|
|
|||||
Research
- 3D Histology
- Computer Aided Diagnosis
- Image Guided Surgery and Interventions
- Endoscopy
- Medical Augmented Reality
Publications
Journal Articles
International Conferences / Symposiums / Workshops
|
F. Kromp, S. Taschner-Mandl, M. Ambros, M. Berneder, L. Fischer, M. Feuerstein, A. Hanbury, I.M. Ambros, P.F. Ambros Deep learning based tool to analyze I-FISH spots in consecutive sections of heterogeneously amplified neuroblastoma tumors Advances in Neuroblastoma Research, San Francisco, USA, May 2018. |
National Conferences / Symposiums / Workshops
| 2010 | |
| T. Sugiura, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
A study on a breathing motion compensation for bronchoscope tracking based on bronchial tree structure information IEICE Medical Imaging, Naha, Japan, January 2010 (bib) |
|
| 2009 | |
| H. Yano, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Study on bronchus region extraction from 3D chest CT images using local intensity structure analysis 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Kugo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
A study on construction of respiratory lung motion model for bronchoscope guidance system 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Sugiura, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
A study on a method for bronchoscope tracking considering breathing motion by using bronchial structure 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, M. Mori, H. Takabatake, H. Natori, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
Improvement of Bronchoscope Tracking by Combining SURF Features Based Camera Motion Estimation and Image Registration 18th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, November 2009 (bib) |
|
| H. Yano, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, K. Mori, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga
Study on bronchus region extraction from 3D chest CT images based on analysis of local intensity value distribution 28th Meeting of the Japanese Society of Medical Imaging Technology, Nagoya, Japan, August 2009 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
SIFT Feature-based Motion Estimation for Bronchoscope Tracking 28th Meeting of the Japanese Society of Medical Imaging Technology, Nagoya, Japan, August 2009 (bib) |
|
| T. Kugo, M. Feuerstein, K. Mori, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, Y. Hasegawa, K. Imaizumi, S. Iwano
A preliminary study on making respiratory motion model for bronchoscope guidance system 28th Meeting of the Japanese Society of Medical Imaging Technology, Nagoya, Japan, August 2009 (bib) |
|
| H. Yano, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori
Study on bronchus region extraction from 3D chest CT images using local intensity structure analysis and CT value distribution features Medical Imaging Workshop of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers, Tokyo, Japan, July 2009 (bib) |
|
| 2008 | |
| H. Yano, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori, Y. Suenaga
A study on bronchial area extraction from 3D chest CT images using CT value distribution features 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| T. Sugiura, D. Deguchi, M. Feuerstein, T. Kitasaka, K. Mori, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa
A study on a method for accelerating bronchoscope tracking based on image registration on GPU 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| X. Luo, M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, Y. Suenaga, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, K. Mori
A Study on Feature Point Extraction from Bronchoscopic Images for Bronchoscope Tracking 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, D. Deguchi, T. Kitasaka, S. Iwano, K. Imaizumi, Y. Hasegawa, Y. Suenaga, K. Mori
Automatic Detection of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Contrast-Enhanced Chest CT 17th Meeting of the Japan Society of Computer Assisted Surgery, Tokyo, Japan, October/November 2008 (bib) |
