is a challenging task, its comparison to the corresponding dataset always remained qualitative.The classic histology procedure can be divided in four steps: pre processing, cutting, post processing and imaging of the tissues. In the first step, the sample is chemically processed to preserve the tissues and is then embedded in a paraffin block. By using a microtome, it is cut in very thin slices, and put on a glass slide. During post processing the sample is stained to enhance the structures of interest. The imaging is performed with a camera mounted in a microscope, or with a dedicated scanner. Several difficulties inherent to this process can have a dramatic influence on the quality of the reconstructed histology volume. For instance, since the cutting process is done manually, problems like flipping, bending or ripping of the slides may happen. If the knife starts to wear off, some banding will appear over the slices. Moreover, a few slices could be missing. Finally since the staining color is time dependent, variation in the color of the slices can occur. In this project, we propose to improve the histology procedure and to develop methods towards a consistent reconstruction of 3D histology volumes. |
Non Invasive Histology of Atherosclerotic PlaqueStroke is the third leading cause of death in Germany. It is a neurology injury, whereby the oxygen supply to parts of the brain gets cut off. About 80% of these strokes are due to ischemia, i.e. an occlusion of a blood vessel leading to an interrupted blood flow. Stenosis inside the carotid artery imaged using four different MR weightings Special setting in this project is the arteria carotis. Plaque is most likely to develop at the branching of the arteria carotis communis into the arteria carotis interna (leading to the brain) and the arteria carotis externa. This can lead to an abnormal narrowing, called a stenosis. According to the American Heart Association these plaques can be divided into different types, based on their consistency and structure. Until now the decision about a surgery was only based on the degree of the stenosis and not on the type of plaque causing it. This is a faulty approach since there is a plaque type (Type IV) which constitutes a relevant clinical danger, although it does not necessary come along with a stenosis. Unlike most other image modalities MR images do not only give information about the degree of the stenosis, but also about the consistency of the plaque. Using different weighted MR images it is possible to correctly classify plaque into the types defined by the AHA. The main goal of this project is to create a classification tool based on T1, T2, Proton Density and 'Time of flight' weighted images. To achieve this goal the arteria carotis and the plaque have to be segmented from the images. Furthermore various features of the plaque have to be extracted in order to get information needed for the classification. |
Navigated BronchoscopyA common task during broncoscopy procedures is to biopsy peripheral lung tumors. The video bronchoscope is not capable to reach the peripheral lung nodes, but only the biopsy needle. Thus there is no video feedback, but only feedback of the current location of the biopsy tool by fluoroscopy imaging during the intervention. This exposes patient and surgical staff to additional radiation. Another drawback is that tumors can not be visualized on the fluoroscope images and they are only a projection, thus do not report the three dimensional position of the biopsy tool. Electromagnetic tracking is capable of tracking the tip of flexible instrument. A field generator with three orthogonal coils introduces current and thus generates a magnetic field. A sensor composed also of three orthogonal coils is capable to estimate its position and orientation with respect to a coordinate system defined by the field generator. Currently we investigate the combination of all available information for navigation and solutions to represent it in one unified user interface. This includes the measurements of the electromagnetic tracking system, the c-arm, techniques of virtual bronchoscopy, and other data. Furthermore, clinical evaluation is conducted. We define the clinical endpoint and show through studies that the procedure will benefit from the usage of the navigation system. |
MosaicingThe creation of mosaics is an interesting application, which leads to many challenging theoretical and practical problems. In this project, we are mainly focusing on viewing the mosaicing as a multiple image alignment task. Therefore, pairwise registration methods with a consecutive normalization and simultaneous registration techniques are in focus. Espcically the simultaneous alignment of images for mosaicing seems very promising. We earlier developed a new type of multivariate extension for similarity measures, which led to a whole new class metrics. They are specifically adapted for their usage in mosaicing, but can also be used for general multiple image alignment tasks, e.g. population studies. Our main interest lied so far on the combination of several ultrasound images. To this end, we are benifiting from a quite recent development in ultrasonographic research; the development of advanced 2D array ultrasound transducers. Their new fabrication process allows for higher resolution images with a higher quality resulting from the increased frequency spectrum that they can be operated with. The instantaneously acquired ultrasound volumes serve as input for our mosaicing framework, where they will be compounded to one lager volume. |
Research Group: Assessment and Training of Medical Expert with Objective Standards (ATMEOS)In highly dynamic and complex high-risk domains - such as surgery - systematic training in the relevant skills is the basis for safe and high-quality performance. Traditionally, assessment and training in surgery traditionally concentrated upon proficiency and acquisition of surgeons' technical skills. As the fundamental impact of non-technical skills - such as communication and coordination - is increasingly acknowledged for safe delivery of surgeries comprehensive training approaches are missing. The overall aim of the project is to investigate a novel learning environment for the assessment and training of both technical and non-technical skills of entire multidisciplinary operating room (OR) teams. |
Ultrasound-Based Brainshift Estimation and CorrectionIn the context of intraoperative navigation for neurosurgery, brainshift still represents one of the main challenges. After skull and dura mater opening, brain tissue undergoes dynamic spatial modification due to gravity, loss of Cerebrospinal fluid and resection of tissue. The goal of this project is the utilization of intra-cranial 3D freehand ultrasound in order to directly estimate ocurring brain-shift and allow for a subsequent correction for it within available neur-navigation systems used for guidance in the operating room. |
Intra-operative Imaging and Navigation for Minimal Invasiveness in Head and Neck Cancer |
Intra-operative Imaging and Navigation for Guidance in Neurosurgical Procedures |
Assessment of Fluid Tissue Interaction Using Multi-Modal Image Fusion for Characterization and Progression of Coronary AtherosclerosisCoronary artery diseases such as atherosclerosis are the leading cause of death in the industrialized world. In this project, we develop computational tools for segmentation and registration problems on intravascular images including IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound) and OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography). One sample component of this project is Automatic Stent Implant Follow-up from Intravascular OCT Pullbacks. The stents are automatically detected and their distribution is analyzed for monitoring of the stents: their malpositioning and/or tissue growth over stent struts. |
Deformable Guide Wire TrackingThese days, X-ray fluoroscopic imaging is the modality used most widely to guide physicians in angiographic interventions. Current guidance procedures are based on a roadmap, e.g. a digital subtracted angiography (DSA) acquired from a fixed viewpoint and the injection of contrast agent to visualize the current vessel anatomy. Such roadmaps cannot directly be blended with the fluoroscopic sequence due to misalignment caused by respiratory motion. A fundamental step toward a successful integration of any navigation application into clinical routine is the estimation and compensation of respiratory motion. We propose a novel method for deformable tracking of multiple ridge segments based on a MAP-MRF formulation and efficient discrete optimization. Ridges are modeled as B-Spline curves which allows us to apply smooth deformations based on a minimal number of parameters. Our tracking framework is well adapted to the noisy domain of fluoroscopic imaging and the handling of multiple segments. |