|
| 2007 | |
| M. Feuerstein, T. Mussack, S.M. Heining, N. Navab
Registration-free Laparoscope Superimposition for Intra-Operative Planning of Liver Resection 3rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Erlangen, Germany, July 2/3 2007 (bib) |
|
| C. Alcérreca, J. Vogel, M. Feuerstein, N. Navab
A New Approach to Ultrasound Guided Radio-Frequency Needle Placement Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2007, Munich, Germany, March 2007 (bib) |
|
| 2005 | |
| J. Traub, S. Wiesner, M. Feuerstein, H. Feußner, N. Navab
Evaluation of Calibration Methods for Laparoscope Augmentation 4. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2005), Berlin, Germany, September 2005 (bib) |
|
| M. Feuerstein, N. Navab, E.U. Schirmbeck, S.M. Wildhirt, R. Lange, R. Bauernschmitt
Endocsope Augmentation for Port Placement and Navigation for Rigid Anatomy 4. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer-und Roboter-Assistierte Chirurgie (CURAC 2005), Berlin, Germany, September 2005 (bib) |
|
| R. Bauernschmitt, M. Feuerstein, E.U. Schirmbeck, N. Augustin, S.M. Wildhirt, R. Lange
Improvement of Endovascular Stent Grafting by Augmented Reality Biomedizinische Technik (BMT 2005), Volume 50, Supplementary vol. 1, Part 2, pp. 1262 - 1263, Nuremberg, Germany, September 2005 (bib) |
|
Dissertation
| M. Feuerstein
Augmented Reality in Laparoscopic Surgery - New Concepts and Methods for Intraoperative Multimodal Imaging and Hybrid Tracking in Computer Aided Surgery Book, ISBN 978-3-8364-7783-3, Vdm Verlag Dr. Müller. (bib) |
||
| M. Feuerstein
Augmented Reality in Laparoscopic Surgery - New Concepts for Intraoperative Multimodal Imaging PhD Thesis. The original (high-resolution) publication is available online at mediatum.ub.tum.de (bib) |
||
| A trend in abdominal surgery is the transition from open procedures to minimally invasive laparoscopic interventions, where visual feedback to surgical staff is only available through the laparoscope camera and direct palpation of organs is impossible. To successfully perform such sophisticated interventions, the provision of additional intraoperative feedback can be of great help to the surgical staff, especially in complex cases. This work introduces several new concepts for the application of augmented reality techniques to laparoscopic surgery. One main idea is to utilize multiple intraoperative imaging devices for the acquisition of up-to-date patient data. Optical and electromagnetic tracking systems are applied to determine the position and orientation of both rigid (mobile C-arm, laparoscope) and flexible (laparoscopic ultrasound) imaging devices. The acquired patient data is intrinsically registered to the tracked laparoscope in one common coordinate system, so it can be directly superimposed on the images of the laparoscope camera in real time without intraoperative registration steps. This intuitive superimposition can visually assist and direct the surgeon, as hidden anatomy such as vessels or tumors below the surface of an organ are revealed. The presented visualization aid can be used during critical phases in the surgical workflow such as port placement and intraoperative resection planning. Whereas superimposition for resection planning is based on intraoperative, implicitly registered imaging data, superimposition for port placement requires an interactive registration of preoperative imaging data to the patient. This interactive process is mostly automated by a newly introduced registration technique that results in a port placement procedure soundly integrated into the current surgical workflow. For resection planning and guidance, where navigated laparoscopic ultrasound can be used to acquire updated images of patient anatomy, a hybrid tracking approach including a method capable of estimating the reliability of electromagnetic tracking data is presented, which is able to automatically notify the surgical staff on possible tracking inaccuracies. The dissertation bases its validation on many experiments, including animal experiments, performed in close partnership with several surgeons. |