Motion Compensation for CatheterizationsIn many minimally-invasive interventions, catheters are inserted into the body and guided to a region of interest with the help of fluoroscopic imaging (low-dose X-ray image sequences). Due to patient motion, the navigation can be disturbed, and the physician needs a longer time for treatment. This is hazardous in terms of radiation for both, physician and patient. In order to overcome these problems, suitable image-based compensation methods to resolve (non-) rigid motion can be applied. In this project, patient motion is analyzed and suitable compensation algorithms are developed. |
Catheter Extraction in Abdominal Fluoroscopic Image SequencesThis work's focus lies in catheter and guide wire extraction from abdominal fluoroscopic sequences. Due to the fact that fluoroscopic X-ray images are of low quality and suffer from a lot of background clutter in the abdominal area the task we are working on is very difficult and not yet solved by the community. The detection process is very important since a properly detected catheter or guide wire is required by many applications that have been proposed in the last few years. One of the major goals is the enhancement of the navigation during abdominal cathterizations in order to reduce the time of interventions and thus the radiation exposure for the patient and especially the physician. |
Simulated UltrasoundWe are simulating Ultrasound images from CT volumes by assuming a correlation between Hounsfield units and acoustic impedance. Rays are cast trough the CT volume to simulate the US image formation. Simulated Ultrasound from CT can be used for CT/Ultrasound registration by comparing a real US image to simulated ones. Another application of simulated US is training. |
Semi-Automatic Patellar Cartilage SegmentationDevelopment and refinement of a software system for semi-automatic segmentation of the patellar cartilage is the main goal of this project. By providing tools for sub-pixel accurate edge tracing, automatic contour completion, and adequate visualization, a remarkable speed-up of the physicians segmentation process can be achieved. Also, improved exactness can be reached for cartilage segmentation if expertise and automation are merged in a meaningful way. |
Assessment of Knee CartilageDegeneration of knee joint cartilage is an important and early indicator of osteoarthritis (OA) which is one of the major socio-economic burdens nowadays. Accurate quantification of the articular cartilage degeneration in an early stage using MR images is a promising approach in diagnosis and therapy for this disease. Particularly, volume and thickness measurement of cartilage tissue has been shown to deliver significant parameters in assessment of pathologies. Here, accurate computer-aided diagnosis tools could improve the clinical routine where image segmentation plays a crucial role. In order to overcome the time-consuming and tedious work of manual segmentation, one tries to automate the segmentation as much as possible. We focus on novel atlas-based segmentation methods for knee cartilage as well as improve today’s clinical routine of manual segmentation methods. In addition, we try to evaluate different methods for the assessment of parameters such as volume and thickness which could allow computer-aided diagnosis of knee cartilage pathologies in an early stage. |
3D user interfaces for medical interventionsThis work group aims at practical user interfaces for 3D imaging data in surgery and medical interventions. The usual monitor based visualization and mouse based interaction with 3D data will not present acceptable solutions. Here we study the use of head mounted displays and advanced interaction techniques as alternative solutions. Different issues such as depth perception in augmented reality environment and optimal data representation for a smooth and efficient integration into the surgical workflow are the focus of our research activities. Furthermore appropriate ways of interaction within the surgical environment are investigated. |
Port Placement in Minimally Invasive Endoscopic SurgeryOptimal port placement is a delicate issue in minimally invasive endoscopic surgery. A good choice of the instruments' and endoscope's ports can avoid time-consuming consecutive new port placement. We present a novel method to intuitively and precisely plan the port placement. The patient is registered to its pre-operative CT by just moving the endoscope around fiducials, which are attached to the patient's thorax and are visible in its CT. Their 3D positions are automatically reconstructed. Without prior time-consuming segmentation, the pre-operative CT volume is directly rendered with respect to the endoscope or instruments. This enables the simulation of a camera flight through the patient's interior along the instruments' axes to easily validate possible ports. |
Laparoscope Augmentation for Minimally Invasive Liver ResectionIn recent years, an increasing number of liver tumor indications were treated by minimally invasive laparoscopic resection. Besides the restricted view, a major issue in laparoscopic liver resection is the precise localization of the vessels to be divided. To navigate the surgeon to these vessels, pre-operative imaging data can hardly be used due to intra-operative organ deformations caused by appliance of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum and respiratory motion.Therefore, we propose to use an optically tracked mobile C-arm providing cone-beam computed tomography imaging capability intra-operatively. After patient positioning, port placement, and carbon dioxide insufflation, the liver vessels are contrasted and a 3D volume is reconstructed during patient exhalation. Without any further need for patient registration, the volume can be directly augmented on the live laparoscope video. This augmentation provides the surgeon with essential aid in the localization of veins, arteries, and bile ducts to be divided or sealed. Current research focuses on the intra-operative use and tracking of mobile C-arms as well as laparoscopic ultrasound, augmented visualization on the laparoscope's view, and methods to synchronize respiratory motion. |
PicoSEC - Endoscopic PET and Ultrasound ImagingPICOSEC (Pico-second Silicon photomultiplier-Electronics- & Crystal research) is an European Marie Curie training project. It aims to bring together early career researchers and experienced colleagues from across Europe, to take part in a structured, integrated and multidisciplinary training program for young researchers in an R&D project geared to develop a new class of ultra-fast photon detectors in PET and HEP. This R&D will be the core activity of a TOF-PET development for clinical applications and would open new perspectives in medical imaging and hence in the quality of patient treatment. The Consortium is composed of public and private organizations and based on a common research program, aiming to increase the skills exchange between public and private sectors.The overall project is divided in to different work packages that focus on specific aims while working towards common project goal. Our work package (WP) 5 has been assigned with the following tasks, 1. Provide tracking solutions for flexible endoscopy, trans-rectal ultrasound probe (TRUS), and endoscopic imaging devices, and evaluate their robustness and accuracy. 2. Based on tracking and imaging data, reconstruct volumes of interest from flexible endoscopic or TRUS detectors. 3. For orientation, guidance to specific regions of interest, and, where appropriate, through specific scanning protocols, provide navigation solutions. |
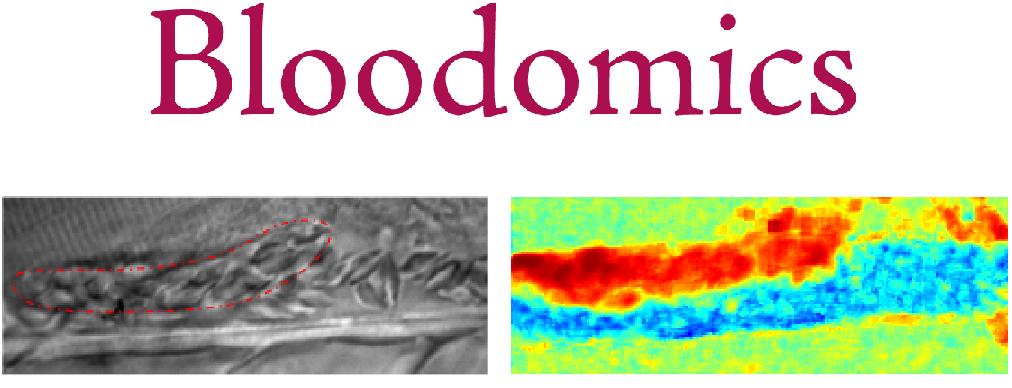
Automatic thrombus segmentation in in vivo micoscopic video sequences under low contrast and highly dynamic conditionsThe Bloodomics EU project aims are to identify the genetic risks factors of coronary heart diseases.One of the most common methods is to study the thrombus formation in the dorsal aorta of mutant Zebrafish larvae. The developing thrombus is imaged in vivo through a microscope/camera setup. The derived time to attachment, growth speed, and time to occlusion permits the characterization of the thrombus formation. However, this step presently remains manual. Our objective is to provide the geneticists in the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute with an image processing tool to automatically detect and segment the growing thrombus. This will significantly speed up and improve the precision of this current analysis. |
EDEN2020: Enhanced Delivery Ecosystem for NeurosurgeryEDEN2020 (Enhanced Delivery Ecosystem for Neurosurgery) aims to develop the gold standard for one-stop diagnosis and treatment of brain disease by delivering an integrated technology platform for minimally invasive neurosurgery. A team of first-class industrial partners (Renishaw plc. and XoGraph ltd.), leading clinical oncological neurosurgery team (Università di Milano, San Raffaele and Politecnico di Milano) lead by Prof. Lorenzo Bello and the involvement of leading experts in shape sensing (Universitair Medisch Centrum Groningen) under supervision of Prof. Dr. Sarthak Misra The project is coordinated by Dr. Rodriguez y Baena, Imperial College London. His team provides the core technology for the envisioned system, the bendable robotic needle. During the course of EDEN2020 this interdisciplinary team will work on the integration of 5 key concepts, namely (1) pre-operative MRI and diffusion-MRI imaging, (2) intra-operative ultrasounds, (3) robotic assisted catheter steering, (4) brain diffusion modelling, and (5) a robotics assisted neurosurgical robotic product (the Neuromate), into a pre-commercial prototype which meets the pressing demand for better and less invasive neurosurgery. Our chair will be focusing on the imaging components (i.e. (1) and (2)), targeting the realtime compensation of tissue movement and accurate localization of the flexible catheters at hand. We will further extend the findings of FP7 ACTIVE, in which we successfully combined pre-operative MRI with intra-operative US through deformable 3D-2D registration, making us most qualified for this role. |
Coupled Curves SegmentationThe term of coupled curves refers to two or more boundaries bounded biomechanically or anatomically. Some examples are luminal and outer borders of the vessel in intravascular ultrasound images, the myocardial borders of heart in different cardiac modalities like Echocardiography and MRI, retinal layers in optical coherent tomography of eye etc. Coupling these boundaries and taking into account their interdependency efficiently assists segmentation of weaker boundaries by the guide of stronger ones. This project is an extension to our recently developed segmentation approaches by modifying the formulation to segment coupled curves. The primary deliverable is segmentation of double boundaries and can be followed to the secondary deliverable, i.e. segmentation of multiple boundaries depending on the performance of the researcher. Platform of the project is visual programing with mevislab. Preferred coding language is C++ Nevertheless matlab coding can be used for development. There are plenty of applications to the segmentation of coupled curves in medical image processing and the project has significant contribution with high impact to the community. |
Prediction of Rupture Risk for Abdominal Aortic AneurysmsAn abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) describes an enlarged aortic diameter in the abdominal part of the body. Due to weakening rupture of the inner aortic wall layer, blood cells accumulate inside the wall layers and lead to a thrombus. In order to choose a suitable individual treatment, a prediction of rupture risk would be helpful. However, it is not possible to predict the ruputure risk only with quantative parameters extracted out of CT-images such as size and diameter. It is important to also include qualitative predictors like characteristics of the aortic wall and fluid dynamics.Together with our medical and academic partners, we are interested in creating a model of the aorta and its thrombus in order to do certain calculations on wall stress and fluid dynamic computations. A further integration of other medical imaging devices such as PET/CT and IVUS into the geometrical model can provide more information about biochemical activities inside the aneurysmatic walls. |
Deformable RegistrationObjects change their form over time. Undoing these changes makes the two images of the same object more comparable. This process of finding a transformation of one of the images, such that it gets as similar as possible to the other one is called deformable registration. Deformable registration can lead to improvement of many medical procedures, both diagnostic and interventional. The main reason is that deformations of the human body are present in many settings and for many imaging techniques. Always, when these deformations occur between different scans, there is potential for the current methods to be improved by using deformable registration techniques. Example applications include follow-up studies, image fusion from different modalities and treatment planning. The focus of our work is two-fold: we try to understand and improve the existing registration methods and to solve clinical problems by applying the developed methods. |
Ultrasound Based Tissue Characterizationclinicians are challenged when colocated heterogeneous tissue backscatter mixed signals appearing as non-unique intensity patterns in B-mode ultrasound image. Tissue characterization algorithms have been developed to assist clinicians to identify such heterogeneous tissues and assess lesion stage. We propose a novel technique coined as Stochastic Driven Histology (SDH) that is able to provide information about co-located heterogeneous tissues. It employs learning of tissue specific ultrasonic backscattering statistical physics and signal confidence primal from labeled data for predicting heterogeneous tissue composition in plaques. We employ a random forest for the purpose of learning such a primal using sparsely labeled and noisy samples. In clinical deployment, the posterior prediction of different lesions constituting the plaque is estimated. |
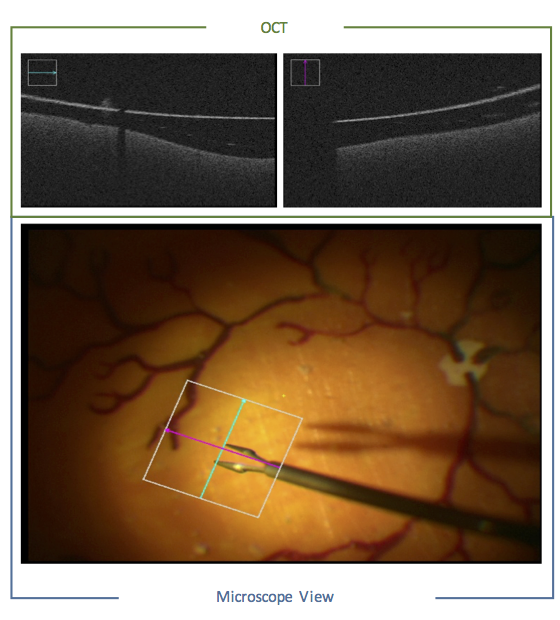
Computer-Aided Ophthalmic ProceduresIn the current workflow of opthamologic surgeries, the surgeon observes the scene in an indirect way through a microscope while performing the surgery with the necessary high handling precision. During membrane peeling, for example, the surgeon has to grasp an anatomical layer of only 10 μm off the retina without damaging it. However, under this limited microscopic view, it becomes very challenging to infer the distance of the surgical instrument to the retina. Issues such as lens distortion, high level of blurriness and lack of haptic feedback complicate the task further. Recently, an intraoperative version of the Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) was introduced, which provides the 3D information along a scanning line. On the one hand, this modality provides depth information during the surgery. On the other hand, the device has to be manually positioned to the region of interest which further complicates the current workflow of the surgeon (who already has to manipulate the surgical tool, the handheld light source and the microscope). The main goal of the project is support the surgeon in the current workflow and provide additional information during the surgery via advanced computer vision, visualization and augmented reality algorithms. |
Related Publications
| 2017 | |
| I. Reinertsen, D. H. Iversen, F. Lindseth, W. Wein, G. Unsgard
Intra-operative ultrasound based correction of brain-shift Intraoperative Imaging Society Conference 2017, Hanover, Germany, February 2017 (bib) |
|
| S. Matl, R. Brosig, M. Baust, N. Navab, S. Demirci
Vascular Image Registration Techniques: A Living Review Medical Image Analysis, Volume 35, pp. 1-7, 2017 (bib) |
|
| 2016 | |
| K. Hofschen, T. Geissler, N. Rieke, C. Schulte-zu-Berge, N. Navab, S. Demirci
Image Descriptors in Angiography Workshop Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM), March 13-15, 2016. (bib) |
|
| 2015 | |
| S. Virga, V. Dogeanu, P. Fallavollita, R. Ghotbi, N. Navab, S. Demirci
Optimal C-arm Positioning for Aortic Interventions Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM 2015), Luebeck, Germany, March 2015 (bib) |
|
| S.-L. Lee, S. Balocco, C. Gatta, S. Demirci, G. A. Tangen
Editorial of the special issue STENT Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, Special Issue STENT, In Press, 2015 (bib) |
|
| 2014 | |
| M. Yigitsoy, J. Fotouhi, N. Navab
Hough Space Parametrization: Ensuring Global Consistency in Intensity-based Registration International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions (MICCAI), Boston, USA, September 2014 (bib) |
|
| M. Müller, M. Yigitsoy, H. Heibel, N. Navab