||
| This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work. Copyright and all rights therein are retained by authors or by other copyright holders. All persons copying this information are expected to adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each authors copyright. In most cases, these works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder. |
Patent Applications
- M. Groher, J. Gardiazabal, M. Feuerstein, H. Heibel
Method for Reconstructing a Histological Volume and Measuring Device
WO/2011/098458
- N. Navab, C. Bichlmeier, M. Feuerstein
Virtual Penetrating Mirror Device for Visualizing Virtual Objects in Endoscopic Applications
WO/2007/128377
- N. Navab, M. Feuerstein
Registration-Free Augmentation Device and Method
WO/2007/115825
Projects at CAMP
Virtual Mirror: Interaction Paradigm for Augmented Reality ApplicationsAugmented Reality offers a higher degree of freedom for the programmer than classical visualization of volume data on a screen. The existing paradigms for interaction with 3D objects are not satisfactory for particular applications since the majority of them rotate and move the object of interest. The classic manipulation of virtual objects cannot be used while keeping real and virtual spaces in alignment within an AR environment. This project introduces a simple and efficient interaction paradigm allowing the users to interact with 3D objects and visualize them from arbitrary viewpoints without disturbing the in-situ visualization, or requiring the user to change the viewpoint. We present a virtual, tangible mirror as a new paradigm for interaction with 3D models. The concept borrows its visualization paradigm in some sense from methodology used by dentists to examine the oral cavity without constantly changing their own viewpoint or moving the patients head. The virtual mirror improves the understanding of complex structures, enables completely new concepts to support navigational aid for different tasks and provides the user with intuitive views on physically restricted areas. |
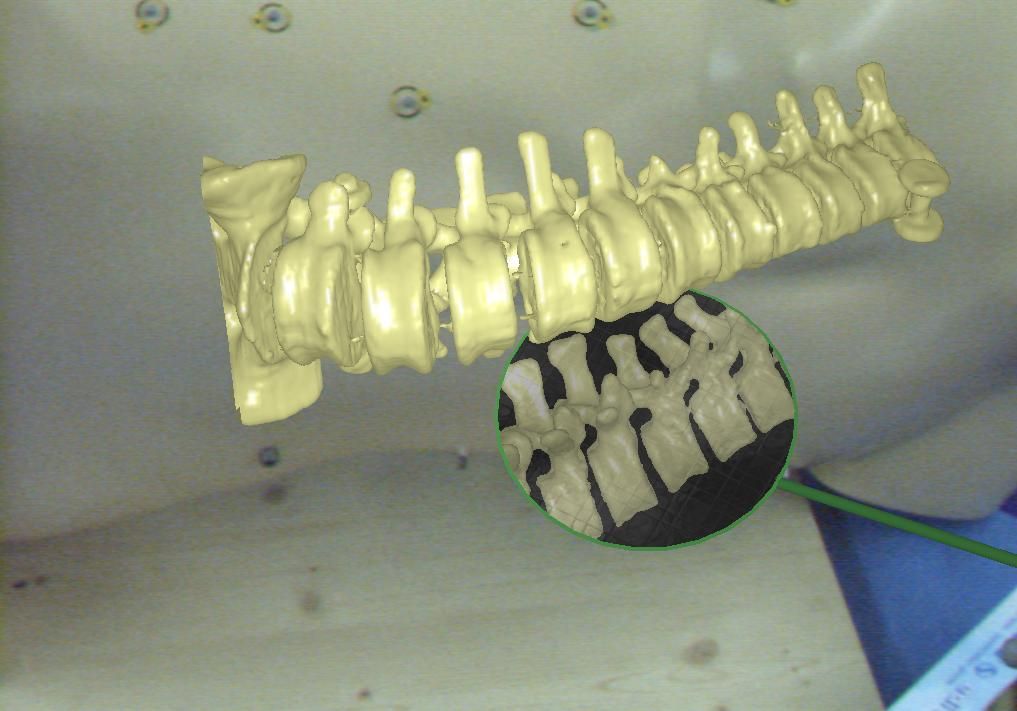
Reconstruction and Registration of Histology and Phase Contrast Images for Clinical Validation of Imaging ModalitiesBefore its introduction into the hospital, a new imaging modality has to be validated. In other words, appearing structures need to be correlated to the imaged tissues. Such a cross validation is only meaningful when performed against the gold standard which is histology. Currently, cross validation is performed by qualitative comparison of 3D datasets to 2D histology slices. Since the acquisition of a consistent 3D histology volume is a challenging task, its comparison to the corresponding dataset always remained qualitative.The classic histology procedure can be divided in four steps: pre processing, cutting, post processing and imaging of the tissues. In the first step, the sample is chemically processed to preserve the tissues and is then embedded in a paraffin block. By using a microtome, it is cut in very thin slices, and put on a glass slide. During post processing the sample is stained to enhance the structures of interest. The imaging is performed with a camera mounted in a microscope, or with a dedicated scanner. Several difficulties inherent to this process can have a dramatic influence on the quality of the reconstructed histology volume. For instance, since the cutting process is done manually, problems like flipping, bending or ripping of the slides may happen. If the knife starts to wear off, some banding will appear over the slices. Moreover, a few slices could be missing. Finally since the staining color is time dependent, variation in the color of the slices can occur. In this project, we propose to improve the histology procedure and to develop methods towards a consistent reconstruction of 3D histology volumes. |