Deformable Reconstruction of Histology Sections using Structural Probability Maps International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions (MICCAI), Boston, USA, September 2014 (bib) |
|
| M. Müller, L.E.S. Helljesen, R. Prevost, I. Viola, K. Nylund, O.H. Gilja, N. Navab, W. Wein
Deriving Anatomical Context from 4D Ultrasound Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine (VCBM), September 3-5 2014, Vienna, Austria (bib) |
|
| T. Peng, M. Yigitsoy, A. Eslami, C. Bayer, N. Navab
Deformable registration of multi-modal microscopic images using a pyramidal interactive registration- learning methodology 6th Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration, London, UK, July, 2014 (bib) |
|
| 2013 | |
| S.-L. Lee, S. Demirci, P. Radeva, G. Unal
Editorial Note Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, vol. 38, pages 69-69, 2014 (bib) |
|
| T. Aksoy, G. Unal, S. Demirci, N. Navab, M. Degertekin
Template-based CTA to X-ray Angio Rigid Registration of Coronary Arteries in Frequency Domain with Automatic X-Ray Segmentation Medical Physics, Volume 40, Issue 10, October 2013, Pages 1903-1918 (bib) |
|
| S. Demirci, F. Manstad-Hulaas, N. Navab
Interventional 2D-3D Registration in the Presence of Occlusion XIII Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2013, IFMBE Proceedings Volume 41, 2014, pp 277-280. (bib) |
|
| M. Yigitsoy, N. Navab
Structure Propagation for Image Registration IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 32, no. 9, pp. 1657-1670, September 2013 (bib) |
|
| S. Demirci, M. Baust, O. Kutter, F. Manstad-Hulaas, H-H. Eckstein, N. Navab
Disocclusion-based 2D-3D Registration for Aortic Interventions Computers in Biology and Medicine, Volume 43, Issue 4, 1 May 2013, Pages 312-322 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, X. Luo, MI. Menzel, H. Hautmann, K. Mori, N. Navab
Hybrid electromagnetic and image-based tracking of endoscopes with guaranteed smooth output International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Available online. (bib) |
|
| T. Aksoy, S. Demirci, M. Degertekin, N. Navab, G. Unal
Template-based CTA X-ray Angio Rigid Registration of Coronary Arteries in Frequency Domain Proc. SPIE 8671, Medical Imaging 2013: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, 867127, March 2013 (bib) |
|
| 2012 | |
| A. Ahmadi, T. Klein, A. Plate, K. Bötzel, N. Navab
Rigid US-MRI Registration Through Segmentation of Equivalent Anatomic Structures - A feasibility study using 3D transcranial ultrasound of the midbrain. Workshop Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin, Berlin (GER), March 18-20, 2012 (bib) |
|
| O. K. Oye, W. Wein, D. M. Ulvang, K. Matre, I. Viola
Real Time Image-Based Tracking of 4D Ultrasound Data Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2012), Nice, France, October 2012 (bib) |
|
| J. Beitzel, A. Ahmadi, A. Karamalis, W. Wein, N. Navab
Ultrasound Bone Detection Using Patient-Specific CT Prior International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, USA, September 1 2012. (bib) |
|
| V. Solteszova, L.E.S. Helljesen, W. Wein, O.H. Gilja, I. Viola
Lowest-Variance Streamlines for Filtering of 3D Ultrasound Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine (VCBM) 2012, Norrköping, Sweden, September 2012 (bib) |
|
| A. Katouzian, A. Karamalis, A. Konig, S. Carlier, N. Navab
Ambiguity in detection of necrosis in IVUS plaque characterization algorithms European Society of Cardiology, Munich, Germany, 2012 (bib) |
|
| A. Karamalis, W. Wein, T. Klein, N. Navab
Ultrasound Confidence Maps using Random Walks Medical Image Analysis, 16, 6, 1101 - 1112, 2012, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2012.07.005 (bib) |
|
| A. Katouzian, A. Karamalis, , A. Eslami, N. Navab
IVUS-Histology Image Registration 5th Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration, Nashville, USA, July, 2012 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, I. Gergel, MI. Menzel, H. Hautmann, I. Wegner, H.P. Meinzer, N. Navab
New methods for tracking error compensation in transbronchial interventions Proceedings of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (CARS 2012), Pisa, Italy, June 2012 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, N. Navab
A Contextual Maximum Likelihood Framework for Modeling Image Registration IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, Rhode Island (USA), June 2012. (bib) |
|
| Y. Yagi, M. Groher, M. Feuerstein, M. Onozato, H. Heibel, N. Navab
Overcoming Challenges in Histology 3D Imaging 11th European Congress on Telepathology and 5th International Congress on Virtual Microscopy, Venice, Italy, June 2011. (bib) |
|
| A. Karamalis, A. Katouzian, S. Carlier, N. Navab
Confidence Estimation in IVUS Radio-Frequency Data with Random Walks In Proc. 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Barcelona, Spain, 2012 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, I. Gergel, MI. Menzel, H. Hautmann, I. Wegner, H.P. Meinzer, N. Navab
Motion compensation for bronchoscope navigation using electromagnetic tracking, airway segmentation, and image similarity Proceedings of Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM 2012), Berlin, Germany, March 2012 (bib) |
|
| A. Katouzian, A. Karamalis, A. Laine, N. Navab
A Systematic Approach Toward Reliable Atherosclerotic Plaque Characterization in IVUS Images Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin, Berlin, 2012, Germany (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, I. Gergel, MI. Menzel, H. Hautmann, I. Wegner, H.P. Meinzer, N. Navab
Real-time motion compensation for EM bronchoscope tracking with smooth output - ex-vivo validation SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, February 2012. (bib) |
|
| 2011 | |
| M. Yigitsoy, C. Wachinger, N. Navab
Temporal Groupwise Registration for Motion Modeling Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), July 3-8 2011. (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, M. Baust, A. Kamen, N. Navab
A General Preconditioning Scheme for Difference Measures in Deformable Registration IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) in Barcelona, Spain, November 06-13 2011. (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, H. Heibel, J. Gardiazabal, N. Navab, M. Groher
Reconstruction of 3-D Histology Images by Simultaneous Deformable Registration Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2011), Toronto, Canada, September 2011. The original publication is available online at www.springerlink.com (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, A. Ladikos
Detecting Patient Motion in Projection Space for Cone-beam Computed Tomography Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2011), Toronto, Canada, September 2011 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, X. Luo, MI. Menzel, H. Hautmann, K. Mori, N. Navab
Deformable Registration of Bronchoscopic Video Sequences to CT Volumes with Guaranteed Smooth Output Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2011), Toronto, Canada, September 2011. (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Robust Bronchoscope Motion Tracking Using Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Navigated Bronchoscopy: Dynamic Phantom and Patient Validation International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
On scale invariant features and sequential Monte Carlo sampling for bronchoscope tracking SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2011 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
A novel bronchoscope tracking method for bronchoscopic navigation using a low cost optical mouse sensor SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2011 (bib) |
|
| 2010 | |
| B. Glocker, H. Heibel, N. Navab, P. Kohli, C. Rother
TriangleFlow: Optical Flow with Triangulation-based Higher-Order Likelihoods 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Crete, Greece, September 5-11 2010. (bib) |
|
| A. Sotiras, Y. Ou, B. Glocker, C. Davatzikos, N. Paragios
Simultaneous Geometric - Iconic Registration Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Bejing, China, September 20-24 2010. (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, B. Glocker, O. Kutter, M. Groher, N. Komodakis, A. Kamen, N. Paragios, N. Navab
Linear Intensity-based Image Registration by Markov Random Fields and Discrete Optimization Medical Image Analysis, 22 April, 2010. (bib) |
|
| O. Fluck, C. Vetter, W. Wein, A. Kamen, B. Preim, R. Westermann
A survey of medical image registration on graphics hardware Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, November 2010 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, T. Hirotsugu, K. Mori
Development and Comparison of New Hybrid Motion Tracking for Bronchoscopic Navigation Medical Image Analysis. Special issue on Computer Assisted Interventions. Accepted for publication, 17 November 2010. (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, T. Reichl, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Modified Hybrid Bronchoscope Tracking Based on Sequential Monte Carlo Sampler: Dynamic Phantom Validation Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Queenstown, New Zealand, November 2010 (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, N. Paragios, N. Navab
Non-rigid Registration using Discrete MRFs: Application to Thoracic CT Images Workshop Evaluation of Methods for Pulmonary Image Registration in conjunction with Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Beijing, China, September 24 2010 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, M. Baust, A. Kamen, N. Navab
Generalization of Deformable Registration in Riemannian Sobolev Spaces International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) in Beijing, China, September 20-24 2010. (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, H. Heibel, N. Navab
A Machine Learning Approach for Deformable Guide-Wire Tracking in Fluoroscopic Sequences. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2010), Beijing, China, September 2010 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Reichl, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
An Application Driven Comparison of Several Feature Extraction Algorithms in Bronchoscope Tracking During Navigated Bronchoscopy 5th International Workshop on Medical Imaging and Augmented Reality, Sep 2010, Beijing (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, T. Sugiura, D. Deguchi, T. Reichl, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Marker-free Registration for Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy under Respiratory Motion 5th International Workshop on Medical Imaging and Augmented Reality, Sep 2010, Beijing (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, A. Kamen, N. Navab
Revisiting Horn and Schunck: Interpretation as Gauß-Newton Optimisation British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) in Aberystwyth, Wales, 31th August - 3rd September 2010. (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, N. Navab
Manifold Learning for Multi-Modal Image Registration 21st British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Aberystwyth, United Kingdom, August 31 - September 3 2010. (bib) |
|
| F. Manstad-Hulaas, G. A. Tangen, S. Demirci, M. Pfister, S. Lydersen, T. A. Nagelhus Hernes
Endovascular Image-Guided Navigation - Validation of Two Volume-Volume Registration Algorithms Minimally Invasive Therapy & Allied Technologies 20(5), pp. 282 - 289, 2011 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, A. Kamen, N. Navab
Unifying Characterization of Deformable Registration Methods Based on the Inherent Parameterization International Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration (WBIR), in Lübeck, Germany, July 11-13 2010. (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, M. Baust, D. Zikic, N. Navab
Monocular Deformable Model-to-Image Registration of Vascular Structures International Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration (WBIR), in Lübeck, Germany, July 11-13 2010. (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, N. Navab
Structural Image Representation for Image Registration IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, California, June 2010. Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (MMBIA). (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, A. Kamen, N. Navab
Natural Gradients for Deformable Registration IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) in San Francisco, CA, USA, June 13-18 2010. (bib) |
|
| C. Weiss, M. Seitz, K. Herrmann, A. Graser, B. Kiefer, M. Requardt, J. Fehre, R. Nanke, M. Diallo, A. Kamen, W. Wein
MR-US Fusion for Targeted Prostate Biopsy International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) conference, Stockholm, Sweden, May 2010 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, O. Kutter, A. Aichert, D. Zikic, A. Kamen, N. Navab
Automatic non-linear mapping of pre-procedure CT volumes to 3D ultrasound IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, April 14 - 17 2010. (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, O. Kutter, Benedikt Schultis, MI. Menzel, H. Hautmann, N. Navab
Video-basiertes Tracking eines Bronchoskops Proceedings of Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM 2010), Aachen, Germany, March 2009 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Sugiura, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa
Towards hybrid bronchoscope tracking under respiratory motion: evaluation on a dynamic motion phantom SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, February 2010 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, B. Glocker, O. Kutter, M. Groher, N. Komodakis, A. Kamen, N. Paragios, N. Navab
Markov Random Field Optimization for Intensity-based 2D-3D Registration SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, 13-18 February 2010 (bib) |
|
| T. Sugiura, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
A study on a breathing motion compensation for bronchoscope tracking based on bronchial tree structure information IEICE Medical Imaging, Naha, Japan, January 2010 (bib) |
|
| 2009 | |
| A. Sotiras, N. Komodakis, B. Glocker, J.-F. Deux, N. Paragios
Graphical Models and Deformable Diffeomorphic Population Registration Using Global and Local Metrics Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), London, UK, September 20-24 2009. (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, N. Navab, G. Tziritas, N. Paragios
Dense Registration with Deformation Priors Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), Williamsburg, VA, USA, July 5-10 2009. (bib) |
|
| M. Baust, S. Demirci, N. Navab
Stent Graft Removal for Improving 2D-3D Registration IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Boston, MA, USA, June 28-July 1 2009. (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, N. Paragios, N. Navab
Approximated Curvature Penalty in Non-rigid Registration using Pairwise MRFs 5th International Symposium on Visual Computing (ISVC), Las Vegs, Nevada, USA, Nov 30-Dec 2 2009. (bib) |
|
| T. Kugo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
A study on construction of respiratory lung motion model for bronchoscope guidance system 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Sugiura, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
A study on a method for bronchoscope tracking considering breathing motion by using bronchial structure 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, M. Mori, H. Takabatake, H. Natori, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
Improvement of Bronchoscope Tracking by Combining SURF Features Based Camera Motion Estimation and Image Registration 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, E. Camus, M. John, M. Diallo, C. Duong, A. Al-Ahmad, R. Fahrig, A. Khamene, C. Xu
Towards Guidance of Electrophysiological Procedures with Real-time 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography Fusion to C-arm CT Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2009), London, UK, September 2009 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, N. Navab
Alignment of Viewing-Angle Dependent Ultrasound Images. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), London, UK, September 20-24 2009 (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, N. Padoy, H. Poppert, I. Esposito, H-H. Eckstein, N. Navab
Towards Application-specific Multi-modal Similarity Measures: a Regression Approach. MICCAI Workshop on Probabilistic Models in Medical Image Analysis (PMMIA), London, UK, September 2009. (bib) |
|
| O. Kutter, W. Wein, N. Navab
Multi-modal registration based Ultrasound Mosaicing Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), London, UK, September 20-24 2009 (bib) |
|
| A. Khamene, D. Zikic, M. Diallo, T. Boettger, E. Rietzel
A Novel Intensity Similarity Metric with Soft Spatial Constraint for a Deformable Image Registration Problem in Radiation Therapy. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), London, UK, September 20-24 2009. (bib) |
|
| Benedikt Schultis
Video-based Bronchoscope Tracking for Navigated Bronchoscopy Bachelor's Thesis. Technische Universität München, September 2009 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