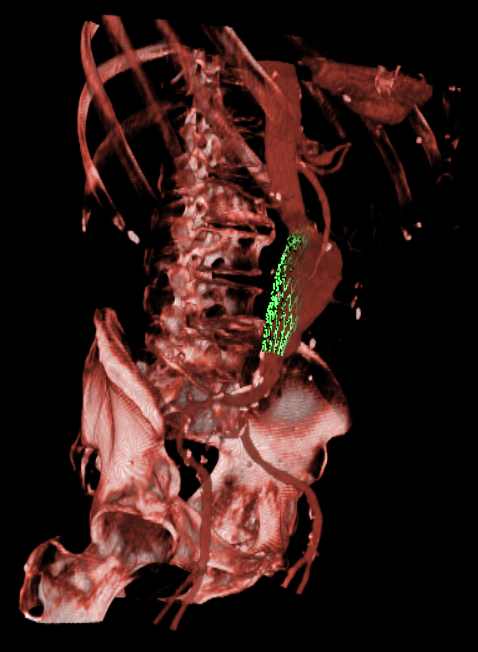
Endovascular Stenting of Aortic AneurysmsEndovascular stenting is a minimally invasive treatment technique for aortic aneurysms or dissections. Thereby, a certain aortic prosthesis (stent graft) is placed inside the aortic aneurysm in order to prevent a life-threatening rupture of the aortic wall. Prior to the intervention, a computed tomography angiography (CTA) is acquired on which the surgical staff can measure the parameter of the desired stent graft and finalize the intervention workflow. The entire interventional catheter navigation is done under 2D angiography imaging where the physician is missing the important 3D information. The purpose of our project is two-fold:1. In the planning phase, a modified graph cuts algorithm automatically segments the aorta and aneurysm, so the surgical staff can choose an appropriate type of stent to match the segmented location, length, and diameter of the aneurysm and aorta. By visualizing the defined stent graft next to the three-dimensionally reconstructed aneurysm, mismeasurements can be detected in an early stage. Our main goal is the creation of an interactive simulation system that predicts the behaviour of the aortic wall and the movement of the implanted stent graft. 2. During implantation of the stent graft, after an intensity based registration of CTA and angiography data, the current navigation can be visualized in the 3D CT data set at any time. This includes solutions for electro-magnetic tracking of catheters as well as guide wires and stent grafts. Eventually, Our main goal is the creation of solutions that enable the surgeon to enhance the accuracy of the navigation and positioning, along with a minimum use of angiography, leading to less radiation exposure and less contrast agent injection. |
Real-time fusion of ultrasound and gamma probe for navigated localization of malignancyIntra-operative localization of non-superficial cancerous lesions in non-hollow organs like liver, kidney, etc is currently facilitated by intra-operative ultrasound (IOUS) and palpation. This yields a high rate of false positives due to benign abnormal regions and thus unnecessary resections with increased complications and morbidity. In this project we integrate functional nuclear information from gamma probes with IOUS, to provide a synchronized, real-time visualization that facilitates the detection of active tumors and metastases intra-operatively. The bet of this project is that the inclusion of an advanced, augmented visualization provides more reliability and confidence on classifying lesions prior to the resection. |
Magneto-Optic Tracking of a Flexible Laparoscopic Ultrasound TransducerIn abdominal surgery, a laparoscopic ultrasound transducer is commonly used to detect lesions such as metastases. The determination and visualization of position and orientation of its flexible tip in relation to the patient or other surgical instruments can be of much help to (novice) surgeons utilizing the transducer intraoperatively. This difficult subject has recently been paid attention to by the scientific community. Electromagnetic tracking systems can be applied to track the flexible tip. However, the magnetic field can be distorted by ferromagnetic material.We present a new method based on optical tracking of the laparoscope and magneto-optic tracking of the transducer, which is able to automatically detect and correct field distortions. This is used for a smooth augmentation of the B-scan images of the transducer directly on the camera images in real time. |