SIFT Feature-based Motion Estimation for Bronchoscope Tracking 28th Meeting of the Japanese Society of Medical Imaging Technology, Nagoya, Japan, August 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Kugo, M. Feuerstein, K. Mori, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, Y. Hasegawa, K. Imaizumi, S. Iwano
A preliminary study on making respiratory motion model for bronchoscope guidance system 28th Meeting of the Japanese Society of Medical Imaging Technology, Nagoya, Japan, August 2009 (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, D. Zikic, N. Komodakis, N. Paragios, N. Navab
Linear Image Registration through MRF Optimization IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Boston, MA, USA, June 28-July 1 2009. (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, N. Navab
Similarity Metrics and Efficient Optimization for Simultaneous Registration IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, Florida (USA), June 2009. (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, N. Padoy, H. Poppert, I. Esposito, N. Navab
Wavelet Energy Map: A Robust Support for Multi-modal Registration of Medical Images IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, Florida (USA), June 2009. (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, J. Passenger, O. Acosta, O. Salvado
Echtzeit-Ultraschallsimulation auf Grafik-Prozessoren mit CUDA Proceedings of Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM 2009), Heidelberg, Germany, March 2009 (bib) |
|
| S. Demirci, F. Manstad-Hulaas, N. Navab
Extracting a Purely Non-Rigid Deformation Field of a Single Structure Proceedings of Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM 2009), Heidelberg, Germany, March 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, J. Passenger, O. Acosta, O. Salvado
Ultrasound goes GPU: real-time simulation using CUDA SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2009 (bib) |
|
| O. Kutter, A. Karamalis, W. Wein, N. Navab
A GPU-Based Framework for Simulation of Medical Ultrasound SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2009 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, S. Baumann, J. Zeltner, B. Glocker, N. Navab
Sphere Extraction in MR Images with Application to Whole-Body MRI. SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, 7-12 February 2009 (bib) |
|
| S. Demirci, F. Manstad-Hulaas, N. Navab
Quantification of Abdominal Aortic Deformation after EVAR Proc. SPIE 7261, Medical Imaging 2009: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling, 72611U, February 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Sugiura, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Mori
A method for accelerating bronchoscope tracking based on image registration by using GPU SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2009 (bib) |
|
| A. Karamalis, W. Wein, O. Kutter, N. Navab
Fast Hybrid Freehand Ultrasound Volume Reconstruction In Proc. SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2009 (bib) |
|
| O. Kutter, R. Shams, N. Navab
Visualization and GPU-accelerated simulation of medical ultrasound from CT images Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, Volume 94, Issue 3, June, 2009 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, D. Zikic, N. Navab
Deformable 2D-3D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 28 (6), pp. 847-860 (bib) |
|
| 2008 | |
| C. Wachinger, B. Glocker, J. Zeltner, N. Paragios, N. Komodakis, M. S. Hansen, N. Navab
Deformable Mosaicing for Whole-body MRI Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), New York, USA, September 6-10 2008 (bib) |
|
| M. S. Hansen, B. Glocker, N. Navab, R. Larsen
Adaptive Parametrization of Multivariate B-splines for Image Registration IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Anchorage, Alaska (USA), June 24-26, 2008 (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, N. Paragios, N. Komodakis, G. Tziritas, N. Navab
Optical Flow Estimation with Uncertainties through Dynamic MRFs IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Anchorage, Alaska (USA), June 24-26, 2008 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger
Insights Into Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Mosaicing: Strategies for the alignment of multiple ultrasound volumes VDM Verlag Dr. Müller, Stuttgart, ISBN: 3836488264, December 23 2008, Amazon (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, G. Tziritas, N. Navab, N. Paragios
Dense Image Registration through MRFs and Efficient Linear Programming Medical Image Analysis, Volume 12, Issue 6, December 2008, pp. 731-741 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, W. Wein, N. Navab
Registration Strategies and Similarity Measures for Three-dimensional Ultrasound Mosaicing Journal of the University Radiologists, Academic Radiology 15 (11), pp.1404-1415. Special issue of MICCAI 2007 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, J. Passenger, O. Acosta, O. Salvado
Real-time ultrasound simulation on GPU CSIRO, Proceedings of CSIRO ICT Centre Conference 2008 (bib) |
|
| T. Sugiura, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa
A study on a method for accelerating bronchoscope tracking based on image registration on GPU 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
A Study on Feature Point Extraction from Bronchoscopic Images for Bronchoscope Tracking 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, S. Brunke, A. Khamene, M.R. Callstrom, N. Navab
Automatic CT-Ultrasound Registration for Diagnostic Imaging and Image-guided Intervention Medical Image Analysis 12(5), pp 577-585, October 2008 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, J.-Z. Cheng, A. Khamene
Ultrasound based Respiratory Motion Compensation in the Abdomen MICCAI 2008 Workshop on Image Guidance and Computer Assistance for Soft-Tissue Interventions, September 10 2008, New York City, USA. (bib) |
|
| E. Gassner, Razvan Ioan Ionasec, B. Georgescu, S. Vogt, U. J. Schoepf, D. Comaniciu
Performance of a Dynamic Aortic Valve Model for Quantification of the Opening Area at Cardiac MDCT . Comparison to Manual Planimetry Radiological Society of North America, RSNA, 2008, Chicago, USA, November 2008 (bib) |
|
| Razvan Ioan Ionasec, B. Georgescu, D. Comaniciu, S. Vogt, U. J. Schoepf, E. Gassner
Patient Specific 4D Aortic Root Models Derived from Volumetric Image Data Sets Radiological Society of North America, RSNA, 2008, Chicago, USA, November 2008 (bib) |
|
| Razvan Ioan Ionasec, B. Georgescu, E. Gassner, S. Vogt, O. Kutter, M. Scheuering, N. Navab, D. Comaniciu
Dynamic model-driven quantification and visual evaluation of the aortic valve from 4D CT Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, MICCAI, 2008, New York, USA, September 6-10 2008 (bib) |
|
| J. Choi, B. Georgescu, Razvan Ioan Ionasec, S. Raman, G. Hong, X. Liu, Helene Houle, M. A. Vannan
Novel Semi-Automatic Quantitative Assessment of The Aortic Valve and Aortic Root from Volumetric 3D Echocardiography: Comparison to Volumetric Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT) AHA, New Orleans, USA, November 2008 (bib) |
|
| F. Bender, M. Groher, A. Khamene, W. Wein, H. Heibel, N. Navab
3D Dynamic Roadmapping for Abdominal Catheterizations Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, MICCAI, 2008, New York, USA, September 6-10 2008 (bib) |
|
| S. Atasoy, D. Noonan, S. Benhimane, N. Navab, G. Z. Yang
A Global Approach for Automatic Fibroscopic Video Mosaicing in Minimally Invasive Diagnosis Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, MICCAI, 2008, New York, USA, September 6-10 2008 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl
Ultrasound Simulation Project Patent Landscape Search August 2008 CSIRO, The Australian e-Health Research Centre, Internal Report 2008/289 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, R. Shams, N. Navab
Estimation of Acoustic Impedance from Multiple Ultrasound Images with Application to Spatial Compounding IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, Alaska (USA), June 2008. Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (MMBIA). (bib) |
|
| R. Lasowski, S. Benhimane, J. Vogel, T. F. Jakobs, C. J. Zech, C. Trumm, M. Brokate, N. Navab
Adaptive visualization using the annealing M-estimator Workshop Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin, Berlin, Germany, April 6-8, 2008 (bib) |
|
| T. Reichl, J. Passenger, O. Acosta, O. Salvado
Transrectal Ultrasound and Biopsy Simulation Literature Review CSIRO, The Australian e-Health Research Centre, Internal Report 2008/108 (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, G. Unal, G. Slabaugh, S. Carlier, T. Fang
Semi-Automatic Matching of OCT and IVUS Images For Image Fusion SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California (USA), February 2008. (bib) |
|
| R. Lasowski, S. Benhimane, J. Vogel, T. F. Jakobs, C. J. Zech, C. Trumm, Ch. Clason, N. Navab
Adaptive visualization for needle guidance in RF Liver Ablation: taking organ deformation into account SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, February 16-21, 2008 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, A. Khamene
Image-Based Method for In-Vivo Freehand Ultrasound Calibration SPIE Medical Imaging, 16-21 February 2008, San Diego, California USA (bib) |
|
| S. Demirci, O. Kutter, F. Manstad-Hulaas, R. Bauernschmitt, N. Navab
Advanced 2D-3D Registration for Endovascular Aortic Interventions: Addressing Dissimilarity in Images Proc. SPIE 6918, Medical Imaging 2008: Visualization, Image-guided Procedures, and Modeling, 69182S, February 2008 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, M. Groher, A. Khamene, N. Navab
Deformable Registration of 3D Vessel Structures to a Single Projection Image. SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, 16-21 February 2008 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, S. Sourbron, X. Feng, H. J. Michaely, A. Khamene, N. Navab
Automatic Alignment of Renal DCE-MRI Image Series for Improvement of Quantitative Tracer Kinetic Studies. SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, 16-21 February 2008 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, N. Navab
Ultrasound Specific Similarity Measures for Three-Dimensional Mosaicing. SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, 16-21 February 2008 (bib) |
|
| S. Atasoy, M. Groher, D. Zikic, B. Glocker, T. Waggershauser, M. Pfister, N. Navab
Real-Time Respiratory Motion Tracking: Roadmap Correction for Hepatic Artery Catheterizations SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, 16-21 February 2008 (bib) |
|
| N. Navab, M. Groher
Novel Navigation and Advanced Visualization Techniques for Abdominal Catheterization Hospital Imaging and Radiology Europe, 2 (4), pp. 29-30, Feb. 2008 (bib) |
|
| 2007 | |
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, N. Paragios, G. Tziritas, N. Navab
Inter and Intra-Modal Deformable Registration: Continuous Deformations Meet Efficient Optimal Linear Programming Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), Kerkrade, Netherlands, July 2-6 2007. This work won the Erbsmann prize for the best oral presentation among all first-time presenters at IPMI 2007. (bib) |
|
| A. Khamene, L. Schwarz, D. Zikic, F. Azar, E. Rietzel, N. Navab
A Unified and Efficient Approach for Free-form Deformable Registration IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, November 2007 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, A. Khamene, D.-A. Clevert, O. Kutter, N. Navab
Simulation and Fully Automatic Multimodal Registration of Medical Ultrasound Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2007), Brisbane, Australia, October 2007. Received the MICCAI 2007 Young Scientist Award. (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, M. Blume, U. Leischner, H.-U. Dodt, N. Navab
Quality-based Registration and Reconstruction of Optical Tomography Volumes Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2007), Brisbane, Australia, October 2007 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, W. Wein, N. Navab
Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Mosaicing Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, MICCAI, 2007, Brisbane, Australia, October 29 - November 2 2007 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, F. Bender, R.T. Hoffmann, N. Navab
Segmentation-driven 2D-3D Registration for Abdominal Catheter Interventions Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, MICCAI, 2007, Brisbane, Australia, October 29 - November 2 2007, LNCS 4792, pp. 527-535 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, T. F. Jakobs, N. Padoy, N. Navab
Planning and Intraoperative Visualization of Liver Catheterizations: New CTA Protocol and 2D-3D Registration Method Academic Radiology 14 (11), pp.1324-1339. Special issue of MICCAI 2006 (bib) |
|
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, N. Paragios, Ch. Glaser, G. Tziritas, N. Navab
Primal/Dual Linear Programming and Statistical Atlases for Cartilage Segmentation Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Brisbane, Australia, October 29 - November 2 2007 (bib) |
|
| M. Blume, D. Zikic, W. Wein, N. Navab
A New and General Method for Blind Shift-Variant Deconvolution of Biomedical Images Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2007), Brisbane, Australia, October 2007 (bib) |
|
| C. Wachinger, W. Wein, N. Navab
Ultrasound Volume Stitching 6. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2007), Karlsruhe, Germany, October 2007 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, B. Röper, N. Navab
Integrating diagnostic B-mode ultrasonography into CT-based radiation treatment planning IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26 (June 2007), pp. 866–879 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, R.T. Hoffmann, C. J. Zech, M. Reiser, N. Navab
An Efficient Registration Algorithm for Advanced Fusion of 2D/3D Angiographic Data in Proceedings of Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin (BVM 2007), Munich, Germany, March 2007 (bib) |
|
| R. Micu, T. F. Jakobs, C. J. Zech, N. Navab
Evaluation of different subvolume visualizations in CT-Fluoroscopy guided RF Liver Ablation SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, 17-22 February 2007 (bib) |
|
| 2006 | |
| R. Micu, T. F. Jakobs, C. J. Zech, M. Reiser, N. Navab
Subvolume visualization based on piecewise 2D CT-Fluoroscopy to 3D CT-Volume registration 5. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2006), Hannover, Germany, Oktober 2006 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, T. F. Jakobs, M. Reiser, N. Navab
Advanced 2D-3D Registration Method for Transarterial Chemoembolizations 5. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2006), Hannover, Germany, September 2006 (bib) |
|
| R. Micu, T. F. Jakobs, M. Urschler, N. Navab
A new registration/visualization paradigm for CT-Fluoroscopy guided RF liver ablation Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2006), Copenhagen, Denmark, October 2006 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, W. Wein, A. Khamene, D.-A. Clevert, N. Navab
Fast Deformable Registration of 3D-Ultrasound Using a Variational Approach Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2006), Copenhagen, Denmark, October 2006 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, F. Pache, B. Röper, N. Navab
Backward-Warping Ultrasound Reconstruction for Improving Diagnostic Value and Registration Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2006), Copenhagen, Denmark, October 2006 (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, N. Padoy, T. F. Jakobs, N. Navab
New CTA Protocol and 2D-3D Registration Method for Liver Catheterization Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2006), Copenhagen, Denmark, October 2006 (bib) |
|
| D. Zikic, A. Khamene, N. Navab
Intensity-Unbiased Force Computation for Variational Motion Estimation. Workshop on Image Registration in Deformable Environments in conjunction with the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2006), Edinburgh, Scotland, September 2006 (bib) |
|
| B. Röper, W. Wein, P. Kneschaurek, M. Molls, M. Dobritz, N. Navab
Image-based fusion of diagnostic ultrasound and planning CT for radiotherapy of head and neck cancer – a way towards improvement of regional target volume delineation 12. Jahreskongress der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Radioonkologie (DEGRO), May 2006, Dresden, Germany (bib) |
|
| A. Khamene, P. Bloch, W. Wein, M. Svatos, F. Sauer
Automatic Registration of Portal Images and Volumetric CT for Patient Positioning in Radiation Therapy Medical Image Analysis 10 (2006), pages 96-112 (bib) |
|
| A. Khamene, R. Chisu, W. Wein, N. Navab, F. Sauer
A Novel Projection Based Approach for Medical Image Registration Third International Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration (WBIR), 9-11 July 2006, Utrecht, The Netherlands. (bib) |
|
| 2005 | |
| W. Wein, B. Röper, N. Navab
Automatic Registration and Fusion of Ultrasound with CT for Radiotherapy 8th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), October 2005, Palm Springs, California USA. (bib) |
|
| M. Groher, T. F. Jakobs, N. Padoy, N. Navab
Towards a Feature-based 2D-3D Registration Method of CTA and 2D Angiograms for Liver Tumor Chemoembolizations 4. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2005), Berlin, Germany, September 2005 (bib) |
|
| W. Wein, B. Röper, N. Navab