Port Placement in Minimally Invasive Endoscopic SurgeryOptimal port placement is a delicate issue in minimally invasive endoscopic surgery. A good choice of the instruments' and endoscope's ports can avoid time-consuming consecutive new port placement. We present a novel method to intuitively and precisely plan the port placement. The patient is registered to its pre-operative CT by just moving the endoscope around fiducials, which are attached to the patient's thorax and are visible in its CT. Their 3D positions are automatically reconstructed. Without prior time-consuming segmentation, the pre-operative CT volume is directly rendered with respect to the endoscope or instruments. This enables the simulation of a camera flight through the patient's interior along the instruments' axes to easily validate possible ports. |
Laparoscope Augmentation for Minimally Invasive Liver ResectionIn recent years, an increasing number of liver tumor indications were treated by minimally invasive laparoscopic resection. Besides the restricted view, a major issue in laparoscopic liver resection is the precise localization of the vessels to be divided. To navigate the surgeon to these vessels, pre-operative imaging data can hardly be used due to intra-operative organ deformations caused by appliance of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum and respiratory motion.Therefore, we propose to use an optically tracked mobile C-arm providing cone-beam computed tomography imaging capability intra-operatively. After patient positioning, port placement, and carbon dioxide insufflation, the liver vessels are contrasted and a 3D volume is reconstructed during patient exhalation. Without any further need for patient registration, the volume can be directly augmented on the live laparoscope video. This augmentation provides the surgeon with essential aid in the localization of veins, arteries, and bile ducts to be divided or sealed. Current research focuses on the intra-operative use and tracking of mobile C-arms as well as laparoscopic ultrasound, augmented visualization on the laparoscope's view, and methods to synchronize respiratory motion. |
Miscellaneous
- Best paper award (endoscopy session) for the paper SIFT Feature-based Motion Estimation for Bronchoscope Tracking
- Reviewed for:
- IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (Impact Factor 2008: 4.004)
- Information Sciences (Impact Factor 2008: 3.095)
- Computer Aided Surgery
- International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery
- International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention
- International Conference on Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions
- IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging
- International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality
- Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin
- Publicity Chair of the International Conference on Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions (IPCAI) 2010 in Geneva, Switzerland
- Organization of the Workshop on Image Guidance and Computer Assistance for Soft-Tissue Interventions at MICCAI 2008 in New York City, USA
- Organization of the Medical AR Tutorial at MICCAI 2007 in Brisbane, Australia
- Cultural Program Coordinator of the 1st Iranian-German Workshop on Medical Engineering 2006 in Munich, Germany
- Live Demonstration of our Laparoscopic Augmented Reality System at ISMAR 2005 in Vienna, Austria
Work Experience
- April 2010 - Feb. 2011
Feodor Lynen Fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation at the Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures and Augmented Reality, Technische Universität München, Germany - Jan. 2008 - March 2010
Postdoctoral Researcher at the Department of Media Science, Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya University, Japan - May 2005 - Nov. 2007
Research associate at the Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures and Augmented Reality, Technische Universität München, Germany - Jan. 2004 - April 2005
Research associate at the Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery, German Heart Center Munich, Germany - March - July 2002