2D/3D Registration Based on Volume Gradients SPIE Medical Imaging, 12-17 February 2005, San Diego, California USA (bib) |
|
| 2004 | |
| W. Wein, B. Röper, N. Navab
2D/3D Registration Based on Volume Gradients CURAC, October 2004, Munich (bib) |
|
| 2015 | |
| F. Milletari, A. Ahmadi, C. Kroll, C. Hennersperger, F. Tombari, A. Shah, A. Plate, K. Bötzel, N. Navab
Robust Segmentation of Various Anatomies in 3D Ultrasound Using Hough Forests and Learned Data Representations MICCAI 2015, the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (bib) |
|
| C. Hennersperger, M. Baust, D. Mateus, N. Navab
Computational Sonography MICCAI 2015, the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (bib) |
|
| 2014 | |
| F. Milletari, M. Yigitsoy, N. Navab, A. Ahmadi
Left Ventricle Segmentation in Cardiac Ultrasound Using Hough-Forests With Implicit Shape and Appearance Priors MICCAI Challenge on Endocardial Three-dimensional Ultrasound Segmentation (CETUS), Boston, MA, September 2014 (bib) |
|
| 2013 | |
| A. Eslami, A. Karamalis, A. Katouzian, N. Navab
Segmentation By Retrieval With Guided Random Walks: Application To Left Ventricle Segmentation in MRI Medical Image Analysis, vol. 17, no. 2, 2013, www.sciencedirect.com.ezproxy.cul.columbia.edu/science/article/pii/S136184151200151X (bib) |
|
| 2012 | |
| A. Ahmadi, T. Klein, A. Plate, K. Bötzel, N. Navab
Rigid US-MRI Registration Through Segmentation of Equivalent Anatomic Structures - A feasibility study using 3D transcranial ultrasound of the midbrain. Workshop Bildverarbeitung fuer die Medizin, Berlin (GER), March 18-20, 2012 (bib) |
|
| J. Beitzel, A. Ahmadi, A. Karamalis, W. Wein, N. Navab
Ultrasound Bone Detection Using Patient-Specific CT Prior International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, USA, September 1 2012. (bib) |
|
| A. Karamalis, W. Wein, T. Klein, N. Navab
Ultrasound Confidence Maps using Random Walks Medical Image Analysis, 16, 6, 1101 - 1112, 2012, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2012.07.005 (bib) |
|
| P. Lo, B. v. Ginneken, J. M. Reinhardt, T. Yavarna, P. A. d. Jong, B. Irving, C. Fetita, M. Ortner, R. Pinho, J. Sijbers, M. Feuerstein, A. Fabijanska, C. Bauer, R. Beichel, C. S. Mendoza, R. Wiemker, J. Lee, A. P. Reeves, S. Born, weinheimer, E. M. v. Rikxoort, J. Tschirren, K. Mori, B. Odry, D. P. Naidich, I. Hartmann, E. A. Hoffman, M. Prokop, J. H. Pedersen, M. d. Bruijne
Extraction of Airways from CT (EXACT'09) IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, July 2012 (bib) |
|
| P. Waelkens, A. Ahmadi, N. Navab
'Frangi goes US': Multiscale Tubular Structure Detection Adapted to 3D Ultrasound In Proc. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Nice (FR), October 01-05, 2012 (bib) |
|
| O. Pauly, A. Ahmadi, A. Plate, K. Bötzel, N. Navab
Detection of Substantia Nigra Echogenicities in 3D Transcranial Ultrasound for Early Diagnosis of Parkinson Disease In Proc. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Nice (FR), October 01-05, 2012 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, B. Glocker, T. Kitasaka, Y. Nakamura, S. Iwano, K. Mori
Mediastinal Atlas Creation from 3-D Chest Computed Tomography Images: Application to Automated Detection and Station Mapping of Lymph Nodes Medical Image Analysis, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 63-74, January 2012. The original publication is available online at www.elsevier.com (bib) |
|
| 2011 | |
| A. Ahmadi, M. Baust, A. Karamalis, A. Plate, K. Bötzel, T. Klein, N. Navab
Midbrain Segmentation in Transcranial 3D Ultrasound for Parkinson Diagnosis In Proc. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Toronto (CA), September 18-22, 2011 (bib) |
|
| D. Ugurlu, S. Demirci, N. Navab, M. S. Celebi
A Vessel Segmentation Method for MRA Images Based on Multi-scale Analysis and Level Set Framework 3rd International MICCAI-Workshop on Computation and Visualization on (Intra)Vascular Imaging, Toronto, Canada, September 18, 2011 (bib) |
|
| L. König, J. M. Raya Garcia del Olmo
Edge Aberration in MRI. Correction of Dislocations in Sub-Voxel Edge Detection—a Proof of Concept Proc. of Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin (BVM 2011), Lübeck, Germany, March 2011. The original publication is available online at www.springerlink.com. (bib) |
|
| 2010 | |
| A. Horng, J. M. Raya Garcia del Olmo, M. Zscharn, L. König, M. Notohamiprodjo, M. Pietschmann, U. Hoehne-Hückstädt, I. Hermanns, U. Glitsch, R. Ellegast, K. G. Hering, M. Reiser, Ch. Glaser
Locoregional Deformation Pattern of the Patellar Cartilage After Different Loading Types—High-Resolution 3D-MRI Volumetry at 3 T in-vivo Fortschr Röntgenstr. 2010; 182:1–9 (bib) |
|
| T. Kitasaka, H. Yano, M. Feuerstein, K. Mori
Bronchial region extraction from 3D chest CT image by voxel classification based on local intensity structure Third International Workshop on Pulmonary Image Analysis, September 2010 (bib) |
|
| G.Gul-Isguder, G. Unal, M. Groher, N. Navab, A.K.Kalkan, M. Degertekin, H.Hetterich, J.Rieber
Manifold Learning for Image-Based Gating of Intravascular Ultrasound(IVUS) Pullback Sequences 5th International Workshop on Medical Imaging and Augmented Reality, Sep 2010, Beijing (bib) |
|
| J. M. Raya Garcia del Olmo, A. Horng, L. König, M. Reiser, Ch. Glaser
Detecting Statistically Significant Changes in Cartilage Thickness with Sub-Voxel Precision Proceedings of the 18th congress of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM 2010), Stockholm, Sweden. Presentation 3192, electronic poster session “Meniscus & Cartilage” (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Adaptive Model Based Pulmonary Artery Segmentation in 3D Chest CT SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, California, USA, February 2010 (bib) |
|
| 2009 | |
| S. Demirci, G. Lejeune, N. Navab
Hybrid Deformable Model for Aneurysm Segmentation Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 2009. ISBI '09. IEEE International Symposium on, pp. 33-36, 2009. (bib) |
|
| H. Yano, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Study on bronchus region extraction from 3D chest CT images using local intensity structure analysis 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Automated Anatomical Likelihood Driven Extraction and Branching Detection of Aortic Arch in 3-D Chest CT Second International Workshop on Pulmonary Image Analysis, September 2009 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Adaptive Branch Tracing and Image Sharpening for Airway Tree Extraction in 3-D Chest CT Second International Workshop on Pulmonary Image Analysis, September 2009 (bib) |
|
| H. Yano, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, K. Mori, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga
Study on bronchus region extraction from 3D chest CT images based on analysis of local intensity value distribution 28th Meeting of the Japanese Society of Medical Imaging Technology, Nagoya, Japan, August 2009 (bib) |
|
| H. Yano, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Study on bronchus region extraction from 3D chest CT images using local intensity structure analysis and CT value distribution features Medical Imaging Workshop of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers, Tokyo, Japan, July 2009 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, S. Iwano, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, Y. Suenaga, K. Mori
Automatic Mediastinal Lymph Node Detection in Chest CT SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando, Florida, USA, February 2009 (bib) |
|
| 2008 | |
| H. Yano, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori, Y. Suenaga
A study on bronchial area extraction from 3D chest CT images using CT value distribution features 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, S. Iwano, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, Y. Suenaga, K. Mori
Automatic Detection of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Contrast-Enhanced Chest CT 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| 2007 | |
| B. Glocker, N. Komodakis, N. Paragios, Ch. Glaser, G. Tziritas, N. Navab
Primal/Dual Linear Programming and Statistical Atlases for Cartilage Segmentation Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Brisbane, Australia, October 29 - November 2 2007 (bib) |
|
| L. König, M. Groher, A. Keil, Ch. Glaser, M. Reiser, N. Navab
Semi-Automatic Segmentation of the Patellar Cartilage in MRI Proc. of Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin (BVM 2007), Munich, Germany, March 2007. The original publication is available online at www.springerlink.com. (bib) |
|
Working Group
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|