Working student in the Function Development Process Department, BMW AG München, Germany - Aug. - Dec. 2000
Internship - Web-Programming (instabus), Siemens AG Singapore, Singapore - March/April 2000
Part time job: Database-Programming, varetis GmbH München, Germany - March - Sept. 1999
Part time job: Web-Design/-Programming, INWEMA AG München, Germany - June - Sept. 1998
Camp Counselor, Indian Lake Camp Burlingham, USA
Education
- Jan. 2004 - Oct. 2007
Ph.D. student of Prof. Nassir Navab - Oct. 2001 - Dec. 2003
Technische Universität München: Main study period of Computer science, focus on practical Computer Science, Minor: Architecture - Aug./Sept. 2002
National Taiwan University, Taipei: Internship at the Communication and Multimedia Laboratory of the Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering in 3D computer graphics - May - Sept. 2001
University of Sydney: Interdisciplinary project on Virtual Architecture at the Design Lab
Submitted Design: M.L. Maher, N. Gu, and M. Feuerstein (2001), Virtual Museum, FEIDAD - Jan. - May 2001
National University of Singapore: Exchange semester at the School of Computing - Oct. 1998 - Aug. 2000
Technische Universität München: Basic study period of Computer Science, Minor: Architecture
Teaching
Summer Term 2007- Ferienakademie
- Lecture Computer Aided Medical Procedures II
- Hauptseminar Recent Advances in Computer Assisted Surgery
- Proseminar History of Computational Science, Vision, and Medical Science
- Lecture Computer Aided Medical Procedures
- Hauptseminar Recent Advances in Computer Assisted Surgery
- Lecture Computer Aided Medical Procedures II
- Programmierpraktikum Graphikprogrammierung in C++
- Doktorandenseminar Current Research and Challenges in Surgical Navigation
- Hauptseminar Recent Advances in Computer Assisted Surgery
- Lecture 3D Computer Vision
- Tutor Einführung in die Informatik 1
- Programmierpraktikum Graphikprogrammierung in C++
- Praktikum Intra-operative Imaging & Visualization
- Praktikum Intra-operative Imaging & Visualization
- Hauptseminar Methods and Tools in Medical Imaging
Theses, SEPs, and IDPs under my Supervision
- Calibration of Endobronchial Ultrasound by Philipp Dressel (Diploma Thesis)
- Error Classification and Propagation for Electromagnetic Tracking by Julian Much (DA/MA/BA)
- Online Error Correction for the Tracking of Laparoscopic Ultrasound by Tobias Reichl (Diploma Thesis)
- Navigated RF Ablation by Claudio Alcérreca (Master Thesis)
- Ultrasound-based Measurement of Anatomical Structures by Jörg Jakobs (Diploma Thesis)
- A Navigation Tool for the Endovascualar Treatment of Aortic Aneurysms - Computer Aided Implantation of a Stent Graft by Konstantinos Filippatos (Diploma Thesis)
- Development of an Automatic Segmentation, Measuring, and Planning Tool for the Aorta and Aneurysms by Oliver Kutter (IDP)
| UsersForm | |
|---|---|
| Title: | Dr. |
| Circumference of your head (in cm): | |
| Firstname: | Marco |
| Middlename: | |
| Lastname: | Feuerstein |
| Picture: | |
| Birthday: | |
| Nationality: | Bavaria |
| Languages: | English, German, Bavarian, Japanese |
| Groups: | Registration/Visualization, Segmentation, Medical Imaging, Computer-Aided Surgery, Medical Augmented Reality |
| Expertise: | Registration/Visualization, Segmentation, Medical Imaging, Computer-Aided Surgery, Medical Augmented Reality |
| Position: | External Collaborator |
| Status: | Alumni |
| Emailbefore: | marco.feuerstein |
| Emailafter: | micro-dimensions.com |
| Room: | microDimensions GmbH |
| Telephone: | |
| Alumniactivity: | Software Engineer at Lyft |
| Defensedate: | 15 October 2007 |
| Thesistitle: | Augmented Reality in Laparoscopic Surgery - New Concepts for Intraoperative Multimodal Imaging |
| Alumnihomepage: | |
| Personalvideo01: | |
| Personalvideotext01: | |
| Personalvideopreview01: | |
| Personalvideo02: | |
| Personalvideotext02: | |
| Personalvideopreview02: | |